
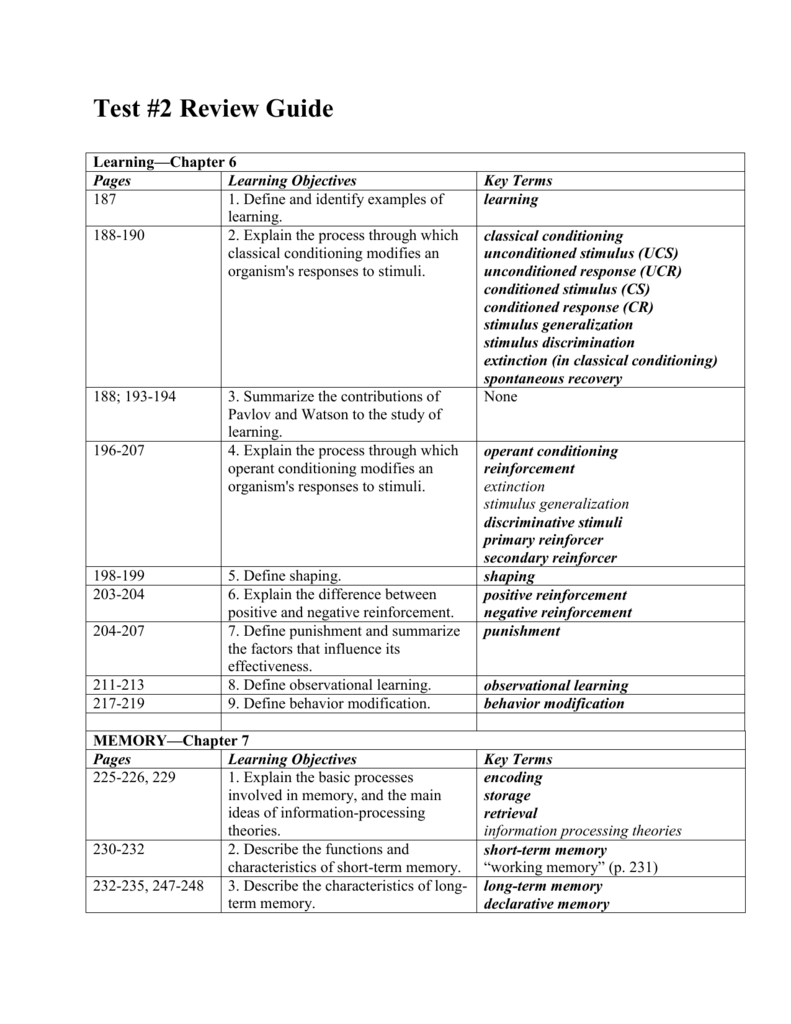
Operant Conditioning is related to B.F. Skinner
B. F. Skinner
Burrhus Frederic Skinner, commonly known as B. F. Skinner, was an American psychologist, behaviorist, author, inventor, and social philosopher. He was the Edgar Pierce Professor of Psychology at Harvard University from 1958 until his retirement in 1974.
What is the difference between operant conditioning and observational learning?
This is the key difference with Observational Learning: Operant Conditioning is active, while Observational Learning can be passive. The “operants” in the process of Skinner's conditioning have to do with environmental and purposeful variables that try to identify which processes make some behaviors happen.
Why are classical and operant conditioning important in the field of psychology?
Both classical and operant conditioning are important in the field of behavioral psychology. Examples of behaviorism include both kinds of conditioning, and it’s fascinating to learn about the way these concepts are applied.
What is observational learning in psychology?
In observational learning, a person's behavior is influenced by what happens to other people when they behave in certain ways. The person who is learning does so by seeing responses are elicited by others' behaviors. The person then bases his or her behavior on the lessons learned by watching what happens to the other people.
What are the operators in the process of Skinner's conditioning?
The “operants” in the process of Skinner's conditioning have to do with environmental and purposeful variables that try to identify which processes make some behaviors happen. These variables are also known as reinforcement.
What describes the main difference between observational learning and operant conditioning?
Observational learning extends the effective range of both classical and operant conditioning. In contrast to classical and operant conditioning, in which learning occurs only through direct experience, observational learning is the process of watching others and then imitating what they do.
Which of the following is a difference between classical conditioning and operant conditioning?
Classical conditioning involves associating an involuntary response and a stimulus, while operant conditioning is about associating a voluntary behavior and a consequence.
Which of the following is a difference between classical conditioning and operant conditioning quizlet?
What is the distinction between classical conditioning and operant conditioning? Classical conditioning involves learning based on associations, and operant conditioning involves learning based on consequences.
In what way is observational learning similar to operant conditioning?
Observational learning is the process of learning to respond in a particular way by watching others, who are called models. Observational learning is also called “vicarious conditioning” because it involves learning by watching others acquire responses through classical or operant conditioning.
