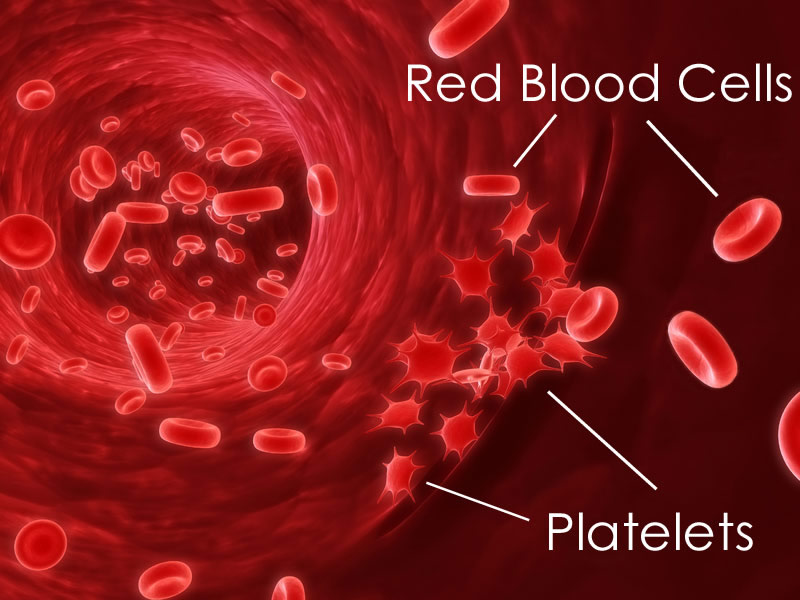
What is the main function of platelets?
What is the function of platelets
- the blood. Blood is a viscous liquid that blood vessels fill with, and it rushes through all the body parts as a result of the contraction of the heart muscle, ...
- Blood platelets. ...
- Platelet function. ...
- blood types. ...
How to rebuild blood platelets?
How to Increase a Low Platelet Count
- Papaya. Both the papaya fruit and its leaves can help increase a low platelet count within just a few days. ...
- Wheatgrass. According to a 2011 study published in International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Life Sciences, wheatgrass can be beneficial in increasing platelet count.
- Pumpkin. ...
- Spinach. ...
- Vitamin C. ...
- Indian Gooseberries. ...
- Sesame Oil. ...
- Beetroot. ...
- Water. ...
What do you need to know about living with low platelets?
Managing Low Platelets
- Avoid medications that contain aspirin, anti-inflammatories (like ibuprofen), or blood thinners, unless your healthcare professional recommends otherwise. ...
- Use an electric razor to shave, which may result in fewer nicks and cuts.
- Use extra care when working with sharp objects such as knives or scissors, so as not to accidentally cut yourself.
How do you give platelets?
What Is It Like to Give Platelets for the First Time?
- “It’s Like a Visit to the Spa, Sort Of”. Spending time at a spa is usually about much more than getting a fun treatment. ...
- “Sitting Back Can Save Lives”. ...
- “Roll Up Not One, But Two Sleeves”. ...
- “It’s Time to Chill Out, Literally”. ...
- “Platelets Expire Faster than My Carton of Milk!”. ...

What happens when a platelet is activated?
Platelets when activated undergo a condformation change, exposing a phospholipid-rich portion of the platelet membrane or "phospholipid platform."
Where is a localized platelet plug formed?
2. Primary hemostasis: a localized platelet plug is formed at the endothelial injury site (a temporary patch)
What happens when activation of the coagulation cascade (involving tissue factor) results in fibrin formation?
activation of the coagulation cascade (involving tissue factor) results in fibrin formation, cementing the platelets into a stable, larger hemostatic plug
How do platelets adhere to the ECM?
Platelet adhesion: platelets adhere to the ECM via vWF
How do recruited platelets aggregate?
Recruited platelets aggregate via filapodia that connect with one anther by incorporating circulating fibrinogen as an interlinking molecule between filapodia of adjacent platelets
What is the most common anticoagulant used to obtain plasma for hemostasis studies?
the most common anticoagulant used to obtain plasma for hemostasis studies is sodium citrate 3.2%
What is the last step in hemostasis?
5. Fibrinolysis: the last major step in normal hemostasis is to dissolve the clot and restore normal blood flow through the vessel
What happens when a platelet is activated?
When the platelet is activated, storage ADP is released from the platelet and then binds to its ligand on the platelet membrane, acting as an agonist. All the other changes listed do occur when the platelet is activated.
Where are platelets stored?
When the circulating platelet count decreases, platelets are first derived from those se- questered or stored in the spleen (normally one third of those available).
What is platelet pool disorder?
Platelet storage pool disorder is a deficiency of α-granules, also called dense bodies.
What happens to the megakaryocyte as it matures?
As the megakaryocyte matures, it undergo es endomitosis. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis normally proceeds to 8N, 16N, or 32N, but no cell division occurs. The nucleus is thus polyploid. Basophilia in the cytoplasm diminishes, but the cytoplasmic volume increases along with the nuclear size so that the cell becomes the largest cell in the bone marrow. The chromatin gradually clumps, and nucleoli become less prominent and eventual- ly cannot be detected.
Which ligand binds to platelet precursors?
Thrombopoietin binds to its ligand Mpl on the membrane of platelet precursors and plays a critical role in the production of platelets.
What adheres to white cells and exits with them?
c.Platelets adhere to white cells and exit with them.
Which receptor does fibrinogen bind to?
Fibrinogen must bind to its receptor GP IIb/IIIa assembled on the platelet membrane after activation for normal platelet aggregation.
