
Some Other Examples of Convergent Evolution
- The evolution of complex eyes in vertebrates, cephalopods (squid and octopus) and arthropods (crustaceans, insects and spiders).
- Streamlined body shape of dolphins, sharks and (extinct) ichthyosaurs.
- The evolution of echolocation in whales and bats.
- The paired shell shape of bivalve mollusks and brachiopods.
- The silk producing ability of spiders, silk worms, silk moths and weaver ants.
What happens in convergent evolution?
What Is Convergent Evolution?
- Characteristics. Species that are linked through convergent evolution oftentimes look very similar. However, they are not closely related on the tree of life.
- Examples. One example of convergent evolution is the Australian sugar glider and the North American flying squirrel.
- Plants. Plants can also undergo convergent evolution to become more similar. ...
What does convergent evolution mean?
In evolutionary biology, convergent evolution is the process whereby organisms not closely related (not monophyletic), independently evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments or ecological niches. It is the opposite of divergent evolution, where related species evolve different traits.
Why does convergent evolution happen?
Convergent evolution is when two species, that are not related via a recent common ancestor, become more similar. Most of the time, the reason behind convergent evolution occurring is the build-up of adaptations over time to fill a certain niche. When the same or similar niches are available in different geographical locations, different species will most likely fill that niche.
What is convergent evolution Quizlet?
What is convergent evolution quizlet? In evolutionary biology, convergent evolution is the process whereby organisms not closely related (not monophyletic), independently evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments or ecological niches. Which best defines the term divergent evolution?
What is an example of convergent evolution?
Convergent evolution is when different organisms independently evolve similar traits. For example, sharks and dolphins look relatively similar despite being entirely unrelated.
Which is an example of convergent evolution quizlet?
Wings of bats, birds and insects are an example of convergent evolution. Each of these species split into a separate lineage, and independently, with no relation to any common ancestor they may or may not have shared, they developed wings.
Which of the following are good examples of convergent evolution?
Examples of convergent evolution include the relationship between bat and insect wings, shark and dolphin bodies, and vertebrate and cephalopod eyes. Analogous structures arise from convergent evolution, but homologous structures do not.
Which of the following is a type of convergent evolution?
Some Other Examples of Convergent Evolution The evolution of complex eyes in vertebrates, cephalopods (squid and octopus) and arthropods (crustaceans, insects and spiders). Streamlined body shape of dolphins, sharks and (extinct) ichthyosaurs. The evolution of echolocation in whales and bats.
What is convergent evolution?
Convergent evolution refers to the evolution in different lineages of structures that are similar or 'analogous', but that cannot be attributed to the existence of a common ancestor; in other words, the fact that the structures are analogous does not reflect homology.
What is the best example of divergent evolution?
A classic example of divergent evolution is the Galapagos finch which Darwin discovered that in different environments, the finches' beaks adapted differently. The individual Galapagos finches looked so different from one another that he was surprised when he found that they were all related.
Are plants an example of convergent evolution?
One of the most dramatic examples of convergent evolution is seen in photosynthesis—the process that plants use to capture energy from the sun and convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates and oxygen.
Why are birds an example of convergent evolution?
Birds and bats have homologous limbs because they are both ultimately derived from terrestrial tetrapods, but their flight mechanisms are only analogous, so their wings are examples of functional convergence. The two groups have independently evolved their own means of powered flight.
What is an example of divergent evolution?
In divergent evolution, two or more distinct species share a common ancestor from which they diverged. A common example is a modern elephant and woolly mammoth. They share a common ancestor and yet evolved into two different species. Another example is the dog, the wolf, and the fox.
What is convergent evolution quizlet?
In evolutionary biology, convergent evolution is the process whereby organisms not closely related (not monophyletic), independently evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments or ecological niches.
Which of the following best explains convergent evolution?
