What are the two types of bone tissue and how do they differ?
There are two types of bone tissue: compact and spongy. The names imply that the two types differ in density, or how tightly the tissue is packed together. There are three types of cells that contribute to bone homeostasis. Osteoblasts are bone-forming cell, osteoclasts resorb or break down bone, and osteocytes are mature bone cells.
What type of tissue is bone classified as?
Bone is a connective tissue containing cells, fibers and ground substance. There are many functions in the body in which the bone participates, such as storing minerals, providing internal support, protecting vital organs, enabling movement, and providing attachment sites for muscles and tendons.
What type of tissue do bones start with?
- Loose connective tissue. (Areolar tissue, adipose tissue)
- Lymphoid tissue
- Dense connective tissue.
- Cartilage tissue
- Bone tissue
- Liquid connective tissue (examples of tissue is blood, W.B.C’s, lymph)
What does bone tissue do for the body?
Walking, running, jumping, and even sitting are only possible because of the structure and strength provided by bone tissue. Bone tissue is one of the strongest tissues in the body, and as such, it plays a big role in supporting other tissues, protecting fragile internal organs from damage, and facilitating movement.

What does bone tissue include?
Bone tissue is a specialized connective tissue composed of organic and inorganic fractions. The organic fraction consists of specialized bone cells, including osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and osteocytes, and of an extracellular matrix mainly composed of type I collagen, osteopontin, osteocalcin, and proteoglycans.
What is another name for bone tissue?
osseous tissue Also found in: Dictionary, Medical, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
How is bone tissue formed?
The process of bone formation is called osteogenesis or ossification. After progenitor cells form osteoblastic lines, they proceed with three stages of development of cell differentiation, called proliferation, maturation of matrix, and mineralization.
What builds bone tissue?
Osteoblasts, the cells that rebuild bone, are derived from mesenchymal stem cells. These stem cells are found in bone marrow, deep inside the bone. They transform into osteoblasts and migrate to the outer bone, where they create new bone tissue.
What are the types of bone tissue?
There are 3 types of bone tissue, including the following:Compact tissue. The harder, outer tissue of bones.Cancellous tissue. The sponge-like tissue inside bones.Subchondral tissue. The smooth tissue at the ends of bones, which is covered with another type of tissue called cartilage.
What type of tissue is bone tissue quizlet?
Recall bone tissue is a type of connective tissue. Like all connective tissues, it is made up of cells, protein fibers, and ground substance. There are 3 major types of cells are found in bones. These are stem cells derived from mesenchyme (embryonic connective tissue).
Is bone tissue a connective tissue?
Bone is a specialized connective tissue consisting of cells, fibers and ground substance. Unlike other connective tissues, its extracellular components are mineralized giving it substantial strength and rigidity.
What is the name of bone cells?
Bone is composed of four different cell types; osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts and bone lining cells. Osteoblasts, bone lining cells and osteoclasts are present on bone surfaces and are derived from local mesenchymal cells called progenitor cells.
Where is bone tissue found?
Bone tissue is found throughout the body. The long bones in the arms and legs contain a very dense, strong type of bone tissue known as compact bon...
What are the functions of bone tissue?
Bone tissue protects internal organs, provides support to other tissues, allows motion by facilitating the attachment of muscles, and also plays a...
What are the two types of bone tissue and where are they found?
There are two types of bone tissue: spongy (or cancellous) bone, and compact (or cortical) bone. Spongy bone is less dense and more flexible, and i...
What Are the Two Types of Bone Tissue?
Bone tissue is primarily constructed of a protein known as collagen that is also found in other types of connective tissue like cartilage . In bone, collagen fibers are reinforced with calcium phosphate, which is a hard ceramic material that gives bone its strength and stability. When calcium phosphate is added to collagen fibers, the collagen becomes mineralized. Although all bone tissue is made of the same basic materials, the structure of the tissue can be quite different depending on its location.
Why is bone tissue important?
Bone tissue is important because it provides structure to other body tissues, allows movement via attached muscles, protects internal organs, and produces blood cells. It is composed primarily of mineralized collagen and is produced, maintained, and repaired by three types of cells:
What is the role of osteoblasts in bone repair?
Osteoclasts are cells that destroy bone tissue. That may seem like a bad thing, but osteoblasts also play a vital role in repairing and healing bone tissue. When a bone is damaged, osteoclasts must first remove all the damaged bone tissue so that osteoblasts can produce new bone. Osteoclasts also remove bone from areas where there is less stress. Through the actions of osteoclasts and osteoblasts working together, bone tissue is constantly being remodeled to meet the demands that are placed on it.
