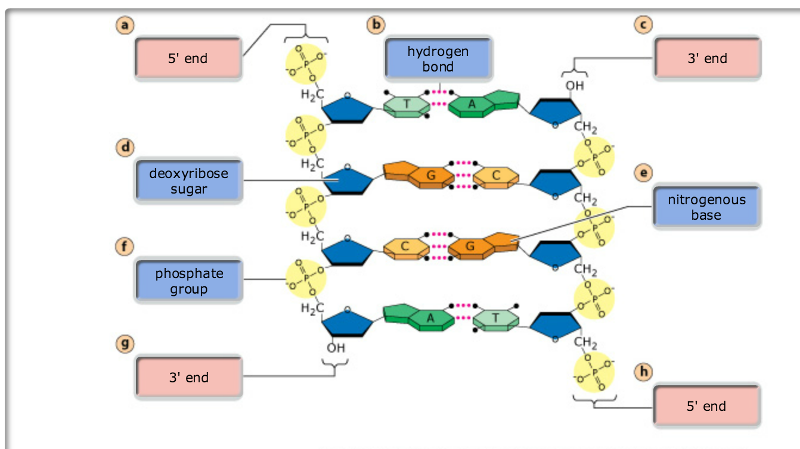
Each base can only bond with one other, A with T and C with G. This is called the complementary base pairing rule or Chargaff's rule. The Four Nitrogenous Bases In DNA nucleotide subunits, there are four nitrogenous bases: Adenine
Adenine
Adenine is a nucleobase. It is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The three others are guanine, cytosine and thymine. Its derivatives have a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both t…
What is the difference between nucleotides and base pairs?
What is the difference between nucleotides and base pairs?
- Nitrogenous base is a part of a nucleotide.
- Base is a heterocyclic ring containing nitrogen. Other than this in a nucleotide, there is a pentose sugar and a phosphate group too.
- Base is the most important and functional unit of nucleotides in DNA or RNA.
- The hydrogen bonding between bases keeps the double helix structure of DNA.
What is the unique pairing pattern between nucleotide bases?
The base pairs in DNA are adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine. In RNA, they are adenine to uracil and guanine to cytosine. A base pair is made of two nucleotides. The nucleotides, located on opposite strands of DNA or RNA, are drawn to each other in a hydrogen bond. These bonds are what hold the strand together in a double helix formation.
What are the five different symbol types of nucleotide bases?
5. List the symbols for the five different types of nucleotide bases: The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U respectively. The name of the base is generally used as the name of the nucleotide, although this is technically incorrect...
Which bases pair up for RNA?
RNA contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T). Keeping this in view, what are the base pairs for RNA? The four bases that make up this code are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). Bases pair off together in a double helix structure, these pairs being A and T, and C and G. RNA doesn't contain thymine bases, replacing them ...
What is a base pair?
Base Pair. =. A base pair is two chemical bases bonded to one another forming a "rung of the DNA ladder.". The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine (A), ...
How many base pairs does a gene have?
We also count DNA and the amount of DNA, or the length of DNA by using units of base pairs, so if we're discussing a gene and we want to describe how big is a gene, we might say that the gene is a thousand base pairs long.
How many nucleotides are in DNA?
So each DNA molecule is made up of two strands, and there are four nucleotides present in DNA: A, C, T, and G. And each of the nucleotides on one side of the strand pairs with a specific nucleotide on the other side of the strand, and this makes up the double helix.
How are adenine and cytosine held together?
The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases, with adenine forming a base pair with thymine, and cytosine forming a base pair with guanine.
How do nucleotides in DNA form?
How Do the Nucleotides in DNA Pair. The double-strand DNA is formed by the hydrogen bonds between the complementary nucleotides of the two strand s. Generally, purines pair with pyrimidines. Thus, adenine pairs with thymine while cytosine pairs with guanine.
What are the two hydrogen bonds that hold DNA together?