Which one of the following statements best describes this concept? Convergent evolution occurs when two species living in different areas evolve similarities through natural selection acting on those characteristics.
What is the example of convergent boundary?
The Pacific Ring of Fire is an example of a convergent plate boundary. At convergent plate boundaries, oceanic crust is often forced down into the mantle where it begins to melt. Magma rises into and through the other plate, solidifying into granite, the rock that makes up the continents.
What is convergent evolution quizlet?
In evolutionary biology, convergent evolution is the process whereby organisms not closely related (not monophyletic), independently evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments or ecological niches.
Which of the following best describes the convergent evolution?
Which one of the following statements best describes this concept? Convergent evolution occurs when two species living in different areas evolve similarities through natural selection acting on those characteristics.
Which of the following is a statement that describes the concept of convergent evolution quizlet?
Which of the following is a statement that describes the concept of convergent evolution? Organisms that are not directly related develop similar traits.
Why does convergent evolution occur quizlet?
Convergent evolution occurs when two species living in the same area are competing for the same resource thus causing one to evolve away from the other.
What is convergent evolution?
Convergent Evolution Definition. Convergent evolution is the process in which organisms that are not closely related independently evolve similar features. Adaptions may take the form of similar body forms, colors, organs and other adaptions which make up the organism ’s phenotype. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures or ’homoplasies’, ...
What is the term for the evolution of different traits between groups?
Divergent Evolution – The evolution and accumulation of different traits between groups, which results in the formation of new species. Vestigial Structures – A structure or attribute, which is present within an organism but has lost its ancestral function.
What are the long structures that evolved for collecting nectar?
The long structures (tongues and beaks) evolved for collecting nectar in hummingbirds, bees, moths and butterflies. The evolution of eyespots on the wings of butterflies and the tails of fish. Spines on the bodies of echidnas (monotremes), hedgehogs (mammals) and porcupines (rodents).
Where did mammals evolve?
Separated by the split of continents, mammals evolved to occupy niches in Europe, Africa and America, while marsupials occupied similar niches in Australia and the surrounding islands; this history has produced many examples of convergent evolution.
Which organisms have complex eyes?
The evolution of complex eyes in vertebrates, cephalopods (squid and octopus) and arthropods (crustaceans, insects and spiders).
Which organisms have neurotoxins?
On a molecular level, the independent evolution of proteins and toxins has also occurred throughout many separate phyla; for example, sea anemones ( Cnidaria ), snakes ( Vertebrates ), scorpions ( Arthropods) and cone snails ( Molluscs) all produce neurotoxins which act similarly upon the neurotransmitter receptors of their prey.
Is analogous structure convergent?
C is correct. Analogous structures are independently evolved features present in two different species as a product of convergent evolution.
What is convergence in evolution?
Convergent evolution — the repeated evolution of similar traits in multiple lineages which all ancestrally lack the trait — is rife in nature, as illustrated by the examples below. The ultimate cause of convergence is usually a similar evolutionary biome, as similar environments will select for similar traits in any species occupying ...
What are some examples of parallel evolution?
Several mammal groups have independently evolved prickly protrusions of the skin – echidnas ( monotremes ), the insectivorous hedgehogs, some tenrecs (a diverse group of shrew-like Madagascan mammals), Old World porcupines ( rodents) and New World porcupines (another biological family of rodents). In this case, because the two groups of porcupines are closely related, they would be considered to be examples of parallel evolution; however, neither echidnas, nor hedgehogs, nor tenrecs are close relatives of the Rodentia. In fact, the last common ancestor of all of these groups was a contemporary of the dinosaurs. The eutriconodont Spinolestes that lived in the Early Cretaceous Period represents an even earlier example of a spined mammal, unrelated to any modern mammal group.
How many times has photosynthesis evolved?
C4 photosynthesis is estimated to have evolved over 60 times within plants, via multiple different sequences of evolutionary events. C4 plants use a different metabolic pathway to capture carbon dioxide but also have differences in leaf anatomy and cell biology compared to most other plants.