What is the difference between spongy and compact bone?
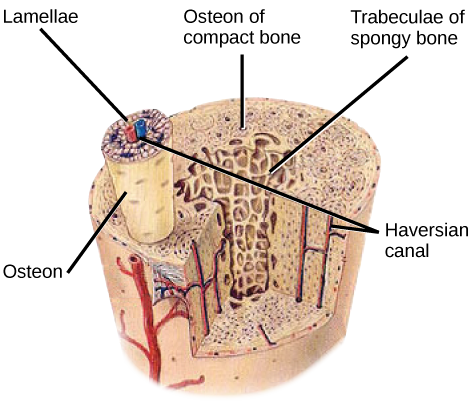
In compact bone, osteons are packed very tightly together to create a very dense, solid structure. In contrast, spongy bone does not contain osteons. Instead, layers of bone tissue are arranged into plates known as trabeculae that surround the open spaces in the bone.
How do osteoblasts make new bone?
They are derived from bone marrow stem cells, and they sit on the outside of bone tissue and synthesize collagen that becomes mineralized with calcium phosphate to produce new bone tissue. Osteoblasts create new bone to allow bones to grow and to repair microcracks and fractures. They also produce new bone in response to increased loading. For example, if a person starts training to run a marathon, the leg bones will suddenly experience a lot more stress than they are used to. This causes osteoblasts to begin producing new bone tissue to reinforce the leg bones and make them stronger.
What is spongy bone?
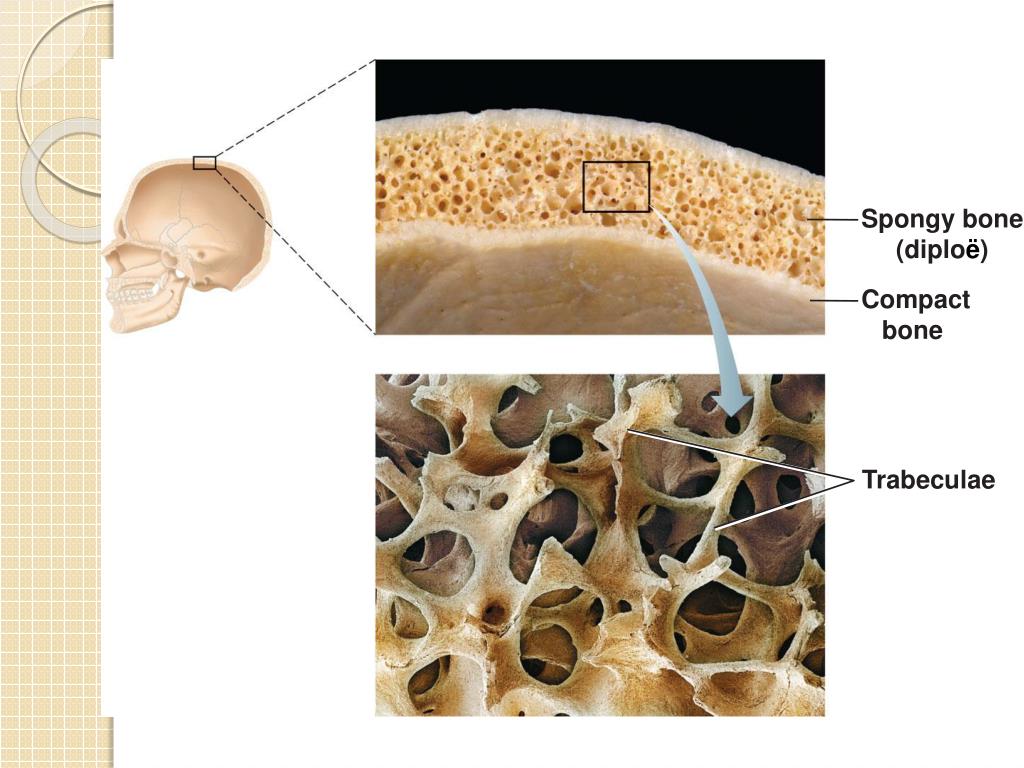
In spongy bone, which is also known as cancellous bone, there are many open spaces that are connected by pieces of bone tissue, giving spongy bone the appearance of a sponge. Spongy bone is typically found in the ends of the long bones, as well as in the pelvic bones, ribs, vertebrae, shoulder blades, and skull bones. Although spongy bone is strong, the presence of all those holes makes it light and somewhat flexible. The holes in spongy bone are not empty, but are full of bone marrow, which plays an important role the production of both red and white blood cells. There are also many blood vessels present in spongy bone that provide nutrients to the bone marrow and bone tissue.