What is operant conditioning of learning?
Operant conditioning, sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning that uses rewards and punishment to modify behavior. Through operant conditioning, behavior that is rewarded is likely to be repeated, and behavior that is punished will rarely occur.
Which is an example of operant conditioning quizlet?
A lion in a circus learns to stand up on a chair and jump through a hoop to receive a food treat. This example is operant conditioning because attendance is a voluntary behavior. The exemption from the final exam is a negative reinforcement because something is taken away that increases the behavior (attendance).
What are the similarities and differences between classical and operant conditioning quizlet?
What is the main difference between classical conditioning and operant conditioning? Classical conditioning requires learning that two events are related, whereas operant conditioning demonstrates that behavior leads to a consequence.
Which of the following statement best describes the operant conditioning?
Answer and Explanation: The answer is B. Organisms learn from the consequences of their behavior. In operant conditioning, a behavior is either reinforced or encouraged through a series of punishments and reinforcements.
What is the major difference between classical and operant conditioning and Nonassociative learning quizlet?
What is the major difference between classical and operant conditioning and nonassociative learning? Nonassociative learning occurs more slowly than classical and operant conditioning. Nonassociative learning requires repeated exposure whereas classical and operant condition usually occur in one trial.
How is observational learning different from operant conditioning quizlet?
What is the main difference between observational learning and operant conditioning? in operant conditioning, the organism itself must receive a stimulus in the form of a reinforcement or punishment. In observational learning, the organism can learn by watching others.
What is a operant conditioning example?
Through operant conditioning, an association is made between a behavior and a consequence (whether negative or positive) for that behavior. 1. For example, when lab rats press a lever when a green light is on, they receive a food pellet as a reward.
What is observational learning why is observational learning difficult to explain in terms of operant conditioning?
Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior becomes more or less probable depending on the consequences. It is associated with the psychologist B.F. Skinner. Observational learning is learning by watching others. The learner does not have to experience consequences personally in order to learn.
What is classical and operant conditioning examples?
While classical conditioning is training dogs to salivate to the sound of a metronome, operant conditioning is training them to sit by giving them a treat when they do. B.F. Skinner proposed the theory of operant conditioning, and he used a simple experiment with a rat to develop the theory.
What is the difference between operant and respondent conditioning?
In operant conditioning, it is the occurrence of a response that causes reinforcement to be delivered. In respondent conditioning, the conditioned and unconditioned stimuli are presented without regard to the animal's behavior.
What is the similarities between classical conditioning and operant conditioning?
Classical and operant conditioning are both similar because they involve making association between behaviour and events in an organism's environment and are governed by several general laws of association - for example, it is easier to associate stimuli that are similar to each other and that occur at similar times.
What is operant conditioning example?
For example, when lab rats press a lever when a green light is on, they receive a food pellet as a reward. When they press the lever when a red light is on, they receive a mild electric shock. As a result, they learn to press the lever when the green light is on and avoid the red light.
What is observational learning?from enotes.com
Observational learning is a way to acquire (learn) a new behavior by paying attention to the actions and behaviors of others, who act like the models of the behavior whether they do it purposely or not.
How does operant conditioning affect behavior?from enotes.com
In operant conditioning, a person's behavior is affected by reinforcements and punishments that the person experiences him or her self. The person behaves a certain way and then observes the responses of others to that behavior. The other people's responses help to shape the first person's behavior.
What are the three laws of learning?from optimistminds.com
Edward Thorndike built up the initial three laws of learning: exercise, readiness and effect. The Law of exercise states that the practice makes the learning association strong and discontinuous of exercise makes the learning weak. Exercise is generally significant and viable to learn any skill.
How did the Thorndike Law of Effect affect psychology?from optimistminds.com
The Thorndike law of effect distinctly affected the development of behaviorism, which proceeded to turn into the predominant way of thinking in psychology research for a great part of the twentieth century.
Which law of effect states that behavioral responses that are most closely followed by a satisfactory result are most likely to become answer?from britannica.com
Thorndike, postulated the Law of Effect, which stated that those behavioral responses (R) that were most closely followed by a satisfactory result were most likely to become established patterns and to reoccur in response to the same stimulus (S). This basic S-R scheme is referred to as unmediated.…
What is a behavior followed by positive results?from optimistminds.com
Behaviors promptly followed by positive results are bound to happen again. For example, being appreciated by a boss for appearing ahead of schedule for work made it more probable that the behavior would occur again. Behaviors followed by negative results are more reluctant to happen again.
What inhibits the conscious recognition of traumatic events such as childhood sexual abuse?from quizlet.com
D) Repression inhibits the conscious recognition of traumatic events such as childhood sexual abuse.
What is the difference between operant and classical conditioning?