What animal has a similar skull to a wolverine?
The marsupial Tasmanian devil has many resemblances to the placental hyena or a wolverine. Similar skull morphology, large canines and crushing carnassial molars. Marsupial kangaroos and wallabies have many resemblances to the maras (a large rodent from the cavy family ( Caviidae )), rabbits and hares ( lagomorphs ).
What are some examples of adaptive radiation?
Legless lizards such as Pygopodidae are snake-like lizards that are much like true snakes. Anole lizards, with populations on isolated islands, are one of the best examples of both adaptive radiation and convergent evolution.
Who suggested that Tiktaalik roseae prop up on its fins to venture onto land?
Tiktaalik roseae - artistic interpretation. Neil Shubin, suggests the animal could prop up on its fins to venture onto land, though many palaeonthologists reject this idea as outdated
Is carbonic anhydrase convergent?
The existence of distinct families of carbonic anhydrase is believed to illustrate convergent evolution. The use of ( Z )-7-dodecen-1-yl acetate as a sex pheromone by the Asian elephant ( Elephas maximus) and by more than 100 species of Lepidoptera.
What is convergence evolution?
January 3, 2019. Convergent evolution refers to the process where different organisms evolve to form similar traits, despite not being closely related. This occurs when independent species have had to evolve to survive in similar habitats or have a specific niche to fill. There tends to be a finite number of ways for nature to deal ...
Why do animals converge in appearance?
Another reason that animals can converge in appearance is because one species has evolved to mimic another. We’ve all heard of the classic explanation for why some species are a specific colour. The picture above is probably a massive giveaway, but we’re talking about reds, yellows and blacks here that usually indicate poison, toxicity or venom. There are two types of mimicry:
What mutations did humans and squids have?
Under unknown environmental pressures that we both must have shared, humans and squids developed (almost) the same mutations to Pax6 that resulted in the evolution of ‘camera eyes’ in both of our species. If there’s anything that you take away from this article, let it be that. 3. Prehensile tails.
What do sharks and dolphins have in common?
What do sharks and dolphins have in common other than their swimmingly good looks? Not much. One’s a mammal and one’s a fish. One extracts oxygen from water through gills, while the other has to go to the surface for oxygen. So why do they look so similar? Both have got pectoral fins, a streamlined body and flippers. Perhaps the introduction has given away the answer, but if not, then you were right if you thought of hunting. Both are predators and need adaptations that maximise their hunting success. They need to swim as fast as possible and this is the shape that achieves this goal best. Try to visualise a penguin in the same pose as the dolphin and you won’t find it that difficult. Mother nature is the queen of recycling success. Whatever works best, natural selection will prevail and make it happen.
Why do dolphins use echolocation?
It involves sending out ultrasonic pulses and listening to their echos to determine where objects are in the water or air, respectively . For both animals, this was necessary for two reasons: to catch prey and also to avoid obstacles. I’ve made it sound like a very simple process but it really isn’t because it also involves having brain structures that are able to interpret the response and create a visual map of surroundings.
Why are hawks and owls called homologous structures?
These would be called ‘homologous structures’ because there is a difference in that they do share a common ancestor that was capable of flight. 2. Human eyes and squid eyes.
Is Map of Life a convergent evolution website?
It’s a website dedicated solely to convergent evolution and it is organised really well therefore making it very user friendly. Which ones surprised you the most?
Which scientist argued that evolution is accomplished by the process of natural selection?
Charles Darwin argued that evolution is accomplished by the process of natural selection.
What selective pressure drove the evolution of beak shape?
The selective pressure driving the evolution of beak shape was food availability, not mate
What is phenotypic variation?
E. Phenotypic variation within a species is due in part to inherited characteristics. B. Phenotypic variation that an organism acquires in its lifetime is passed on to its offspring. Natural selection varies the shape of the beaks among Darwin's finches in response to: A. the available food supply.