How are bone cells arranged?
Bone tissue is arranged in functional units known as osteons. Within each osteon, there are layers of mineralized collagen that are arranged in concentric rings called lamellae, surrounding a central Haversian canal. These layers of bone tissue look similar to the rings inside a tree trunk. Within each Haversian canal, there are blood vessels that supply nutrients to the cells living within the bone. The blood and nerve supply of bone (remember, it's a living tissue; therefore, oxygen is delivered to bone via red blood cells and carbon dioxide is taken away) runs through the Haversian canal. In between the lamellae, there are small holes called lacunae, and inside each lacuna, there is a cell known as an osteocyte that helps maintain the bone. Osteocytes are connected to other osteocytes through very tiny channels known as canaliculi. This allows them to communicate with each other.
What is the outer membrane of the bone called?
The tough, thin outer membrane covering the bones is called the periosteum. Beneath the hard outer shell of the periosteum are tunnels and canals through which blood and lymphatic vessels run to carry nourishment for the bone. Muscles, ligaments, and tendons may attach to the periosteum.
What is the tissue that makes up the body's skeleton?
What is bone? Bone is living tissue that makes up the body's skeleton. There are 3 types of bone tissue, including the following: Compact tissue. The harder, outer tissue of bones. Cancellous tissue. The sponge-like tissue inside bones. Subchondral tissue. The smooth tissue at the ends of bones, which is covered with another type ...
What are the functions of bone?
Bone provides shape and support for the body, as well as protection for some organs. Bone also serves as a storage site for minerals and provides the medium—marrow—for the development and storage of blood cells.
What is the soft tissue at the ends of bones called?
The smooth tissue at the ends of bones, which is covered with another type of tissue called cartilage. Cartilage is the specialized, gristly connective tissue that is present in adults. It is also the tissue from which most bones develop in children. The tough, thin outer membrane covering the bones is called the periosteum.
How many bones are there in the human body?
Bones are classified by their shape—as long, short, flat, and irregular. Primarily, they are referred to as long or short. There are 206 bones in the human skeleton, not including teeth and sesamoid bones (small bones found within cartilage): 80 axial bones.
Why are bones important?
Because of the complexities of a bone's function, from providing strength and support for the body, to serving as a site for development and storage of blood cells, there are many disorders and diseases that can affect bone.
What is the function of osteoblasts?
Osteoblast. Found within the bone, its function is to form new bone tissue.
Which part of the bone is the outer surface of the bone?
The periosteum forms the outer surface of bone, and the endosteum lines the medullary cavity. Flat bones, like those of the cranium, consist of a layer of diploë (spongy bone), lined on either side by a layer of compact bone ( [link] ).
What type of cells are found in bone?
Four types of cells are found within bone tissue. Osteogenic cells are undifferentiated and develop into osteoblasts. When osteoblasts get trapped within the calcified matrix, their structure and function changes, and they become osteocytes. Osteoclasts develop from monocytes and macrophages and differ in appearance from other bone cells.
What is the role of osteoblasts in bone formation?
The osteoblast is the bone cell responsible for forming new bone and is found in the growing portions of bone, including the periosteum and endosteum. Osteoblasts, which do not divide, synthesize and secrete the collagen matrix and calcium salts. As the secreted matrix surrounding the osteoblast calcifies, the osteoblast become trapped within it; as a result, it changes in structure and becomes an osteocyte, the primary cell of mature bone and the most common type of bone cell. Each osteocyte is located in a space called a lacuna and is surrounded by bone tissue. Osteocytes maintain the mineral concentration of the matrix via the secretion of enzymes. Like osteoblasts, osteocytes lack mitotic activity. They can communicate with each other and receive nutrients via long cytoplasmic processes that extend through canaliculi (singular = canaliculus), channels within the bone matrix.
What is the red marrow in the bone?
Red marrow fills the spaces in the spongy bone. Each epiphysis meets the diaphysis at the metaphysis, the narrow area that contains the epiphyseal plate (growth plate), a layer of hyaline (transparent) cartilage in a growing bone.
What are the two parts of a long bone?
The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone ( [link] ). A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The hollow region in the diaphysis is called the medullary cavity, which is filled with yellow marrow. The walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone.
What is the medullary cavity?
