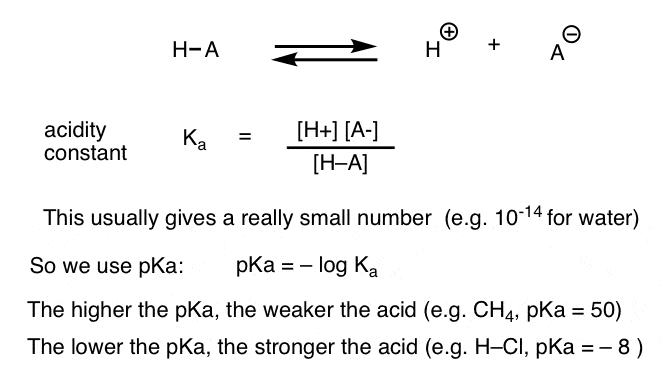In the Brønsted–Lowry definition of acids and bases, a conjugate acid–base pair consists of two substances that differ only by the presence of a proton (H⁺). A conjugate acid is formed when a proton is added to a base, and a conjugate base is formed when a proton is removed from an acid. Created by Yuki Jung.
How do you identify Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base pairs?
Identify a Brønsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base pair in the reaction. The key to idenitifying Bronsted-Lowry acid-base pair and realizing that acid and base must differ in only one Hydrogen. According to the theory, Bronsted-Lowry acid is a proton (H+) donor, and Bronsted-Lowry base is a proton (H+) acceptor.
What is the Brønsted–Lowry reaction theory?
The Brønsted–Lowry theory is an acid–base reaction theory. The fundamental concept of this theory is that when an acid and a base react with each other, the acid forms its conjugate base, and the base forms its conjugate acid by exchange of a proton. So the anwer could only be the first pair: N H 3 and ammonium catione.
What is a Brønsted-Lowry acid/base equation?
Finally, the chemical formulas of a Brønsted-Lowry acid, a Brønsted-Lowry base, and the conjugate products that are generated when these reactants lose and gain protons, H +1, are all represented in a Brønsted-Lowry acid/base equation.
What is the conjugate product of a Brønsted base?
In contrast, a conjugate product has an additional proton, relative to a base that was initially present, and, consequently, has the potential to be a proton, H +1, donor. Therefore, the substance that is generated upon the gain of a proton, H +1, by a Brønsted-Lowry base is the conjugate acid of that base.
Which is a Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base pair HSO4?
H2SO4/HSO4- is an acid/conjugate base pair. H20 is the base in the forward rxn, because it accepts a proton, and becomes H3O+. H20/H3O+ is a base/conjugate acid pair. The acid and base are the reactants in the forward reaction.
How do you identify a Bronsted-Lowry acid-base pair?
0:419:39Identifying Bronsted Lowry Acids and Bases - Real Chemistry - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo bronsted-lowry acids donate H pluses or protons bronsted-lowry bases accept H pluses or protons.MoreSo bronsted-lowry acids donate H pluses or protons bronsted-lowry bases accept H pluses or protons.
What are examples of Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases?
The Bronsted-Lowry acids and their Conjugated BasesAcidsConjugated baseHydrobromic acid (HBr)Bromide ion (Br–)Hydrochloric acid (HCl)Chloride ion (Cl–)Sulphuric acid (H2SO4)Hydrogen sulphate ion (HSO4–)Nitric acid (HNO3)Nitrate ion (NO3–)12 more rows
What is a Brønsted acid and base give an example of conjugate pair in acid-base reaction?
The Brønsted-Lowry Theory of Acids and Bases Therefore, HCl is a Brønsted-Lowry acid (donates a proton) while the ammonia is a Brønsted-Lowry base (accepts a proton). Also, Cl- is called the conjugate base of the acid HCl and NH4+ is called the conjugate acid of the base NH3.
Is NH3 a Brønsted base or acid?
the NH3 accepts a proton and is a Bronsted-Lowry base.
Is NH4+ a Brønsted base?
Yes, it is bronsted lowry acid because the Theory can give away one proton to other species (like water or hydroxide ion).
What is an example of a Bronsted-Lowry acid?
Some examples of Brønsted–Lowry acids are ammonium (NH4+), hydronium (H+), and hydrated metal cation [Al(H2O)6]3+.
What is Bronsted base give an example?