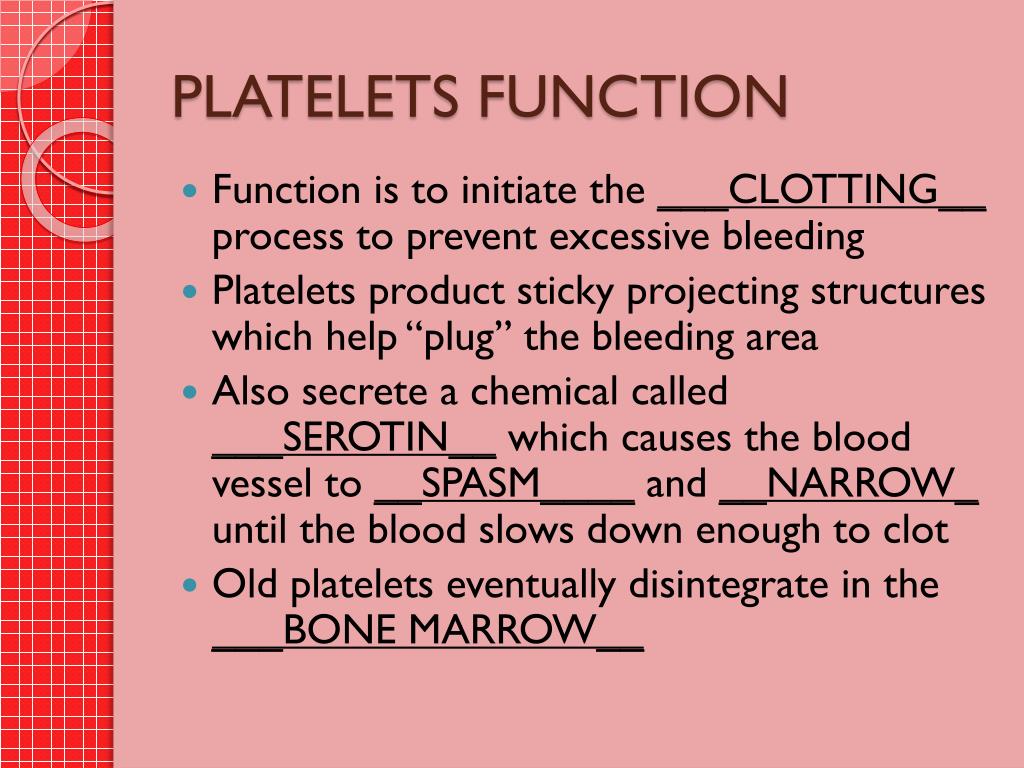
What is platelet function chemical?
platelet function chemicals. releasing enzymes and other factors at the propriate times. platelets function -chemicals. platelets initiate and control the clotting process. platelet function- temporary patch. platelets clump together at an injury site, forming a platelet plug. platelet plug.
What are the filaments in platelets?
platelets contain filaments of actin and myosin
How long do platelets stay in the body?
is preferred when referring to our blood in human. platelets. are continuously replaced/circulates for 9-12 days before being removed by phagocytes, mainly in the spleen. roughly one-third of the platelets. in the body at any moment are held in the spleen and ther vascular organs, rather then in the bloodsteam.
Where do platelets clump together?
platelets clump together at an injury site, forming a platelet plug
Why are platelets count exceeded?
platelets counts are exceed, generally results from accelerated platelet formation in a response to infection, inflammation, or cancer. platelets function. release of chem. important to the clotting process , formation of temporary patch in the walls of damaged bld ves., active contraction after clot formation has occurred.
How do platelets work?
Platelets work to plug holes in blood vessels due to trauma
How is iron transported in the blood?
Iron is transported in the blood by transferrin.
How do leukocytes differ from erythrocytes?
D. Leukocytes differ from erythrocytes in that they do not retain their organelles throughout life.
What is the purpose of the lungs?
E. To pick up oxygen from the lungs and deliver it to tissues and to pick up carbon dioxide from the tissues and unload it in the lungs
Which plasma solute is the second most abundant?
C. Protein is the second most abundant plasma solute by weight.
What causes vasoconstriction and vasodilation?
Vasoconstriction and vasodilation due to temperature changes
Example
- A real-life example of normal blood clotting is if you cut your finger and it stops bleeding, but it also happens in blood vessels throughout your body.
Prognosis
- If there are not enough platelets (a condition called thrombocytopenia) the risk of uncontrolled or prolonged bleeding increases. When there are too many platelets in the blood (a condition called thrombocytosis), it may lead to abnormal blood clot formation, which can be serious and life-threatening.
Treatment
- Aspirin and some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit platelet function, which is why you may be asked to stop using them for a period of time before a surgery or procedure.
Significance
- Looking at the numbers, size, and health of platelets (thrombocytes) is a part of a complete blood count (CBC) test. A platelet count is an important number for your doctor to know before and after surgery in order to predict bleeding and clotting problems. It is also an important number during chemotherapy and radiation therapy as these can inhibit the production of platelets in the bone …
Diagnosis
- Platelet function tests may also be performed if there are symptoms or potential for excessive bleeding, and to also monitor anti-platelet medications.
Causes
- There are a number of potential causes for a low platelet count. When you undergo chemotherapy or radiation therapy, you may have a low platelet count due to the suppressive effects on the blood-producing cells in your bone marrow. Other examples of conditions that may cause thrombocytopenia include viral infections that attack the bone marrow, autoimmune syndromes …
Risks
- A platelet count below 20,000 per microliter is a life-threatening risk as spontaneous bleeding may occur and be hard to stop. At that level, you may be given a platelet transfusion.
Clinical significance
- High platelet counts can also be seen in cancer, especially with gastrointestinal cancer, as well as lymphoma, lung, ovarian, and breast cancer. This is thought to be due to the inflammation associated with the malignancy stimulating the production of platelets in the bone marrow.