The medullary cavity has a delicate membranous lining called the endosteum (end- = “inside”; oste- = “bone”), where bone growth, repair, and remodeling occur. The outer surface of the bone is covered with a fibrous membrane called the periosteum (peri – = “around” or “surrounding”).
What is the microscopic structure of compact bone called?
The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon, or Haversian system. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae (singular = lamella). Running down the center of each osteon is the central canal, or Haversian canal, which contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels. These vessels and nerves branch off at right angles through a perforating canal, also known as Volkmann’s canals, to extend to the periosteum and endosteum.
Which part of the bone is the outer surface of the bone?from pressbooks-dev.oer.hawaii.edu
The periosteum forms the outer surface of bone, and the endosteum lines the medullary cavity. Flat bones, like those of the cranium, consist of a layer of diploë (spongy bone), lined on either side by a layer of compact bone ( [link] ).
What is the bridge between the jaws of a shark and a bony fish?from zoology.ubc.ca
In modern bony fish and modern day sharks (e.g. dogfish) the hyomandibular of the hyoid arch forms a bridge attaching the jaws to the skull. The jaws, free from the skull, can be swung forward a little. Connective tissue and devices like optic pegs help position the jaws. This type of suspension is known as hyostylic. In bony fish, the quadrate and articular bones replaced the cartilage and several dermal bones covered the jaw cartilages. The hyomandibular becomes more firmly attached to the skull and a new bone, the symplectic bone, is formed to aid in jaw movement.
How do osteoblasts move?from biologydictionary.net
Having sensed the break in the network of osteocytes within the osteon, the osteoblasts move toward the fracture. They surround the fracture, and bridge the gap by laying down new material. In doing so, they increase the thickness of the bone on the fracture line, and increase the strength of the bone in that spot.
What is the dermal bone?from zoology.ubc.ca
Dermal bone is from mesenchyme and ectomesenchyme of the dermis and it overlies the neurocranium and splancnocranium. Learn all the bones on the dorsal drawing of the wolf (pg. 38) plus the lower jaw of mammals ( dentary bone) and the new bones, the palatine and bulla.
What is the main structure of the body?from biologydictionary.net
The compact bone is the main structure in the body for support, protection, and movement. Due to the strong nature of compact bone , compared to spongy bone, it is the preferred tissue for strength. Spongy bone is used for more active functions of the bones, including blood cell production and ion exchange. However, compact bones also serve a function in storing and releasing calcium to the body when needed. The compact bone also provide strong mechanical levers, against which the muscles can create movement. This function is supported by the joints created by spongy bone and connective tissues, such as tendons and ligaments.
What type of cells are found in bone?from pressbooks-dev.oer.hawaii.edu
Four types of cells are found within bone tissue. Osteogenic cells are undifferentiated and develop into osteoblasts. When osteoblasts get trapped within the calcified matrix, their structure and function changes, and they become osteocytes. Osteoclasts develop from monocytes and macrophages and differ in appearance from other bone cells.
What is the neurocranium?from zoology.ubc.ca
Neurocranium (Chondrocranium) is from neural crest cells and mesodermal mesenchyme. It can remain catrilage or become replacement bone. We will study three groups of bones the Occipitals, the Sphenoids and the Ethmoids. Splanchnocranium comes from neural crest cells and is either cartilage or replacement bone.
What is the tissue in a bone called?
The hemopoietic tissue in a bone is otherwise known as myeloid tissue.
Which part of the bone is covered in cartilage?
The posterior head of the end of the long bone, covered in articular cartilage, enabling the bone to move at the joints without grinding on each other
What is the pelvic bone made of?
pelvic... made of spongy bone covered with a thin layer of compact bone, and contains red bone marrow
What are the bones of the arms, legs, hands and feet made of?
bones of the arms , legs, hands and feet, each consist of a diaphysis made of compact bone and epiphyses made of spongy bone, the marrow canal contains yellow bone marrow
What is the role of red bone marrow in the body?
support the body, storage of excess Ca and lipids, contain Red Bone Marrow that produce blood cells, protection of organs and of red bone marrow, leverage, and attached to muscles that make movement
What is a cylindrical arrangement of osteocytes within matrix?
a system of interconnecting canals in the microscopic structure of adult compact bone; cylindrical arrangements of osteocytes within matrix, very dense, offers strenght.
Which layer of cartilage separates the epiphysis from the diaphysis?
Layer of hyaline cartilage separating the epiphysis from the diaphysis at each end of a long bone; the site where bone growth occurs
What are the two types of bone tissue?