Solution : The substance which accepts a proton from the other substance is called Bronsted base eg. : `NH_(3),H_(2)O` etc.
What is a conjugate acid-base pair give an example?
HOCN and OCN- are an example of a conjugate acid-base pair. The only difference between the two is a proton (H+). All acids have a conjugate base and all bases have a conjugate acid.
Is H2O a Brønsted base?
As the proton acceptor, H2O is a Brønsted-Lowry base.
What is the conjugate acid and conjugate base of NH3?
Ammonia or NH3 is a base. It accepts a proton to give its conjugate and NH4+. Similarly, NH4+ loses a proton to give conjugate base NH3. Therefore, NH4+ is the conjugate acid of ammonia.
Is HF a Brønsted-Lowry base?
Furthermore, because hydrofluoric acid, HF, loses a proton, H+1, to generate its conjugate in the reaction that is shown above, this reactant can be classified as a Brønsted-Lowry acid, and, consequently, the fluoride ion, F–1, is the conjugate base of this acid.
What is the theory of the reaction between an acid and a base?from askinglot.com
The Brønsted–Lowry theory is an acid–base reaction theory. The fundamental concept of this theory is that when an acid and a base react with each other, the acid forms its conjugate base, and the base forms its conjugate acid by exchange of a proton. So the anwer could only be the first pair: NH3 and ammonium catione.
Is HCl a strong acid?from askinglot.com
Solution: HCl is a strong acid. When it donates a proton, a Cl– ion is produced, and so Cl– is the conjugate base.
Is NH3 a bronsted lowry base?from askinglot.com
Let's now look at the reaction between ammonia (NH3) and hydrochloric acid (HCl). If we identify each substance, then NH3 is the Bronsted-Lowry base, HCl is the Bronsted-Lowry acid , NH4+ is the conjugate acid and Cl- is the conjugate base. The conjugate acid-base pairs are: HCl/Cl- and NH3/NH4+.
What is a conjugate acid-base pair?from khanacademy.org
Now that we have an understanding of Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases, we can discuss the final concept covered in this article: conjugate acid-base pairs. In a Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction, a conjugate acid is the species formed after the base accepts a proton. By contrast, a conjugate base is the species formed after an acid donates its proton. The two species in a conjugate acid-base pair have the same molecular formula except the acid has an extra compared to the conjugate base.
What is the Bronsted-Lowry theory of acid-base reaction?from byjus.com
The Bronsted-Lowry theory of an acid-base reaction involves the transfer of protons or H + ions between the acid and base. Consider a reaction in which ammonia (base) is dissolved in water (acid).
What happens to a bronsted lowry base after it donates a proton?from thoughtco.com
After a Bronsted-Lowry acid donates a proton, it forms its conjugate base. The conjugate acid of a Bronsted-Lowry base forms once it accepts a proton. The conjugate acid-base pair have the same molecular formula as the original acid-base pair, except the acid has one more H + compared to the conjugate base.
Why is Bronsted Lowry acid HCl?from thoughtco.com
In this reaction, the Bronsted-Lowry acid is HCl because it donates a hydrogen (proton) to NH 3, the Bronsted-Lowry base. Because the reaction does not occur in water and because neither reactant formed H + or OH -, this would not be an acid-base reaction according to the Arrhenius definition.
How do acid and base react?from thoughtco.com
According to the theory, an acid and base react with each other, causing the acid to form its conjugate base and the base to form its conjugate acid by exchanging a proton. The theory was proposed independently by Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923. In essence, Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory is a general form ...
What is the Bronsted Lowry theory?from byjus.com
The Bronsted-Lowry theory is an extended version of an Arrhenius theory of acid-base. According to the Arrhenius theory, in aqueous solution, acid increases the concentration of H + ions and base increases the concentration of OH – ions.
What is the difference between an acid and an Arrhenius base?from thoughtco.com
According to the Arrhenius theory, an Arrhenius acid is one that can increase the hydrogen ion (H +) concentration in aqueous solution, while an Arrhenius base is a species that can increase the hydroxide ion (OH -) concentration in water.
Which of the following represents A Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid base pair
Carolynclough4 is waiting for your help. Add your answer and earn points.
Get more Answers for FREE
Snap questions with the app, get community help, find expert textbook explanations, and see instant step-by-step math solutions.