What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)?
What is ALS? Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a fatal type of motor neuron disease. It is characterized by progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the spinal cord and brain.
Does ALS affect the brain?
ALS it is one of the most devastating of the disorders that affects the function of nerves and muscles. ALS does not affect mental functioning or the senses (such as seeing or hearing), and it is not contagious. Currently, there is no cure for this disease.
What are the disease mechanisms of ALS?
Below are some common known disease mechanisms: Transport of materials up and down the length of the motor neuron is an important cellular process that may play into the damage seen in ALS. Neurons normally move cellular materials along their axons, to keep nerve cell messages flowing and to maintain the health of the whole nerve cell itself.
What types of cells are involved in ALS?
Other cell types in the central nervous system that support motor neurons, called glia, including, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes are also involved in ALS disease. From years of research, scientists have identified various disease processes involved in ALS.
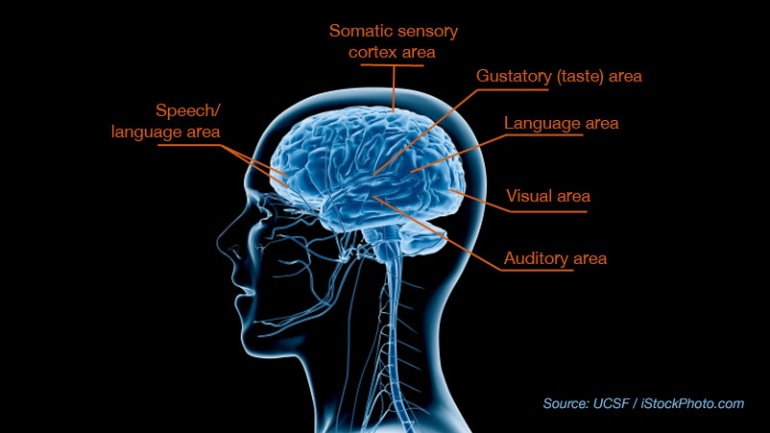
How is the brain affected by ALS?
ALS affects the nerve cells that control voluntary muscle movements such as walking and talking (motor neurons). ALS causes the motor neurons to gradually deteriorate, and then die. Motor neurons extend from the brain to the spinal cord to muscles throughout the body.
Does ALS affect the cerebellum?
The nuanced characterisation of cerebellar involvement in ALS is hugely important as cerebellar pathology is likely to contribute to motor disability, bulbar dysfunction, respiratory compromise and cognitive problems.
Does ALS affect the brain stem?
The results revealed that ALS patients encounter specific brainstem volume loss and white matter degeneration. The volume loss in the brainstem is mainly characterized by the local shape deformation in the medulla oblongata and pons. Selective degeneration in the CST and FPT related to clinical disease deterioration.
Is ataxia a symptom of ALS?
While ataxia patients survive much longer than ALS patients after diagnosis, ataxia resembles ALS in its most severe cases. As ALS progresses, patients lose the ability to move their muscles, which weaken and waste away, ultimately leading to paralysis and death.
What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a rare neurological disease that primarily affects the nerve cells (neurons) responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movement (those muscles we choose to move). Voluntary muscles produce movements like chewing, walking, and talking. The disease is progressive, meaning the symptoms get worse over time.
What are the symptoms?
The onset of ALS can be so subtle that the symptoms are overlooked but gradually these symptoms develop into more obvious weakness or atrophy.
Who gets ALS?
ALS is a common neuromuscular disease worldwide. It affects people of all races and ethnic backgrounds.
What causes ALS?
The cause of ALS is not known, and scientists do not yet know why ALS strikes some people and not others. However, scientific evidence suggests that both genetics and environment play a role in motor neuron degeneration and the development of ALS.
How is ALS diagnosed?
There is no single test that provides a definitive diagnosis of ALS. It is primarily diagnosed based on a detailed history of the symptoms observed by a physician during physical examination, along with a review of the individual’s full medical history and a series of tests to rule out other diseases.
How is ALS treated?
There is no treatment to reverse damage to motor neurons or cure ALS. However, treatments can help control symptoms, prevent unnecessary complications, and make living with the disease easier.