What are the trends in horse evolution?
The general trends during horse evolution are increase in body size, lengthening of limbs, reduction of digits on both sets of limbs, and tooth development for a grazing life style. C. Global climate change during the Miocene and early Oligocene epochs caused many of the. changes in the evolution of horses.
Can artificial selection produce maladaptive structures?
selection, it cannot . C. Artificial selection can produce maladaptive structures, natural selection cannot. Considerably more phenotypic variation exists in domesticated varieties of species like. dogs and cabbages than exists in non-domesticated species like lions and maple trees.
Why does C evolution occur?
C Evolution occurs because some individuals are heterozygous at some loci.
What is the theory of natural selection?
The theory of natural selection postulates that: A in each generation, individuals well adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and tend to produce more progeny than less well adapted individuals. B individual deaths occur completely at random, with no relationship to an individual's trait.
What is the theme that ties together all aspects of biology?
Evolution is often described as "the theme that ties together all aspects of biology." This#N#is because the process of evolution#N#A. explains how organisms become adapted to their environment.#N#B. explains the diversity of organisms.#N#C. explains why all organisms have characteristics in common.#N#D. explains why distantly related organisms sometimes resemble one another.#N#E. all of the above are appropriate answers.
Who chooses which individuals reproduce based on desirability of traits?
D breeders and farmers choose which individuals reproduce based on desirability of traits.
Can artificial selection produce large evolutionary changes?
A artificial selection is not capable of producing large evolutionary changes.
What did Darwin discover about the Galapagos Islands?
While Darwin was investigating the organisms on the Galapagos Islands, he noticed that all the islands had finches, but the types of finches found on each island were unique to that island. The finches on each island were best described as members of the same
What did paleontologists find in an area that was once a shallow lake?
Paleontologists excavating an area that was once a shallow lake find fossils of two extinct species that were ancestors to modern horses. Why would scientists look for animal fossils in areas that were once near shallow water?
Why did Darwin delay publishing his work?
Because he was well aware of the effect his theory of evolution would have on the public and on the Church of England, Darwin delayed publishing his work for several decades while he gathered additional evidence. After invoking selective breeding of domesticated species as evidence that groups of organisms are capable of change, he then proposed that natural populations can change as well. On which two lines of evidence did he base this proposal
What makes bacteria resistant to antibiotics?
Some members of the bacteria population must have had a genetic variation that made them resistant to antibiotics.
Is evolution based on modification?
Evolution is based on descent with modification.
How does natural selection produce closely related species?
Natural selection can, through common descent, produce closely related species that have similarities due to their shared ancestry. Natural selection can also, through convergent evolution, lead to distantly related species appearing very similar. Identify which examples reflect common descent and which reflect convergence.
What percentage of fish have alleles that cause them to swim to the bottom of a lake when they see?
b. 82% of a population of fish possess alleles that cause them swim to the bottom of a lake when they see a shadow. One year after a population of bald eagles preys on the fish at the surface, close to 100% of the fish in the population show this behavior.
What percentage of crayfish have alleles?
a. 5% of a population crayfish in a stream possess alleles that allow them to generate some ATP without oxygen. A large drought occurs and dries up the stream, leaving only oxygen poor ponds behind. After the drought ends, 95% of the crayfish in the population possess the low oxygen ATP-generating alleles.
Is Staphylococcus aureus a natural selection?
Natural selection is not the only mechanism for evolution.
Convergent Evolution Definition
Examples of Convergent Evolution
- Convergent Evolution of Wings
A widespread example of convergent evolution is the evolution of wings and powered flight in birds, bats and (now extinct) pterosaurs, each of which belong to a different classof organism and therefore have very distant common ancestors. Fossil evidence has determined that flight evolv… - Convergent Evolution between Placental Mammals and Marsupials
Placental mammals, which have offspring that undergo gestation within the uterusand are born fairly advanced, and marsupials whose offspring are born very immature and continue to develop within a pouch on the mother’s body, diverged from a common ancestor around 100 million year…
Related Biology Terms
- Divergent Evolution– The evolution and accumulation of different traits between groups, which results in the formation of new species.
