What is the function of pepsin in the stomach?
Pepsin is a stomach enzyme that serves to digest proteins found in ingested food. Gastric chief cells secrete pepsin as an inactive zymogen called pepsinogen. Parietal cells within the stomach lining secrete hydrochloric acid that lowers the pH of the stomach. Where does pepsin get secreted? PEPSIN.
Where is pepsin secreted from?
Pepsin is produced and secreted by the gastric chief cells present in the stomach lining. Pepsin is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of many animals. Pepsin plays a major role in the digestion of food.
Which enzyme is present in inactive form as pepsinogen?
Pepsin is an enzyme which is present in an inactive form as pepsinogen. It is secreted by the gastric glands of the stomach when Hcl act on pepsinogen it can it is converted into pepsin which is the active form. Was this answer helpful?
What enzymes are produced in the stomach?
Intrinsic factor, an enzyme-like compound which helps the small intestine absorb vitamin B12, is also produced in the stomach. The pancreas is a leaf-shaped organ that lies below the stomach. It secretes juices rich in enzymes capable of digesting the 3 main energy nutrients -- carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
Is This an Emergency?
What organ is responsible for digesting fats and carbohydrates?
What organ secretes the most energy?
What are the secretions in the villi?
What is the liver's main function?
What are the deep spaces between the villi called?
What is the main organ of the digestive system?
See 4 more
About this website
Which organ secretes enzyme pepsin and trypsin?
Origin: Pepsin is the chief digestive enzyme in stomach, which is produced by the gastric gland in stomach and is a component of gastric juice, while trypsin in produced by the pancreas and is a component of pancreatic juice.
Which organ secretes which enzyme?
The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum and hormones into the bloodstream. The digestive enzymes (such as amylase, lipase, and trypsin) are released from the cells of the acini and flow into the pancreatic duct.
Is pepsin secreted?
Pepsin enzyme is secreted by gastric glands of the stomach as inactive pepsinogen to protect the cells of these secretory glands from strong protein digesting action of the enzyme. The inactive form of the enzyme is activated by acidic pH of stomach lumen and the stomach wall is protected by mucus lining.
Where is the pepsin produced?
the stomachGlands in the mucous-membrane lining of the stomach make and store pepsinogen. Impulses from the vagus nerve and the hormonal secretions of gastrin and secretin stimulate the release of pepsinogen into the stomach, where it is mixed with hydrochloric acid and rapidly converted to the active enzyme pepsin.
Does pancreas secrete pepsin?
Pancreatic juice is secreted by the pancreas, which contains a variety of enzymes, including trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, elastase, carboxypeptidase, pancreatic lipase and amylase. Pepsin in not present in pancreatic juice. It is secreted by the peptic cells of the stomach.
Which enzymes are secreted by pancreas?
Pancreatic enzymesLipase. This enzyme works together with bile, which your liver produces, to break down fat in your diet. ... Protease. This enzyme breaks down proteins in your diet. ... Amylase. This enzyme helps break down starches into sugar, which your body can use for energy.
Where is pepsin and trypsin found?
Pepsin is secreted in stomach, trypsin is secreted in small intestine. Pepsin is situated in gastric glands, trypsin is situated in pancreas.
How is pepsin produced?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl), another component of the gastric juice, plays a crucial role in creating the pH required for pepsin activity. Parietal cells produce HCl by secreting hydrogen and chloride ions. When pepsinogen and hydrochloric acid exist together in the gastric juice, pepsin takes its active form.
How do you get pepsin?
While pepsin doesn't exist in food, you may be able to boost your body's own production of it by eating more protein- and fat-rich foods. Research in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition suggests that high-fat/keto diets may produce greater amounts of pepsin.
Where is pepsin active in the body?
Pepsin is an enzyme made by the stomach. It also functions in the stomach. This enzyme is created when stomach acid changes a protein called pepsinogen into pepsin. (1) Pepsinogen is inactive, but it is converted to the active enzyme pepsin by the action of hydrochloric acid.
What enzyme does the stomach produce?
pepsinIn your stomach, unique chief cells secrete digestive enzymes. One is pepsin, which breaks down proteins. Another is gastric lipase, which breaks down triglycerides.
In what organ is pepsin active quizlet?
The chief cells of the stomach secrete pepsinogen into the stomach lumen; which in the presence of HCl becomes pepsin, the active form of the enzyme.
Which organ secretes the digestive enzymes amylase lipase and trypsin?
The pancreasThe pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum and hormones into the bloodstream. The digestive enzymes (such as amylase, lipase, and trypsin) are released from the cells of the acini and flow into the pancreatic duct.
Which organ secretes enzymes that digest carbohydrates proteins and fats?
The pancreasThe pancreas produces a juice containing several enzymes that break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in food. The pancreas delivers digestive juice to the small intestine through small tubes called ducts.
What organ secretes an enzyme that digests carbohydrates?
pancreasThe accessory organ that secretes digestive enzymes which digest carbohydrates, fats, and proteins is the (c) pancreas. This organ secretes enzymes such as amylase, pancreatic lipase, and proteolytic enzymes like chymotrypsin and trypsin.