What research is being done?
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke ( NINDS) is the primary federal funder of research on the brain and nervous system, including disorders such as ALS. NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health ( NIH ), the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world.
Support Brain Research
We need your help to continue to fund brain research projects and find cures. Stand with us in the fight against brain diseases and disorders.
News and Articles
Discover the latest news in brain disease research, hear stories from people affected by brain disease and their caregivers, read up on brain disease-specific information, and more.
What happens to the brain in ALS?
In ALS, both the upper motor neurons and the lower motor neurons degenerate or die, ceasing to send messages to muscles. Unable to function, the muscles gradually weaken, waste away, and twitch. Eventually the ability of the brain to start and control voluntary movement is lost.
What is the ALS Association?
ALS Association#N#Nonprofit voluntary health organization dedicated to the fight against amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Funds global research and sponsors advocacy programs, a network of chapters, and certified centers and clinics located nationwide.
What is the address of Les Turner ALS Foundation?
Supports medical research, patient services, and promotes awareness and education to find the cause (s), effective treatments, and ultimately, a cure for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 5550 W. Touhy Avenue.
How long does it take for ALS to die?
Most people with ALS die from respiratory failure, usually within 3 to 5 years from the onset of symptoms. However, about 10 percent of those individuals with ALS survive for 10 or more years.
What is the name of the disease that attacks the nerve cells responsible for controlling voluntary muscles?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), sometimes called Lou Gehrig's disease, is a rapidly progressive, invariably fatal neurological disease that attacks the nerve cells (neurons) responsible for controlling voluntary muscles. In ALS, both the upper motor neurons and the lower motor neurons degenerate or die, ceasing to send messages to muscles.
What is the best treatment for ALS?
Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and rehabilitation may help to prevent joint immobility and slow muscle weakness and atrophy. Individuals with ALS may eventually consider forms of mechanical ventilation (respirators).
How do you know if you have ALS?
Symptoms are usually first noticed in the arms and hands, legs, or swallowing muscles. Individuals with ALS lose their strength and the ability to move their arms, legs, and body. When muscles in the diaphragm and chest wall fail to function properly, individuals lose the ability to breathe without ventilatory support.
What is the inflammatory process in ALS?
The inflammatory process apparently is a reaction to the death of the cells, and not the instigator. Several places in the inflammatory events that appear to accompany ALS might be amenable to drug action that could help in the disease.
Which cell type is involved in ALS?
Other cell types in the central nervous system that support motor neurons, called glia, including, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes are also involved in ALS disease. From years of research, scientists have identified various disease processes involved in ALS. Below are some common known disease mechanisms:
How do nerve cells communicate with each other?
Nerve cells pass signals to each other and to their target organs by releasing messenger molecules, called neurotransmitters. Many are simple amino acids such as the one called glutamate. The message is intended to tell the recipient neuron whether to fire off its own neurotransmitters. As with all neurotransmitters, glutamate docks at specific recognition molecules on the receiving neuron. Glutamate is then swiftly cleared from the nerve cell junctions to keep the message brief.
What is the transport of materials up and down the length of the motor neuron?
Transport of materials up and down the length of the motor neuron is an important cellular process that may play into the damage seen in ALS. Neurons normally move cellular materials along their axons, to keep nerve cell messages flowing and to maintain the health of the whole nerve cell itself.
What is the ALS Association?
What The ALS Association is Doing. The ALS Association encourages research in all areas highlighted above. Biochemical studies, cell and animal model systems and “OMIC” studies bring us closer to identifying pathways that may be involved in disease.
What happens when motor neurons die?
When the motor neurons die, the ability of the brain to initiate and control muscle movement is lost. With voluntary muscle action progressively affected, patients in the later stages of the disease may become totally paralyzed. Motor neurons are unique cells, the longest in the body.
What is the name of the disease that attacks motor neurons?
Image. Overview. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) attacks motor neurons (a type of nerve cell) in the brain and spinal cord. There are two types of motor neurons: upper motor neurons (UMNs) that send nerve fibers down the from the motor cortex in the brain (part of the brain that controls movement) to the spinal cord;
Who funded the ALS research?