- Vestigial Structures– A structure or attribute, which is present within an organism but has lost its ancestral function.
- Analogous Structures– An organ or structure, which is visually similar or performs the same …
- Divergent Evolution– The evolution and accumulation of different traits between groups, which results in the formation of new species.
- Vestigial Structures– A structure or attribute, which is present within an organism but has lost its ancestral function.
- Analogous Structures– An organ or structure, which is visually similar or performs the same function in two different species, although, is not present in their common ancestor.
- Homologous Structures– An organ or structure in the body, which is inherited from a common ancestor between species.
Quiz
- 1. Analogous structures are: A. Structures that remain unchanged throughout evolution B. Structures that are shared with the common ancestors of other species C. Structures that are similar in function or appearance in two species that are not present in their common ancestor D.Structures that are present in the common ancestors of two species and are not still present 2…
Overview
Convergent evolution — the repeated evolution of similar traits in multiple lineages which all ancestrally lack the trait — is rife in nature, as illustrated by the examples below. The ultimate cause of convergence is usually a similar evolutionary biome, as similar environments will select for similar traits in any species occupying the same ecological niche, even if those species are only distantly related. In the case of cryptic species, it can create species which are only distingu…
In animals
• Several groups of ungulates have independently reduced or lost side digits on their feet, often leaving one or two digits for walking. That name comes from their hooves, which have evolved from claws several times. For example, horses have one walking digit and domestic bovines two on each foot. Various other land vertebrates have also reduced or lost digits.
In plants
• Leaves have evolved multiple times - see Evolutionary history of plants. They have evolved not only in land plants, but also in various algae, like kelp.
• Prickles, thorns and spines are all modified plant tissues that have evolved to prevent or limit herbivory, these structures have evolved independently a number of times.
In fungi
• There are a variety of saprophytic and parasitic organisms that have evolved the habit of growing into their substrates as thin strands for extracellular digestion. This is most typical of the "true" fungi, but it has also evolved in Actinomycetota (Bacteria), oomycetes (which are part of the stramenopile grouping, as are kelp), parasitic plants, and rhizocephalans (parasitic barnacles).
• Slime molds are traditionally classified as fungi, but molecular-phylogeny work has revealed that most …
In proteins, enzymes and biochemical pathways
Here is a list of examples in which unrelated proteins have similar functions with different structure.
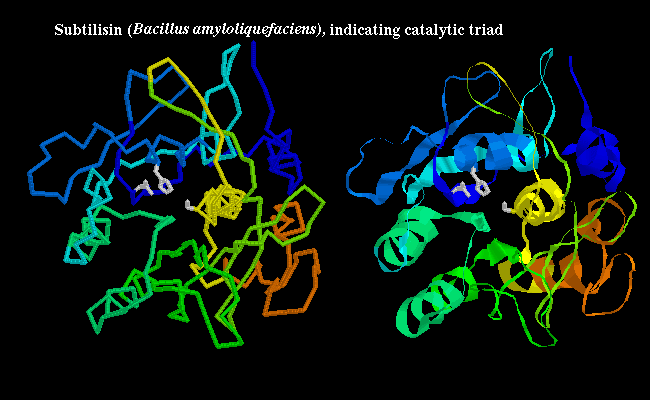
• The convergent orientation of the catalytic triad in the active site of serine and cysteine proteases independently in over 20 enzyme superfamilies.
• The use of an N-terminal threonine for proteolysis.
Further reading
• McGhee, G.R. (2011) Convergent Evolution: Limited Forms Most Beautiful. Vienna Series in Theoretical Biology: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, Cambridge (MA). 322 pp.