Which organ secretes enzymes that break down nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) in foods are digested in the small intestine with the help of both pancreatic enzymes and enzymes produced by the small intestine itself. Pancreatic enzymes called ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease break down RNA and DNA, respectively, into smaller nucleic acids.
What digestive juice is secreted in the esophagus? - Answers
How much pancreatic juice is produced daily? Nearly 1.6 quarts (1.5 liters) of digestive juices are secreted by the cells of the pancreas daily.Read more: how-much-pancreatic-digestive-juice-is ...
How do digestive juices in each organ of the GI tract break down food ...
How do digestive juices in each organ of the GI tract break down food? Digestive juices contain enzymes—substances that speed up chemical reactions in the body—that break food down into different nutrients.
A List of Digestive Enzymes and Their Functions - Bodytomy
Digestive enzymes play a key role in regulating and maintaining the functions of the digestive system properly. These enzymes not only helps in digestion but due to excess or lack of these enzymes, one can face difficulties in digestions too.
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Topic 4: Secretion
Page 6: The esophagus secretes mucus • The only secretion of the esophagus is mucus Page 7: Gastric secretions are produced regionally • The gastric mucosa produces exocrine, endocrine, and paracrine
What organs produce and secrete enzymes?
The pancreas is made up of 2 types of glands: Exocrine. The exocrine gland secretes digestive enzymes. These enzymes are secreted into a network of ducts that join the main pancreatic duct.
Where does digestion take place in the human body?
While the digestive process begins in the mouth and stomach, digestion gains momentum when food enters the small intestines. This is where secretions from the pancreas, liver and small intestines do most of the digestive work.
Is This an Emergency?
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, please see the National Library of Medicine’s list of signs you need emergency medical attention or call 911. If you think you may have COVID-19, use the CDC’s Coronavirus Self-Checker .
What organ is responsible for digesting fats and carbohydrates?
The pancreas is a leaf-shaped organ that lies below the stomach. It secretes juices rich in enzymes capable of digesting the 3 main energy nutrients -- carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Pancreatic juice also contains large amounts of sodium bicarbonate, which neutralizes the acid from the stomach and optimizes the environment for these enzymes to work. Pancreatic enzymes do most of the fat digestion, secreting pancreatic lipase, esterase and phospholipase, which break down chemically complex fats into simple, easy-to-absorb fats. Similarly, trypsin and carboxypolypeptidase break down proteins, and pancreatic amylase breaks down carbohydrates.
What organ secretes the most energy?
The pancreas is a leaf-shaped organ that lies below the stomach. It secretes juices rich in enzymes capable of digesting the 3 main energy nutrients -- carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Pancreatic juice also contains large amounts of sodium bicarbonate, which neutralizes the acid from the stomach and optimizes the environment for these enzymes to work. Pancreatic enzymes do most of the fat digestion, secreting pancreatic lipase, esterase and phospholipase, which break down chemically complex fats into simple, easy-to-absorb fats. Similarly, trypsin and carboxypolypeptidase break down proteins, and pancreatic amylase breaks down carbohydrates.
What are the secretions in the villi?
The deep spaces between the villi are called crypts, which secrete mucus, bicarbonate and water.
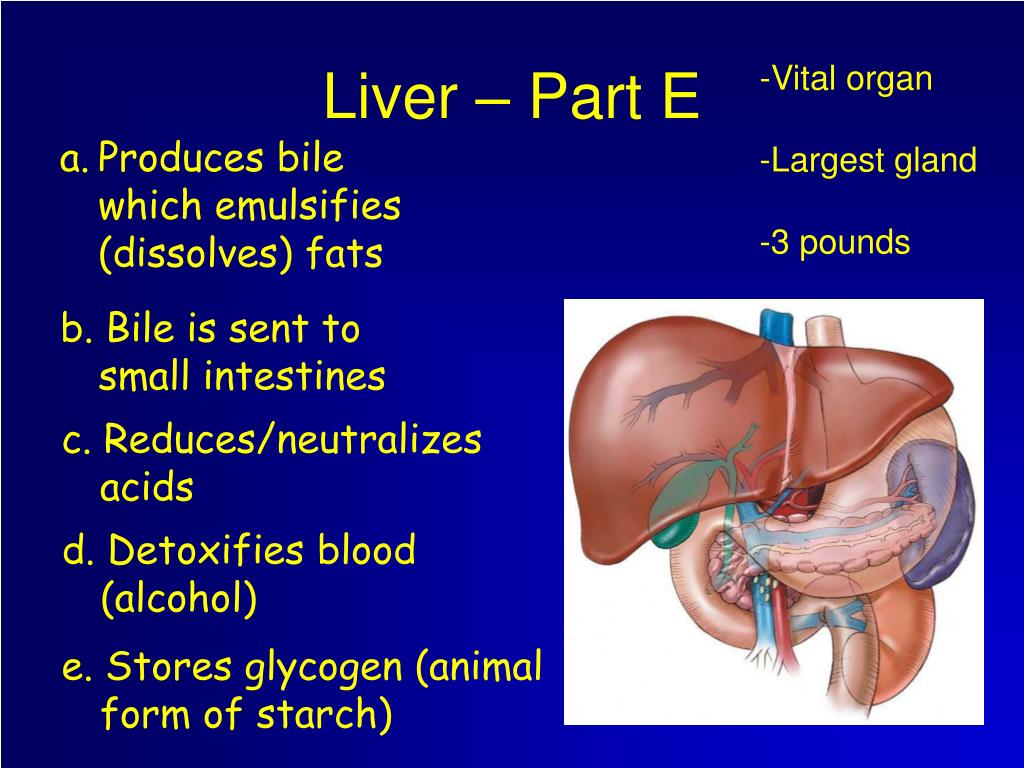
What is the liver's main function?