Funding for this research was provided by the University Hospital Foundation, the MSI Foundation of Alberta, ALS Society of Canada, ALS Association, and the Shelly Mrkonjic ALS Research Fund.
What is Lou Gehrig's disease?
Recently published studies by a researcher in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry demonstrate that ALS -- known as Lou Gehrig's disease -- damages neurons in parts of the brain responsible for cognition and behaviour.
What is the cause of paralysis in 2021?
June 30, 2021 — Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, attacks nerve cells known as motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord, gradually leading to paralysis. The loss of function of an important gene, C9orf72, may ...
What does Kalra use to measure the brain?
Kalra uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) not to just look at pictures of the brain, but also as a means of measuring the levels of various chemicals in the brain. In his most recently published paper, he looked at two different chemicals called NAA and mIns. NAA is known as a neural marker, which means it is only found in neurons, while levels of mIns increase when there is abnormal scarring in the brain.
Where is NAA decreasing?
His paper published in early 2011 looked at decreasing levels of NAA in the cingulate cortex -- the first time MRI had been used to measure chemicals in this region of the brain in ALS. And his most recently published paper, which came out late this summer, was the first to demonstrate that NAA was decreasing and mIns was increasing in the frontal lobe, even when there weren't signs of cognitive or behavioural issues in patients. The frontal lobe is considered the hub for cognition and behaviour in the brain.
Does ALS affect the motor cortex?
Sanjay Kalra, a researcher in the faculty's Division of Neurology and a practising neurologist, has published two papers this year in the American Journal of Neuroradiology providing evidence that ALS affects more than just the motor cortex, the part of the brain responsible for motor function.
How does ALS affect people?
For others with ALS, there will be mild changes in how they think or behave but they are still able to function independently and make informed decisions about their care. Finally, for some people with ALS, changes in thinking and behavior are quite significant and severe such that these people are challenged to make informed decisions about their care and activities and require others to act on their behalf. Educating people about thinking and behavior changes unique to ALS helps to empower a person with ALS, to validate the experience of caregivers and family members, and to educate providers working with an affected person so that decisions are made in a manner consistent with honoring the individual’s longstanding values, preferences, and desires.
What are the changes in thinking and behavior of ALS patients?
Finally, for some people with ALS, changes in thinking and behavior are quite significant and severe such that these people are challenged to make informed decisions about their care and activities and require others to act on their behalf.
What is the difference between dementia and ALS?
Healthcare providers may refer to “impairment” or “dementia” when discussing thinking and behavior symptoms. “Impairment” recognizes that the person with ALS is acting in a way that is different than who he/she has always been but not to the extent that he/she cannot still complete activities and think through decisions as he/she has always has done. “Dementia” recognizes that the person with ALS is acting in a way that is different than who he/she has always been AND he/she can no longer complete activities and think through decisions as he/she has always done. Different diseases can cause dementia. We now know that ALS can, but does not always, result in dementia. The type of thinking and behavioral impairment observed in ALS is often different than the rapid forgetting that marks the onset of Alzheimer’s type dementia.
What are the risk factors for ALS?
Although older age, bulbar onset disease , family history of dementia, and pre-ALS neurologic injury have been cited as risk factors for developing cognitive and behavioral impairment in ALS, there are examples of individuals who develop the symptoms without these risk factors. Currently the only consistently documented risk factor for the evolution of cognitive or behavioral impairment in ALS is the presence of abnormal repeats in a gene called “ C9ORF72
How to evaluate if you have ALS?
The neuropsychologist will give you various paper and pencil tests to determine how you process information. You may be asked to recite as many words as you can, beginning with a specific letter of the alphabet. You may be asked to remember words or stories and say these back to the examiner. You may be asked to spell some words. The data collected are compared to normative data for people of your same age and education and compared to estimates of your longstanding level of function. This helps to determine if there is impairment and what type it could be. The neuropsychologist may speak to the person with ALS and also a caregiver or family member who knows the person well.
What is the relief of ALS?