One of the simplest ways to remember the differences between classical and operant conditioning is to focus on whether the behavior is involuntary or voluntary. Classical conditioning involves associating an involuntary response and a stimulus, while operant conditioning is about associating a voluntary behavior and a consequence.
How can operant conditioning help people?
In addition to being used to train people and animals to engage in new behaviors, operant conditioning can also be used to help people eliminate unwanted ones. Using a system of rewards and punishments, people can learn to overcome bad habits that might have a negative impact on their health such as smoking or overeating. 4
What is the process of pairing a previously neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus?
The classical conditioning process involves pairing a previously neutral stimulus (such as the sound of a bell) with an unconditioned stimulus (the taste of food). This unconditioned stimulus naturally and automatically triggers salivating as a response to the food, which is known as the unconditioned response.
How does classical conditioning work?
Classical conditioning, on the other hand, involves forming an association with some sort of already naturally occurring event. 1
How does reinforcement affect behavior?
How often the response is reinforced, known as a schedule of reinforcement, can play an important role in how quickly the behavior is learned 2 and how strong the response becomes.
What is instrumental conditioning?
Operant conditioning (or instrumental conditioning) focuses on using either reinforcement or punishment to increase or decrease a behavior. Through this process, an association is formed between the behavior and the consequences of that behavior. 1
What is observational learning?
Observational learning uses punishment and reinforcement of models to condition the behaviors of observers.
How many pairings of the CS and UCS are needed to produce a taste aversion?
Contrary to most classically conditioned reactions, only one pairing of the CS with the UCS is needed to produce a taste aversion.
Is habituation the same as learning?
Habituation is a form of learning, but they aren't the same thing.
What is a similarity between observational learning and operant conditioning?
SIMILARITIES The learner is active in both learning processes. It is reinforcement (rather than the learning itself) that influences the likelihood of the behaviour being imitated by the observer.
What is the difference between observational learning?
Observational learning is the process of learning to respond in a particular way by watching others, who are called models. Observational learning is also called “vicarious conditioning” because it involves learning by watching others acquire responses through classical or operant conditioning.
What is the difference between classical conditioning operant conditioning and social learning theories?
Classical conditioning is based on pain to stimulus and getting results. Operant conditioning uses reinforcements and punishments and the social learning theory uses observation. All of these elements have an impact on learning.
What is the difference between operant and classical learning?
Classical Conditioning is one in which the organism learns something through association, i.e. Conditioned Stimuli and Unconditioned Stimuli. Operant Conditioning is the type of learning in which the organism learns by way of modification in behaviour or pattern through reinforcement or punishment.
What is observational learning in psychology?
observational learning, method of learning that consists of observing and modeling another individual's behavior, attitudes, or emotional expressions.
What are examples of operant conditioning?
By repeatedly pairing the desired behavior with a consequence, an association is formed to create new learning. E.g. a dog trainer gives his dog a treat every time the dog raises its left paw. The dog learns that raising its left paw can earn him food reward. It will raise his paw again and again for more treats.
What is the major difference between classical and operant conditioning and Nonassociative learning?
What is the major difference between classical and operant conditioning and nonassociative learning? Nonassociative learning occurs more slowly than classical and operant conditioning. Nonassociative learning requires repeated exposure whereas classical and operant condition usually occur in one trial.
What Is Operant Conditioning?
In contrast to classical conditioning, operant conditioning involves encouraging or discouraging a specific behavior using reinforcement. While classical conditioning is training dogs to salivate to the sound of a metronome, operant conditioning is training them to sit by giving them a treat when they do.
What is the difference between operant and classical conditioning?
The main difference between classical and operant conditioning is the way the behavior is conditioned. In classical conditioning, a neutral stimulus is paired with a conditioned response. In operant conditioning, a desired behavior is paired with a consequence.
What was Pavlov's conditioned response?
Pavlov would use the metronome every time the dogs were fed, and the dogs began to associate the sound with food. Salivating was their conditioned response. You can see real-world examples of classical conditioning in everything from your response to your cell phone to the way you react when you hear holiday music.
What is classical conditioning?
Classical conditioning is when a conditioned response is paired with a neutral stimulus. The most famous example of this is Pavlov’s dogs, where Ivan Pavlov trained dogs to salivate at the sound of a metronome. The metronome was a neutral stimulus, since the dogs previously had no reaction to it. Pavlov would use the metronome every time ...
Who developed operant conditioning?
B.F. Skinner proposed the theory of operant conditioning, and he used a simple experiment with a rat to develop the theory. In the experiment, a hungry rat is placed in a box. As the rat explores, it discovers a lever. When it pushes the lever, it gets food. Over time, the rat learns to push the lever to receive food.
Is operant conditioning a part of behavioral psychology?
Both Are Part of Behaviorism. Both classical and operant conditioning are important in the field of behavioral psychology. Examples of behaviorism include both kinds of conditioning, and it’s fascinating to learn about the way these concepts are applied.
