The trigeminal nerve is also called cranial nerve V. The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the 12 cranial nerves. Its main function is transmitting sensory information to the skin, sinuses, and mucous membranes in the face. It also stimulates movement in the jaw muscles. The trigeminal nerve has three different divisions.
Is the trigeminal nerve a motor or sensory nerve?
While some nerves have only sensory or motor functions, others can have both. The trigeminal nerve is one of the cranial nerves that has both sensory and motor function. Cranial nerves are also classified using Roman numerals based on their location. The trigeminal nerve is also called cranial nerve V.
Which cranial nerves have both sensory and motor functions?
Those that send motor information have motor functions. While some nerves have only sensory or motor functions, others can have both. The trigeminal nerve is one of the cranial nerves that has both sensory and motor function. Cranial nerves are also classified using Roman numerals based on their location.
What are the divisions of the trigeminal nerve?
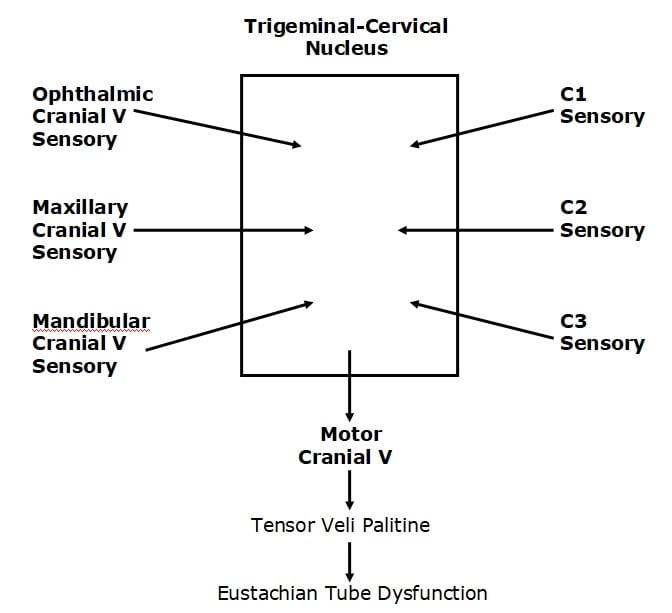
The trigeminal nerve is a mixed cranial nerve that has both sensory and motor functions. There are three divisions of the trigeminal nerve: Ophthalmic division (CN V1 or Va), Maxillary division (CN V2 or Vb), Mandibular division (CN V3 or Vc).
How to test the function of the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerve plays a role in many sensations that are felt in different parts of the face. As a result, there are several ways to test the function of the trigeminal nerve. Pin or cotton swab test. One or both sides of the face are touched with either a pin or cotton swab.
Which is a function of the trigeminal V nerve quizlet?
The trigeminal nerve is the major sensory nerve of the head and face serving the skin and mucous membranes and therefore providing GSA properties. It has a division which innervates the muscles of mastication. This serves as an SVE function since the muscles of mastication are derived from the first pharyngeal arch.
What is the name function and purpose of cranial nerve V?
V. The trigeminal nerve is the largest of your cranial nerves and has both sensory and motor functions. The trigeminal nerve has three divisions, which are: Ophthalmic. The ophthalmic division sends sensory information from the upper part of your face, including your forehead, scalp, and upper eyelids.
What is sensory function of nerve V?
The sensory function of the trigeminal nerve is to provide the tactile, motion, position, and pain sensations of the face and mouth. The motor function activates the muscles of the jaw, mouth, and inner ear.
What function does cranial nerve V test?
5th Cranial nerve For the 5th (trigeminal) nerve, the 3 sensory divisions (ophthalmic, maxillary, mandibular) are evaluated by using a pinprick to test facial sensation and by brushing a wisp of cotton against the lower or lateral cornea to evaluate the corneal reflex.
What is the trigeminal nerve responsible for?
The trigeminal nerve is one set of the cranial nerves in the head. It is the nerve responsible for providing sensation to the face. One trigeminal nerve runs to the right side of the head, while the other runs to the left. Each of these nerves has three distinct branches.
Where is cranial nerve 5 located?
Motor branches of the trigeminal nerve are distributed in the mandibular nerve. These fibers originate in the motor nucleus of the fifth nerve, which is located near the main trigeminal nucleus in the pons.
Which of the following is a branch of the trigeminal V nerve?
The mandibular nerve is the only branch of the trigeminal nerve that has both sensory and motor components.
How do you check cranial nerve V?
3:074:02Trigeminal Nerve | Cranial Nerve V Assessment - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd what you want to do is take your hands and you're gonna feel the masseter muscle in the temporalMoreAnd what you want to do is take your hands and you're gonna feel the masseter muscle in the temporal muscle. And you should feel a nice ball of muscle that is equal on both sides.
Which of the following is not a branch of the trigeminal V nerve?
Answer and Explanation: All of the following are branches of the trigeminal nerve except d) greater petrosal. The trigeminal nerve (CN V) has three major branches: ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2) and mandibular (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary are sensory fibers, and the mandibular is both sensory and motor.
How will the nurse assess the function of cranial nerve V?