Often times when a person has cognitive and behavioral changes in ALS, it can be a relief to know that the person is not acting abnormally due to psychological reasons or trying to be oppositional or challenging to others. If insight and self-awareness is present, an impaired person can make sure that he/she attends to advanced directives and documents wishes and intentions for later on in the disease process. This is particularly important because cognitive and behavioral impairments, like other symptoms of ALS, advance with disease progression and worsen over time.
How many people with ALS experience changes in thinking and behavior?
How many people with ALS experiencing changes in thinking and behavior? Current research data suggest that up to 50% of people with ALS will never develop significant changes in thinking or behavior, over and beyond normal psychological reaction to diagnosis and symptoms.

What Are The Symptoms of ALS?
- With ALS, you may first have weakness in a limb that develops over a matter of days or, more commonly, a few weeks. Then, several weeks to months later, weakness develops in another limb. Sometimes the initial problem can be one of slurred speech or trouble swallowing. As ALS progr…
What Are The Complications of ALS?
- There is no cure for ALS. Over a period of 3 to 5 years, the disease will progress, making voluntary movements of arms and legs impossible. In time, you will need help with personal care, eating, and mobility. Movement of the diaphragm for breathing is also impaired. You may need a ventilator for breathing. Most people with ALS die from respiratory failure.
How Is Als Treated?
- For most people with ALS, the main treatment may involve the management of symptoms, This may include physical, occupational, speech, respiratory, and nutritional therapies. Some medicines, and heat or whirlpool therapy may help relieve muscle cramping. Exercise, in moderation, may help maintain muscle strength and function. There is no cure and no proven tre…
What Is Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis?
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a rare neurological disease that primarily affects the nerve cells (neurons) responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movement (those muscles we choose to move). Voluntary muscles produce movements like chewing, walking, and talking. The disease is progressive, meaning the symptoms get worse over time. Cur...
What Are The Symptoms?
- The onset of ALS can be so subtle that the symptoms are overlooked but gradually these symptoms develop into more obvious weakness or atrophy. Early symptomsinclude: 1. Muscle twitches in the arm, leg, shoulder, or tongue 2. Muscle cramps 3. Tight and stiff muscles (spasticity) 4. Muscle weakness affecting an arm, a leg, the neck, or diaphragm 5. Slurred and n…
Who Gets ALS?
- ALS is a common neuromuscular disease worldwide. It affects people of all races and ethnic backgrounds. Risk factors for ALS include: 1. Age. Although the disease can strike at any age, symptoms most commonly develop between the ages of 55 and 75. 2. Gender. Men are slightly more likely than women to develop ALS. However, as people age the difference between men an…
What Causes ALS?
- The cause of ALS is not known, and scientists do not yet know why ALS strikes some people and not others. However, scientific evidence suggests that both genetics and environment play a role in motor neuron degeneration and the development of ALS. Genetics In 1993, scientists supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) discovered that mutation…
How Is Als Diagnosed?
- There is no single test that provides a definitive diagnosis of ALS. It is primarily diagnosed based on a detailed history of the symptoms observed by a physician during physical examination, along with a review of the individual’s full medical history and a series of tests to rule out other diseases. A neurologic examination at regular intervals can assess whether symptoms such as …
How Is Als Treated?
- There is no treatment to reverse damage to motor neurons or cure ALS. However, treatments can help control symptoms, prevent unnecessary complications, and make living with the disease easier. Supportive health care is best provided by multidisciplinary teams of professionals such as physicians; pharmacists; physical, occupational, speech, and respiratory therapists; nutritioni…
What Research Is Being done?
- The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) is the primary federal funder of research on the brain and nervous system, including disorders such as ALS. NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world. The goals of NINDS’s ALS research are to understand the cellular mechani…
How Can I Be Involved in Research?
- National ALS Registry The National ALS Registry is a program to collect, manage, and analyze data about people with ALS in the United States. Developed by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR), this registry establishes information about the number of ALS cases, collects demographic, occupational and environme…
Where Can I Get More Information?
- For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network (BRAIN) at: BRAIN P.O. Box 5801 Bethesda, MD 20824 800-352-9424 Information also is available from the following organizations: The ALS Association(link is exter…