Each DNA nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group attached to a deoxyribose sugar. The two strands are held together by the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the DNA nucleotides. Generally, purines pair with pyrimidines. Thus, adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine while cytosine forms three hydrogen ...
How many hydrogen bonds does DNA have?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule made up of combining four DNA nucleotides alternatively. The two strands are held together by the hydrogen bonds formed between purine and pyrimidines. Generally, adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine while cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine.
How are DNA strands held together?
The two DNA strands are held together by the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the two strands. The two strands are further coiled to form a DNA double-helix. Each strand in the double helix runs in opposite directions. One strand runs from 5′ to 3′ direction while the other strand runs from 3′ to 5′ direction.
What are the four strands of DNA?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule. Each strand of the DNA is formed by the alternative combining of four DNA nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Adenine and guanine are purines while cytosine and thymine are pyrimidines.
Which is weaker, adenine or cytosine?
Therefore, the interaction between adenine and thymine is weaker than the interaction between cytosine and guanine.
Where is DNA found in the body?
What is DNA. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the hereditary material of most organisms. In eukaryotes, the majority of DNA is located in the nucleus. Some may remain inside mitochondria and chloroplasts as well. In prokaryotes, DNA can be found within a special region known as the nucleoid in the cytoplasm.
What determines the way nucleotides interact with each other?
The chemical nature of the bases and the base pairing rules, defined by experimental evidence, determine the way the nucleotides interact with each other and form the structurally stable double helical DNA strands.
How many bases are in DNA?
The DNA of all the living beings is composed of just four bases i.e. Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), and Cytosine (C). The various juxtapositions of these 4 bases give rise to the genetic codes of all the biota on the planet.
What is the chemical name for cytosine?
The chemical IUPAC name for cytosine is 4-aminopyrimidin-2 (1H)-one. It is a pyrimidine derivative with substitutions of an amine group at 4 and a keto group at 2 positions. It was first discovered from calf thymus tissues, by Albrecht Kossel and Albert Neumann in 1894. It is found in DNA as a nucleotide, cytidine. Methylation of cytosine yields 5-methylcytosine, whereas its hydroxylation yields 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. It occurs in DNA as deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP).
What is the role of ATP in DNA?
It forms the nucleotide, adenine. Its triphosphate form, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is extensively utilized in cellular processes as the basic form of chemical energy. In its other phosphate forms, it plays the role of catalyst and co-factor. It occurs in DNA as deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP).
What is the name of the compound that is a heterocyclic aromatic compound?
Purines . Purines are heterocyclic aromatic compounds with an imidazole ring fused to the pyrimidine ring. They were first synthesized by Emil Fischer in 1899, by treating uric acid with phosphorous pentachloride to produce purines. They are also naturally found in high concentrations in meat and meat products.
How is thymidine formed?
It is formed by the methylation of the uracil molecule at the 5th carbon. It was discovered alongside cytosine, by Kossel and Neumann. It forms the nucleotide, thymidine. In presence of UV light, this base forms dimers between two adjacent thymidine molecules along the DNA strand.
What is the structure of pyrimidines?
Pyrimidines are heterocyclic aromatic compounds, that have a molecular structure similar to that of pyridine molecules. It falls under the category of diazines, which are benzene rings that contain 2 nitrogen atoms. Pyrimidines exhibit the presence of nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 3 positions of their ring structure. There are two types of pyrimidines in the form of DNA bases.
What is the order of nucleotides?
The order of the nucleotide sequence encodes genetic information. Since the nucleotides pair in a predictable way — A with T, and C with G — each strand of the DNA is always complementary to the other.
What is the structure of DNA?
Description. This animation describes the general structure of DNA: two strands of nucleotides that pair in a predictable way. DNA is well-known for its double helix structure. The animation untwists the double helix to show DNA as two parallel strands. Each strand is made up of a sequence of four nucleotides, A, C, G, and T.