The nurse should evaluate facial sensation to assess the trigeminal nerve (CN V) because the trigeminal nerve innervates the muscles of the face. The nurse should evaluate the strength of the jaw to assess the trigeminal nerve (CN V) because the trigeminal nerve innervates the muscles of the face.
What instruction would you give to a patient when assessing the trigeminal nerve cranial nerve V?
Cranial Nerve V – Trigeminal Ask the patient to close their eyes, and then use a wisp from a cotton ball to lightly touch their face, forehead, and chin. Instruct the patient to say ”Now” every time they feel the placement of the cotton wisp.
Where does the trigeminal nerve start?
The origin of the trigeminal nerve is the annular protuberance at the limit of the cerebellar peduncles. It originates from three sensory nuclei (mesencephalic, principal sensory, spinal nuclei of trigeminal nerve) and one motor nucleus (motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve) extending from the midbrain to the medulla.
Which of the following is cranial nerve V?
The trigeminal nerveThe trigeminal nerve (V) is the largest cranial nerve, and it has both a sensory and a motor division.
What are the 12 cranial nerves and their uses?
Table: Overview of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs)NerveCNTypeOlfactoryISensory Nervous System: HistologyOpticIISensory Nervous System: HistologyOculomotorIIIMotor Nervous System: HistologyTrochlearIVMotor Nervous System: Histology8 more rows•Aug 18, 2022
What are the names of the cranial nerves?
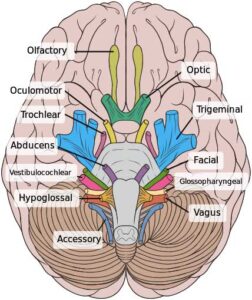
In higher vertebrates (reptiles, birds, mammals) there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves: olfactory (CN I), optic (CN II), oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), trigeminal (CN V), abducent (or abducens; CN VI), facial (CN VII), vestibulocochlear (CN VIII), glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X), accessory (CN XI), and ...
What is the function of olfactory nerve?
Your olfactory nerve is the first cranial nerve (CN I). This nerve enables your olfactory system and sense of smell. Cranial nerve 1 is the shortest sensory nerve. It starts in your brain and ends in the upper, inside part of your nose.
What is the function of the trigeminal nerve?
Its main function is transmitting sensory information to the skin, sinuses, and mucous membranes in the face. It also stimulates movement in the jaw muscles. The trigeminal nerve has three different divisions.
Which cranial nerve has both sensory and motor function?
The trigeminal nerve is one of the cranial nerves that has both sensory and motor function. Cranial nerves are also classified using Roman numerals based on their location. The trigeminal nerve is also called cranial nerve V.
Why does my trigeminal nerve hurt?
This is part of a chronic condition called trigeminal neuralgia. It happens when the trigeminal nerve is under pressure or irritated. This can happen when a vein or artery presses against the nerve.
How long does it take for trigeminal neuralgia to hurt?
People often describe it as a shooting or jabbing pain that lasts anywhere from a few seconds to several hours. Pain can also be achy or burning. It tends to occur more often over time.
What type of information does the cranial nerve transmit?
Cranial nerves can transmit two types of information: Sensory information includes details about smells, sights, tastes, touch, and sounds to the brain. Motor information refers to signals that affect the movement or activity of muscles and glands.
What test is used to test for ophthalmic division?
Pin or cotton swab test. One or both sides of the face are touched with either a pin or cotton swab. The person will then be asked whether they felt anything, and if so, where they felt it. A doctor may also lightly touch the cornea of the eye with a cotton swab to test the ophthalmic division. If the person doesn’t blink, the ophthalmic division of their trigeminal nerve may be damaged.
How to relieve pain from trigeminal nerve?
Sometimes surgery is needed to remove what’s irritating the trigeminal nerve. In other cases, injecting a numbing agent into the nerve can help. Mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can also help to relax nearby muscles and ease pain. Last medically reviewed on July 27, 2018.
What are the functions of the cranial nerves?
Their functions are usually categorized as being either sensory or motor. Sensory nerves are involved with your senses, such as smell, hearing, and touch. Motor nerves control the movement and function of muscles or glands. Keep reading to learn more about each of the 12 cranial nerves and how they function.
Where does the trigeminal nerve originate?
It also controls the movement of muscles within your jaw and ear. The trigeminal nerve originates from a group of nuclei — which is a collection of nerve cells — in the midbrain and medulla regions of your brainstem.
What is the function of the oculomotor nerve?
The oculomotor nerve has two different motor functions: muscle function and pupil response. Muscle function. Your oculomotor nerve provides motor function to four of the six muscles around your eyes. These muscles help your eyes move and focus on objects.
How many cranial nerves are there?
What are cranial nerves? Your cranial nerves are pairs of nerves that connect your brain to different parts of your head, neck, and trunk. There are 12 of them, each named for their function or structure. Each nerve also has a corresponding Roman numeral between I and XII.
How many divisions does the trigeminal nerve have?
The trigeminal nerve has three divisions, which are:
Which nerve is located in the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions?