There are two types of bone tissue: compact and spongy. The names imply that the two types differ in density, or how tightly the tissue is packed together. There are three types of cells that contribute to bone homeostasis. Osteoblasts are bone-forming cell, osteoclasts resorb or break down bone, and osteocytes are mature bone cells.
Where are the bone cells located in the matrix?
Between the rings of matrix, the bone cells (osteocytes) are located in spaces called lacunae. Small channels ( canaliculi) radiate from the lacunae to the osteonic (haversian) canal to provide passageways through the hard matrix.
What is compact bone?
Compact Bone. Compact bone consists of closely packed osteons or haversian systems. The osteon consists of a central canal called the osteonic (haversian) canal, which is surrounded by concentric rings (lamellae) of matrix. Between the rings of matrix, the bone cells (osteocytes) are located in spaces called lacunae.
Which canals contain blood vessels that are parallel to the long axis of the bone?
The osteonic canals contain blood vessels that are parallel to the long axis of the bone. These blood vessels interconnect, by way of perforating canals, with vessels on the surface of the bone.
What type of tissue is bone and cartilage?
Cartilage and Bone are specialised forms of connective tissue. They are both made up of cells embedded in an extracellular matrix. It is the nature of the matrix that defines the properties of these connective tissues.
What tissue is cartilage made of?
What is cartilage made of? Cartilage a strong and smooth substance made up of “chondrocytes,” or specialized cartilage cells, that produce a matrix of collagen, proteoglycans (a special type of protein) and other non-collagenous proteins.
What type of tissue is bone tissue quizlet?
Osseous tissue is connective tissue with the matrix hardened by mineralization. The skeletal system is an group of bones and other tissues working together to form an organ of the body.
What is the outer part of a bone made of?
Almost every bone in your body is made of the same materials: The outer surface of bone is called the periosteum (say: pare-ee-OSS-tee-um). It’s a thin, dense membrane that contains nerves and blood vessels that nourish the bone. The next layer is made up of compact bone.
Is cartilage a connective tissue?
Cartilage is a form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is abundant and of a firmly gelated consistency that endows this tissue with unusual rigidity and resistance to compression. The cells of cartilage, called chondrocytes, are isolated in small lacunae within the matrix.
Where is compact bone tissue found?
Compact bone is the denser, stronger of the two types of bone tissue ( (Figure)). It can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones, where it provides support and protection.
Is bone an organ or tissue?
Bones are organs that consist primarily of bone tissue, also called osseous tissue. Bone tissue is a type of connective tissue consisting mainly of a collagen matrix that is mineralized with calcium and phosphorus crystals.
What type of bone tissue is found in the inner portions of the bone and on the ends of the bone primarily?
There are two main types of bone tissue. The first type is cancellous bone, often referred to as spongy bone. It is referred to this way because it looks the same way a sponge looks with multiple holes throughout it. This type of bone tissue is found in the inner portions of the bone and on the ends of the bone primarily. It contains red bone marrow.
What is Bone Anatomy?
Rarely are the bones of the body thought of as being living tissue, but they are. Similar to all other tissues in the body, the bones are made up of living cells that carry out many functions. The main cells found in the bones of the body are called osteocytes. They are the longest living of all of the bone cells, and they make up about 95% of the cells in the bone. Osteoblasts are bone cells that are responsible for creating the extracellular matrix of the bone. Osteoclasts are the bone cells that are responsible for the resorption of bone material during bone remodeling. They are also responsible for maintaining the proper blood calcium levels. There are many different parts of bone that all have specific functions.
What is the purpose of the sesamoid bone?
The most commonly known and referred to as sesamoid bone is the knee cap. These bones function to reinforce the tendons and make them stronger. They also protect the tendons from the wear and tear that comes from constant use.
What type of bone tissue is compacted together?
The other type of bone tissue is cortical bone which is also referred to as compact bone. It gets that name because it appears to be compacted together and looks like a solid mass rather than a tissue composed of cells. This type of tissue is primarily found in the outer portions of the bone.
What are irregular bones?
Irregular bones - These are the bones of varying structure and shape that do not fit into any other category of bone shape. They function to help protect the internal organs such as the spinal cord and those of the pelvic region. These bones also allow for flexibility and movement.
How many layers are there in the bone?
The anatomy of the bone is that it contains living cells that make up the different tissues of the bone. There are three layers and five parts of the bone.
How many types of tissues are there in the human body?
There are three main types of tissues or bone cavities found in the body. They are discussed below.