Heterotroph
A heterotroph is an organism that cannot fix carbon and uses organic carbon for growth. Heterotrophs can be further divided based on how they obtain energy; if the heterotroph uses light for energy, then it is considered a photoheterotroph, while if the heterotroph uses chemical energy, it i…
What animals are heterotrophs?
Heterotrophs are the organisms that cannot make their food by carbon fixation and consume producers and other consumers hence are known as consumers. Dogs, fish, and humans are some examples of heterotrophs. In this article, we will learn more about heterotrophs and their types. What are Heterotrophs? What are Heterotrophs?
What are the five types of heterotrophs?
What is a Heterotroph?
- TheTypes of Heterotrophs. There are three main types of heterotroph called photoheterotrophs, chemoheterotrophs, detritivores.
- Importance of Heterotrophs In The Ecosystem. Heterotrophs help maintain balance in the ecosystem by providing organic compounds for autotrophs. ...
- Ecology. ...
What are facts about heterotrophs?
heterotroph, in ecology, an organism that consumes other organisms in a food chain. In contrast to autotrophs, heterotrophs are unable to produce organic substances from inorganic ones. They must rely on an organic source of carbon that has originated as part of another living organism.
Why are humans called heterotrophs?
Why humans are called heterotrophs? Humans do not possess the physiological mechanism to produce their own food from the raw materials in their surroundings like the plants. Hence, humans consume plants and other animals to fulfill their energy needs. As they derive food or energy from other sources they are referred to as heterotrophs.
What are the 5 types of heterotrophs?
What Types Are There?Carnivores eat the meat of other animals.Herbivores eat plants.Omnivores can eat both meat and plants.Scavengers eat things left behind by carnivores and herbivores.Decomposers break down dead plant or animal matter into soil.Detritivores eat soil and other very small bits of organic matter.
What are 10 heterotrophs examples?
Fungi are heterotrophic. These organisms are plant-like in having cell walls but they lack chlorophyll (green pigment essential in photosynthesis). Protists (Kingdom Protista) that are heterotrophs include protozoans, certain nonphotosynthetic algae, water molds, and slime molds.
What makes an organism a Heterotroph?
A heterotroph (/ˈhɛtərəˌtroʊf, -ˌtrɒf/; from Ancient Greek ἕτερος (héteros) 'other', and τροφή (trophḗ) 'nutrition') is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter.
Is a Heterotroph an animal?
Heterotrophic organisms depend on other organisms for deriving nutrition. Example: Fungi, animals, etc. Animals are heterotrophs. They do not possess chlorophyll pigment to undergo photosynthesis, hence they feed on living organisms.
What are the 3 types of heterotrophs?
Heterotrophic nutrition can be one of three types – holozoic, saprophytic or parasitic. Holozoic nutrition can be seen in most vertebrates and some unicellular organisms like the amoeba. Saprophytic nutrition is where the organisms feed on dead and decaying matter. Examples include bacteria and fungi.
What is a heterotroph example?
Heterotrophs are known as consumers because they consume producers or other consumers. Dogs, birds, fish, and humans are all examples of heterotrophs. Heterotrophs occupy the second and third levels in a food chain, a sequence of organisms that provide energy and nutrients for other organisms.
Are fungi heterotrophs?
All fungi are heterotrophic, which means that they get the energy they need to live from other organisms. Like animals, fungi extract the energy stored in the bonds of organic compounds such as sugar and protein from living or dead organisms. Many of these compounds can also be recycled for further use.
What is also called a heterotroph?
Heterotrophs are also called 'other feeders,' and because they need to consume energy to sustain themselves, they are also known as 'consumers. ' Some organisms are actually able to survive by making their own food. These organisms are called autotrophs.
Is a plant a heterotroph?
Modes Of Nutrition Autotrophic – Plants exhibit autotrophic nutrition and are called primary producers. Plants synthesis their food by using light, carbon dioxide and water. Heterotrophic – Both animals and human beings are called heterotrophs, as they depend on plants for their food.
Are all animals heterotrophs?
A heterotroph is any living organism that obtains its energy from carbohydrates and other organic material. In simpler terms, heterotrophs are organisms that cannot produce their own food, therefore they eat other organisms that CAN produce their own food. All animals and most bacteria and fungi are heterotrophic.