The sensory root of your trigeminal nerve branches into the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions. The motor root of your trigeminal nerve passes below the sensory root and is only distributed into the mandibular division. VI. Abducens nerve.
Which nerve transmits sensory information to your brain regarding smells that you encounter?
The olfactory nerve transmits sensory information to your brain regarding smells that you encounter.
What is the function of the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Its primary function is to provide sensory and motor innervation to the face. The trigeminal nerve consists of three branches on either side that extend to different territories of the face. These branches join at the trigeminal ganglia which are located within the Meckel cave of the cranial cavity. The different branches are namely the ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) nerves. The ophthalmic nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the face and skull above the palpebral fissure as well as the eye and portions of the nasal cavity. The maxillary nerve is also a sensory branch and innervates portions of the nasal cavity, sinuses, maxillary teeth, palate, and the middle portion of the face and skull above the mouth and below the forehead. The mandibular nerve is unique in that it contains both sensory and motor fibers. It provides sensory innervation of the buccal mucosa, mandibular teeth, and the skin below the mouth. The motor portion of V3 innervates all the muscles of mastication. Additionally, V3 provides sensory information from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue; this is differentiated from taste which is produced by CN VII.[1][2]
What is the best treatment for trigeminal neuralgia?
One of the most common surgical procedures related to the trigeminal nerve is surgical therapy for trigeminal neuralgia (discussed later). Even though surgery can offer the patient significant pain relief, it also has a considerable risk of permanent damage to the trigeminal nerve which could result in facial numbness. For this reason, surgical intervention is often recommended only after several pharmaceutical therapies have been attempted. The surgical interventions that are done for trigeminal neuralgia are split into two categories: non-destructive and destructive. The goal of non-destructive surgery is to alleviate nerve compression by removing any structure that may be impinging on the nerve and maintaining the nerve intact. Destructive procedures aim to disrupt the trigeminal nerve completely so that pain is no longer transmitted by the nerve. The result of a destructive procedure is the irreversible loss of sensation of the affected side of the face. [7][8][9]
What is the ophthalmic nerve?
The ophthalmic nerve is primarily responsible for the sensory innervation of the face and scalp above the orbits. It also contains sympathetic nerve fibers responsible for pupil dilation and supplies the ciliary body, iris, lacrimal gland, conjunctiva, and cornea. In addition to these superficial sensory functions, the ophthalmic nerve also supplies the superior portion of the nasal cavity, the frontal sinus, and even deeper structures including the dura mater and portions of the anterior cranial fossa.
What is Wallenberg syndrome?
Wallenberg syndrome is a condition that occurs when the lateral portion of the medulla in the brainstem becomes damaged, typically due to stroke. A lesion in this region of the brain stem results in an ipsilateral sensory loss in the territory of the trigeminal nerve and contralateral sensory loss in the rest of the body. Wallenberg syndrome is often recognized in the clinical setting to localize brainstem lesions. [10]
Which nerve is responsible for innervation of the facial muscles?
The only branch of the trigeminal nerve that has a motor component in the mandibular nerv e (V3). This branch supplies motor innervation to the facial muscles involved in mastication which include the masseter, temporalis muscle, and the lateral and medial pterygoids. Additionally, V3 gives off branches that innervate the tensor veli palatini, the mylohyoid, the tensor tympani, and the anterior portion of the digastric muscle.
Which nerve innervates the muscles of mastication?
The mandibular nerve is the only branch of the trigeminal nerve that has both sensory and motor components. The motor component innervates all of the muscles of mastication (enumerated below). The sensory portion is responsible for pain and temperature information from the mandibular teeth, buccal mucosa, temporomandibular joint, the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and the face below the territory of the maxillary nerve.
Which nerve supplies the territory just below the orbits and above the mouth?
The maxillary nerve is also a sensory branch, and it supplies the territory just below the orbits and above the mouth. This includes the inferior portion of the nasal cavity, the maxillary teeth, and maxillary sinus.
What are the functions of the cranial nerves?
Each has a different function for sense or movement. The functions of the cranial nerves are sensory, motor, or both: Sensory cranial nerves help a person to see, smell, and hear. Motor cranial nerves help control muscle movements in the head and neck.
What nerve helps the body sense changes in the position of the head with regard to gravity?
The vestibular nerve helps the body sense changes in the position of the head with regard to gravity. The body uses this information to maintain balance.
How many cranial nerves are there?
The twelve cranial nerves are a group of nerves that start in the brain and provide motor and sensory functions to the head and neck. Each cranial nerve has its unique anatomical characteristics and functions. Doctors can identify neurological or psychiatric disorders by testing cranial nerve functions. Last medically reviewed on October 10, 2019.
Which nerve provides movement to most of the muscles that move the eyeball and upper eyelid, known as extraocular?
The oculomotor nerve provides movement to most of the muscles that move the eyeball and upper eyelid, known as extraocular muscles.
Which nerve is involved in eye movement?
The trochlear nerve is also involved in eye movement.
Which nerves help control muscle movements in the head and neck?
Motor cranial nerves help control muscle movements in the head and neck.
How many nuclei are in the facial nerve?
The facial nerve is made up of four nuclei that serve different functions: