The macronutrients Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth, plant metabolism and their external supply. This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients.Plant nutrition
What are the different types of nutrient classes?
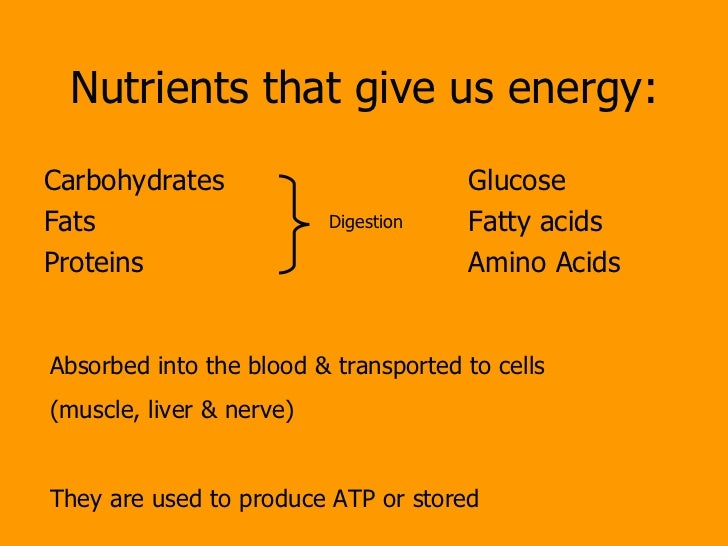
These nutrient classes can be categorized as either macronutrients (needed in relatively large amounts) or micronutrients (needed in smaller quantities). The macronutrients include carbohydrates (including fiber), fats, protein, and water.
What are nutrients and why are they important?
Nutrients are chemical substances found in food that are required by the body to provide energy, give the body structure, and help regulate chemical processes. There are six classes of nutrients:
What is the role of micronutrients in energy metabolism?
In contrast to carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, micronutrients are not a source of energy, but they assist in the process of energy metabolism as cofactors or components of enzymes (known as coenzymes).
What are micronutrients and macronutrients?
Macronutrients are eaten in large amounts and include the primary building blocks of your diet — protein, carbohydrates, and fat — which provide your body with energy. Vitamins and minerals are micronutrients, and small doses go a long way. There are six main groups of essential micronutrients and macronutrients.
Calories
Calorie is the measure of how much energy is in food. The official definition of calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise 1 gram of water {eq}1^oC {/eq}. But when referring to Calories used in food, the technical term is kilocalories.
Fats
Fat, also called lipids, include several different categories, including:
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates include simple and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates include foods such as sugar, while complex carbohydrates are found in foods such as oats. The body takes both, simple and complex carbohydrates, and breaks them down into glucose to use for energy.
Proteins
Proteins comprise the third type of energy-yielding nutrient. Protein, just like carbohydrates, also includes 4 grams of Calories per gram. The Calories per gram is calculated in the same way as carbohydrates:
What are the different types of nutrients?
The macronutrients include carbohydrates (including fiber), fats, protein, and water. The micronutrients are minerals and vitamins. The macronutrients (excluding fiber and water) provide structural material (amino acids from which proteins are built, and lipids from which cell membranes and some signaling molecules are built) and energy.
How much energy does a carbohydrate have?
Carbohydrates and proteins provide 17 kJ approximately (4 kcal) of energy per gram, while fats provide 37 kJ (9 kcal) per gram. , [17] though the net energy from either depends on such factors as absorption and digestive effort, which vary substantially from instance to instance.
What are the macronutrients in the cell?
The macronutrients include carbohydrates (including fiber), fats, protein, and water. The micronutrients are minerals and vitamins. The macronutrients (excluding fiber and water) provide structural material (amino acids from which proteins are built, and lipids from which cell membranes and some signaling molecules are built) and energy.
How much energy does a protein have?
Some of the structural material can be used to generate energy internally, and in either case it is measured in Joules or kilocalories (often called "Calories" and written with a capital Cto distinguish them from little 'c' calories). Carbohydrates and proteins provide 17 kJ approximately (4 kcal) of energy per gram, while fats provide 37 kJ (9 kcal) per gram. , [17] though the net energy from either depends on such factors as absorption and digestive effort, which vary substantially from instance to instance.
What are the molecules of carbohydrates and fat?
Molecules of carbohydrates and fats consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Carbohydrates range from simple monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose) to complexpolysaccharides (starch). Haven’t found the relevant content? Hire a subject expert to help you with Six Major Classes of Nutrients. Hire writer.
What are the components of a protein?
Protein molecules contain nitrogen atoms in addition to carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. The fundamental components of protein are nitrogen-containing amino acids, some of which are essential in the sense that humans cannot make them internally.
What are the elements that make up proteins?
Protein molecules contain nitrogen atoms in addition to carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. The fundamental components of protein are nitrogen-containing amino acids, some of which are essential in the sense that humans cannot make them internally.
What are essential nutrients?
Essential nutrients are compounds that the body can’t make or can’t make in sufficient quantity. According to the World Health Organization. , these nutrients must come from food, and they’re vital for disease prevention, growth, and good health.
What are the two categories of nutrients?
While there are many essential nutrients, they can be broken into two categories: macronutrients and micronutrients.
How many groups of micronutrients are there?
Vitamins and minerals are micronutrients, and small doses go a long way. There are six main groups of essential micronutrients and macronutrients.
How many vitamins are needed for the body to function properly?
The body needs these micronutrients to support its functions. There are 13 essential vitamins that the body needs to function properly, including vitamins A, C, B 6, and D. Each vitamin plays an important role in the body, and not getting enough of them can cause health problems and disease.
Why do we need vitamins?
Vitamins are essential for healthy vision, skin, and bones. Vitamins may lower the risk of lung and prostate cancer, and they’re powerful antioxidants. Vitamins like vitamin C boost the immune system and help the body heal. Healthy sources.
What are some good sources of protein?
While meat, fish, and eggs are good sources of essential amino acids, you can also get protein from plant sources like beans, soy, nuts, and some grains . Exactly how much protein you need daily depends on a variety of factors including how active you are, and your age.
Why is water important for your body?
Water improves your brain function and mood. It acts a shock absorber and a lubricant in the body. It also helps flush out toxins, carry nutrients to cells, hydrate the body, and prevent constipation. Even mild dehydration can make you feel tired and impair your concentration and physical performance. Trusted Source.