Is algae a heterotroph?
Algae are autotrophs, meaning they produce their own food. Heterotrophs, conversely, feed on other organisms and organic materials in their environment.
What are 4 types of heterotrophs and what do they eat?
Heterotrophs include herbivores (plant-eaters), carnivores (meat-eaters), omnivores (organisms that eat both plants and animals), and decomposers (organisms that eat dead and decaying stuff).
What are 10 examples of autotrophs?
What are Autotrophs?Algae.Cyanobacteria.Maize plant.Grass.Wheat.Seaweed.Phytoplankton.
What are the 4 types of heterotrophic plants?
Plants show four types of heterotrophic behaviour, namely:Parasitism.Saprophytism.Symbionts.Insectivore.
Is Grass a heterotroph?
Grass, like the majority of green plants, is autotrophic. Thus, Grass produces its food through the photosynthesis process, which uses solar energy, water, and carbon dioxide. Thus, it is not a Heterotroph.
Is a Mouse a heterotroph?
Examples of Carnivorous Heterotrophs Carnivorous heterotrophs and their food sources include: Wolves: deer, goats, rabbits. Hawks: smaller birds, mice, lizards.
What are the two forms of heterotrophs?
Heliobacteria and certain proteobacteria are photoheterotrophs. Alternatively, chemoheterotrophs obtain their energy from ingesting preformed ...
What is heterotrophic food?
A heterotroph is an organism that cannot manufacture its own food by carbon fixation and therefore derives its intake of nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are secondary and tertiary consumers.
What is it called when a heterotroph eats plants?
Heterotrophs that eat plants to obtain their nutrition are called herbivores, or primary consumers.
What is the name of the organism that can fix inorganic carbon as an energy source?
Related Biology Terms. Autotroph – Also known as ‘primary producers’, these are organisms that can fix inorganic carbon as an energy source; most plants are autotrophs. Energy pyramid – The flow of energy through a food chain can be visualized as a pyramid, as energy is lost throughout each level.
What do carnivores eat?
Carnivores may also be scavengers, animals such as vultures or cockroaches, which eat animals which are already dead; often this is the carrion (meat) of animals that has been left over from the kill of a predator.
What are some examples of herbivores?
Examples of herbivores include cows, sheep, deer and other ruminant animals, which ferment plant material in special chambers containing the symbiotic organisms, within their stomachs.
What do fungi eat?
Fungi feed on a variety of different substrates, such as wood, cheese or flesh, although most of them specialize on a restricted range of food sources; some fungi are highly specialized, and are only able to obtain nutrition from a single species.
What is a heterotroph?
A heterotroph ( / ˈhɛtərəˌtroʊf, - ˌtrɒf /; from Ancient Greek ἕτερος héteros "other" and τροφή trophḗ "nutrition") is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but not producers. Living organisms that are heterotrophic include all animals and fungi, some bacteria and protists, and many parasitic plants. The term heterotroph arose in microbiology in 1946 as part of a classification of microorganisms based on their type of nutrition. The term is now used in many fields, such as ecology in describing the food chain .
How are animals classified as heterotrophs?
Animals are classified as heterotrophs by ingestion, fungi are classified as heterotrophs by absorption.
What do photoorganoheterotrophs use to make organic compounds?
Photoorganoheterotrophs, such as Rhodospirillaceae and purple non-sulfur bacteria synthesize organic compounds using sunlight coupled with oxidation of organic substances. They use organic compounds to build structures. They do not fix carbon dioxide and apparently do not have the Calvin cycle. Chemolithoheterotrophs like Oceanithermus profundus obtain energy from the oxidation of inorganic compounds, including hydrogen sulfide, elemental sulfur, thiosulfate, and molecular hydrogen. Mixotrophs (or facultative chemolithotroph) can use either carbon dioxide or organic carbon as the carbon source, meaning that mixotrophs have the ability to use both heterotrophic and autotrophic methods. Although mixotrophs have the ability to grow under both heterotrophic and autotrophic conditions, C. vulgaris have higher biomass and lipid productivity when growing under heterotrophic compared to autotrophic conditions.
What is the process of respiration in heterotrophs?
Respiration in heterotrophs is often accompanied by mineralization , the process of converting organic compounds to inorganic forms. When the organic nutrient source taken in by the heterotroph contains essential elements such as N, S, P in addition to C, H, and O, they are often removed first to proceed with the oxidation of organic nutrient and production of ATP via respiration. S and N in organic carbon source are transformed into H 2 S and NH 4+ through desulfurylation and deamination, respectively. Heterotrophs also allow for dephosphorylation as part of decomposition. The conversion of N and S from organic form to inorganic form is a critical part of the nitrogen and sulfur cycle. H 2 S formed from desulfurylation is further oxidized by lithotrophs and phototrophs while NH 4+ formed from deamination is further oxidized by lithotrophs to the forms available to plants. Heterotrophs’ ability to mineralize essential elements is critical to plant survival.
What do autotrophs use to sustain their life?
Autotrophs use energy from sunlight ( photoautotrophs) or oxidation of inorganic compounds ( lithoautotrophs) to convert inorganic carbon dioxide to organic carbon compounds and energy to sustain their life. Comparing the two in basic terms, heterotrophs (such as animals) eat either autotrophs (such as plants) or other heterotrophs, or both.
What is the cycle of heterotrophs and autotrophs?
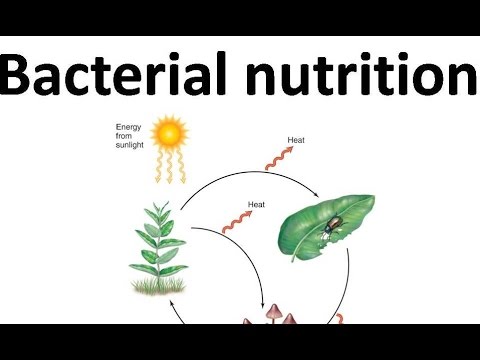
Cycle between autotrophs and heterotrophs. Autotrophs use light, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), and water to form oxygen and complex organic compounds, mainly through the process of photosynthesis ( green arrow). Both types of organisms use such compounds via cellular respiration to both generate ATP and again form CO 2 and water (two red arrows).
What are the two types of heterotrophs?
Types. Heterotrophs can be organotrophs or lithotrophs. Organotrophs exploit reduced carbon compounds as electron sources, like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from plants and animals. On the other hand, lithoheterotrophs use inorganic compounds, such as ammonium, nitrite, or sulfur, to obtain electrons. Another way of classifying different ...
What is a heterotroph?
A heterotroph is a living organism that eats other organisms for their energy source. Heterotrophic organisms are consumers in the ecosystem because they cannot manufacture their own food. Examples of heterotrophic organisms are humans, dung beetles, and hyenas.
What are the three types of heterotrophs?
Most biologists name three types of heterotrophs: herbivores (plant eaters), carnivores and omnivores (meat-eaters and eaters of meat and plants), and detritivores (debris eaters).
What is the difference between heterotrophs and autotrophs?
Heterotrophs contrast with autotrophs. Autotrophic organisms are living organisms that can manufacture their own nourishment from their environment.
What do carnivores eat?
Carnivores and Omnivores – Carnivores eat meat, meaning they eat other heterotrophs; omnivores eat both plants and meat , and both types of heterotrophs occupy the third level of food chains.
What is a heterotroph with no arms, legs, or brain?
A heterotroph with no arms, legs, or brain could be a mushroom, toadstool, or bacterium.
Which level of the food chain do heterotrophs occupy?
Heterotrophs occupy the second and third levels of food chains, feeding on autotrophs (second level) or feeding on autotrophs and other heterotrophs (third level).
How is the trophic level of an organism determined?
The trophic level of an organism is determined by where it is positioned in a food web.
What is a consumer in biology?
Consumers are organisms that cannot make their food supply and example of consumer are animals. Thus, Consumer are commonly refers to as heterotrophy in the food chain and they eat food that are produced by producer. However, very few exotic plants and few protists are also consumers.
Is a consumer an autotroph?
Consumers are heterotrophs. The other three are all autotrophs, meaning they produce their own "food."
