Correct Answer: To act as receptors for hormones One function of membrane proteins is to receive (amino acid-based) hormones that cannot pass through the plasma membrane. rikazzz | October 11, 2021 | Cells and Tissues
What are the functions of the plasma membrane?
Functions of plasma membrane 1. Physical isolation - separates inside of cell from the surrounding extracellular fluid. 2. Regulation of exchange with the environment - controls the entry of ions and nutrients, elimination of wastes, and release of secretions.
Why are membrane proteins confined to a portion of the membrane?
The mouse and human proteins remained confined to the portion of the plasma membrane that derived from their original cell type. This suggests that cells can restrict the movement of their membrane proteins to establish cell-specific functional domains. D.
What determines the shape of a cell's plasma membrane?
The shape of a cell and the mechanical properties of its plasma membrane are determined by a meshwork of fibrous proteins called what? On what side of the plasma membrane are the carbohydrate chains of glycoproteins, proteoglycans, and glycolipids located? In this figure, what do the areas shown in red represent?
Can cells restrict the movement of membrane proteins to establish functional domains?
The mouse and human proteins remained confined to the portion of the plasma membrane that derived from their original cell type. This suggests that cells can restrict the movement of their membrane proteins to establish cell-specific functional domains.

What are the functions of the proteins in the plasma membrane?
Plasma membrane proteins that are exposed on the cell surface have important biological functions, such as signaling into and out of the cells, ion transport, and cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions.
What is the function of proteins in the cell membrane quizlet?
What are the 4 functions of proteins in the cell membrane? Determining blood type, connecting one cell to another, receptor sites for hormones, receptor sites that certain bacteria, toxins can bind to, etc.
What is the main function of proteins answer?
Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs.
Which is the main function of proteins?
It helps repair and build your body's tissues, allows metabolic reactions to take place and coordinates bodily functions. In addition to providing your body with a structural framework, proteins also maintain proper pH and fluid balance.
Which proteins form large, water-filled pores in mitochondrial and bacterial outer membranes?
Porin proteins—which form large, water-filled pores in mitochondrial and bacterial outer membranes—fold into β-barrel structures. The amino acids that face the outside of the barrel have what kind of side chains?Choose one:
How did scientists study fluidity of membranes?
When scientists were first studying the fluidity of membranes, they did an experiment using hybrid cells. Certain membrane proteins in a human cell and a mouse cell were labeled using antibodies coupled with differently colored fluorescent tags. The two cells were then coaxed into fusing, resulting in the formation of a single, double-sized hybrid cell. Using fluorescence microscopy, the scientists then tracked the distribution of the labeled proteins in the hybrid cell.Which best describes the results they saw and what they ultimately concluded?
Which direction do carbohydrates face?
All of the carbohydrates in the plasma membrane face the cell exterior. Which direction do the carbohydrates on internal cell membranes face?
Can proteins move freely?
This suggests that proteins, like lipids, can move freely within the plane of the bilayer.
Do mouse and human proteins form hybrid cells?
A. At first, the mouse and human proteins were confined to their own halves of the newly formed hybrid cell, but over time, the two sets of proteins became divided such that half faced the cytosol and half faced the hybrid cell exterior. This suggests that flippases are activated by cell fusion.
Which compounds must pass through a membrane channel?
Ions and water-soluble compounds that are not lipid soluble. These must pass through a membrane channel.
What controls the entry of ions and nutrients, elimination of wastes, and release of secretions?
2. Regulation of exchange with the environment - controls the entry of ions and nutrients, elimination of wastes, and release of secretions. 3. Sensitivity to the environment - first part of cell to be affected by changes in the pH of the extracellular fluid.
What is the outermost boundary of a cell?
AKA cell membrane, the outermost boundary of a cell. Extremely thin (6-10 nm). Contains lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. Functions of plasma membrane. 1. Physical isolation - separates inside of cell from the surrounding extracellular fluid. 2.
What is the role of physical isolation in the cell?