The liver produces a greenish juice called bile, which is stored and concentrated by the gall bladder. After a high-fat meal, such as one containing cheese, cream or bacon, the fats from the food tend to stick together to form large fat spheres. These are too big for the enzymes to work on, so the fat can be absorbed by the body. Bile acts like soap, breaking the bonds that hold these spheres together and turning them into tiny globules that are easily taken up by the body. Bile is not an enzyme but is is essential for the fat-digesting enzymes to work.
What are the deep spaces between the villi called?
The deep spaces between the villi are called crypts, which secrete mucus, bicarbonate and water. In addition to these secretions, the cells of the small intestine also produce hormones, like secretin and cholecystokinin, which stimulate the other organs to release their digestive juices. Advertisement.
What is the main organ of the digestive system?
The stomach , an important organ for digestion, produces gastric juice which is comprised of hydrochloric acid, water and enzymes. Hydrochloric acid works with the main gastric enzyme called pepsin to aid the digestion of protein-rich foods like eggs, meat and tofu. The production of acid is increased by a hormone known as gastrin, which is made by specific cells lining the stomach. The stomach also produces gastric lipase, which assists in digesting fats. Intrinsic factor, an enzyme-like compound which helps the small intestine absorb vitamin B12, is also produced in the stomach.
Is This an Emergency?
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, please see the National Library of Medicine’s list of signs you need emergency medical attention or call 911. If you think you may have COVID-19, use the CDC’s Coronavirus Self-Checker .
What organ is responsible for digesting fats and carbohydrates?
The pancreas is a leaf-shaped organ that lies below the stomach. It secretes juices rich in enzymes capable of digesting the 3 main energy nutrients -- carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Pancreatic juice also contains large amounts of sodium bicarbonate, which neutralizes the acid from the stomach and optimizes the environment for these enzymes to work. Pancreatic enzymes do most of the fat digestion, secreting pancreatic lipase, esterase and phospholipase, which break down chemically complex fats into simple, easy-to-absorb fats. Similarly, trypsin and carboxypolypeptidase break down proteins, and pancreatic amylase breaks down carbohydrates.
What organ secretes the most energy?
The pancreas is a leaf-shaped organ that lies below the stomach. It secretes juices rich in enzymes capable of digesting the 3 main energy nutrients -- carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Pancreatic juice also contains large amounts of sodium bicarbonate, which neutralizes the acid from the stomach and optimizes the environment for these enzymes to work. Pancreatic enzymes do most of the fat digestion, secreting pancreatic lipase, esterase and phospholipase, which break down chemically complex fats into simple, easy-to-absorb fats. Similarly, trypsin and carboxypolypeptidase break down proteins, and pancreatic amylase breaks down carbohydrates.
What are the secretions in the villi?
The deep spaces between the villi are called crypts, which secrete mucus, bicarbonate and water.
What is the liver's main function?
The liver produces a greenish juice called bile, which is stored and concentrated by the gall bladder. After a high-fat meal, such as one containing cheese, cream or bacon, the fats from the food tend to stick together to form large fat spheres. These are too big for the enzymes to work on, so the fat can be absorbed by the body. Bile acts like soap, breaking the bonds that hold these spheres together and turning them into tiny globules that are easily taken up by the body. Bile is not an enzyme but is is essential for the fat-digesting enzymes to work.
What are the deep spaces between the villi called?
The deep spaces between the villi are called crypts, which secrete mucus, bicarbonate and water. In addition to these secretions, the cells of the small intestine also produce hormones, like secretin and cholecystokinin, which stimulate the other organs to release their digestive juices. Advertisement.
What is the main organ of the digestive system?
The stomach , an important organ for digestion, produces gastric juice which is comprised of hydrochloric acid, water and enzymes. Hydrochloric acid works with the main gastric enzyme called pepsin to aid the digestion of protein-rich foods like eggs, meat and tofu. The production of acid is increased by a hormone known as gastrin, which is made by specific cells lining the stomach. The stomach also produces gastric lipase, which assists in digesting fats. Intrinsic factor, an enzyme-like compound which helps the small intestine absorb vitamin B12, is also produced in the stomach.