2. Regulation of exchange with the environment - controls the entry of ions and nutrients, elimination of wastes, and release of secretions. 3.
How many layers are there in a phospholipid?
Phospholipid molecules in the cell membrane form two layers, laying with their hydrophilic heads along the membrane surface and hydrophobic tails inside.
Which cells recognize other cells as normal or abnormal based on the presence of this characteristic?
AKA glycoproteins. Cells of the immune system recognize other cells as normal or abnormal based on the presence of this characteristic.
Can an ion cross a channel?
Whether or not an ion can cross a specific channel is dependent on the size and charge of the ion, the size of the hydration sphere, and interactions between the ion and channel walls. Leak channels. AKA passive channels. Channels that remain open and allow the passage of ions across the plasma membrane.
What is a blank protein?
Cell recognition protein. If a particular protein was identified in the plasma membrane to cause organ transplant rejection, such a protein would be considered a blank protein. Cell recognition. A blank protein allows a particular molecule or ion to freely cross the plasma membrane as it enters or exits the cell.
Which solution has a higher solute concentration of that inside of a cell?
Hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration of that inside of a cell. Water leaves cell and causes it to shrivel
When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, what happens?
When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution. Water enters the cell toward the area of higher solute concentration. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution. Water exits the cell toward the area of higher solute concentration.
What is the membrane of a cell?
a single-layered membrane that surrounds the nucleus of the cell. a membrane composed of tiny shelves or cristae. a double layer of protein enclosing the plasma. the phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell. the phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell.
What is the membrane that surrounds the nucleus of the cell?
a single-layered membrane that surrounds the nucleus of the cell. a membrane composed of tiny shelves or cristae. a double layer of protein enclosing the plasma. the phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. the phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell.
What is the function of the ion encloser?
It is selectively permeable but permits water and gases to cross. It prevents potassium ions from leaking out and sodium ions from crossing into the cell.
What is the membrane of a cell?
The plasma (cell) membrane is a phospholipid bilayer, compose d of two parallel sheets of phospholipid molecules lying tail to tail, with their polar heads exposed to water on either side of the membrane. This allows the plasma membrane to separate the intracellular fluid (the ICF) from the extracellular fluid (ECF).
Why is the cell membrane semipermeable?
The cell membrane is semipermeable, or selectively permeable, because some things can easily pass through it while others cannot.
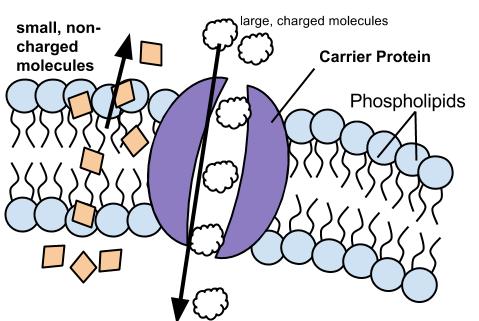
What is the transporter of glucose?
Glucose, a small polar solute, uses a membrane transporter (a protein carrier) to cross the plasma membrane via facilitated diffusion. In simple diffusion, small nonpolar and lipid-soluble substances (including gases) diffuse directly through the lipid bilayer.
What organelle contains enzymes?
Born as endosomes that contain inactive enzymes, lysosomes are spherical, membranous organelles containing activated digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are large and abundant within phagocytes, the cells that dispose of invading bacteria and cell debris. Lysoso mal enzymes can digest almost all kinds of biological molecules. They work best in acidic conditions and so are called acid hydrolases.
What is the name of the organelle that provides the most ATP?
Mitochondria are threadlike or lozenge-shaped membranous organelles. In living cells they squirm, elongate, and change shape almost continuously. They are the power plants of a cell, providing most of its ATP supply.
What is epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue is a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity (epithe = laid on, covering). In addition to coverings and linings, epithelial cells can also form glands.
Which epithelium has polarity?
All epithelia exhibit polarity, which is defined by the presence of an apical, or free, surface and a basal, or attached, surface that differ in both structure and function.