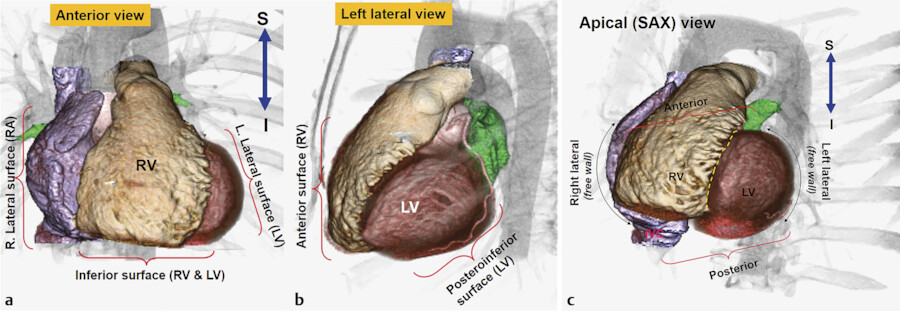
What is the left border of the heart?
The left border is marked out by the left auricle and left ventricle. Finally, the right border is comprised of the sliver of the right atrium that can be seen between the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. Heart in situ seen from the anterior view.
How is the cardiac silhouette formed on the lateral projection?
On the lateral projection the cardiac silhouette is formed by 1: 1 the anterior border by right ventricle 2 the posterior border by left atrium (superiorly) and left ventricle (inferiorly) and the inferior vena cava More ...
Where is the lateral wall of the heart located?
Go to the U of M home page. Location: The lateral wall is generally considered to include the wall of the right atrium from the ostia of the superior and inferior vena cava anteriorly to the ostium of the right appendage or auricle.
What structures are seen on the anterior view of the heart?
Structures seen on the anterior view of the heart. The superior border of the heart is a convex line that runs from the inferior border of the second left costal cartilage to the superior border of the third right costal cartilage.

What part of the heart is lateral?
The lateral wall is generally considered to include the wall of the right atrium from the ostia of the superior and inferior vena cava anteriorly to the ostium of the right appendage or auricle.
What structures form the borders of the heart?
The right border of the heart extends just over 1 cm to the right of the sternum, between the 3rd and 6th intercostal cartilages. It is composed mainly of the right atrium. The inferior border runs from the 6th costal cartilage on the right, through the xiphisternal joint, to the 5th intercostal space on the left.
What part of the heart forms the left border?
left ventricleThe left border of the heart separates the sternocostal surface from the left surface. It is convex laterally. The left ventricle forms the majority of the border but a small section is formed superiorly by the left atrium.
What forms the inferior border of the heart?
The inferior border of the heart is formed predominantly by the right ventricle. The left ventricle contributes near the apex. It is the most acutely angled border of the heart and it is roughly horizontal. It separates the sternocostal from the diaphragmatic surfaces of the heart.
How many borders are there in heart?
The heart has four borders: right border: IVC, right atrium, SVC. left border: left ventricle, left atrium, pulmonary trunk and arch of aorta. inferior border: right ventricle.
What is the superior border of the heart?
The superior border of the heart is a line that connects the inferior border of the second left costal cartilage and the superior border of the third right costal cartilage.
What are the 4 borders of the heart?
The heart has four borders:right border: IVC, right atrium, SVC.left border: left ventricle, left atrium, pulmonary trunk and arch of aorta.inferior border: right ventricle.superior border: right and left atria, SVC, ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk.
Is the heart lateral to the lungs?
The lungs lie lateral to the heart. Towards the mid line of the body. The heart lies medial to the lungs. Towards the external surface of the body.
What forms the anterior surface of the heart?
The sternocostal surface of the heart is directed anteriorly, superiorly and slightly to the left. It is formed by the left, right, superior and inferior borders of the heart.
Which border of the heart is formed mainly by the inferior wall of the right ventricle?
This border marks the entry and exit of three of the great vessels—the aorta, the pulmonary trunk, and the superior vena cava. The inferior border, which is nearly horizontal, is formed mainly by the right ventricle and slightly by the apex of the left ventricle.
What is the most posterior part of heart?
left atriumIt is also important to visualize that the most anterior portion of the heart is the right ventricle, and the most posterior portion of the heart is the left atrium, which lies directly anterior to the esophagus.
What is the inferior portion of the heart?
The inferior tip of the heart, the apex, lies just to the left of the sternum between the junction of the fourth and fifth ribs near their articulation with the costal cartilages. The right side of the heart is deflected anteriorly, and the left side is deflected posteriorly.
What forms the apex of the heart?
The left ventricle forms the apex of the heart and is conical in shape. Blood passes from the left ventricle to the ascending aorta through the aortic semi-lunar valve. From here some of the blood flows into the coronary arteries, which branch from the ascending aorta and carry blood to the heart wall.
Which border of the heart is formed mainly by the inferior wall of the right ventricle?
This border marks the entry and exit of three of the great vessels—the aorta, the pulmonary trunk, and the superior vena cava. The inferior border, which is nearly horizontal, is formed mainly by the right ventricle and slightly by the apex of the left ventricle.
Which structure is visible on the surface of the heart quizlet?
the interventricular septum separates the left and right ventricles. the septum lies just deep to the iterventricular sulcus, which is visible on the superficial surface of the heart.
Which feature marks the border between the atria and the ventricles?
The septum between the atria and ventricles is known as the atrioventricular septum. It is marked by the presence of four openings that allow blood to move from the atria into the ventricles and from the ventricles into the pulmonary trunk and aorta.
What is the left border of the heart?
The left border corresponds to a line drawn from the inferior border of the second left costal cartilage to the intersection point between the fifth left intercostal space and midclavicular line. More simply, the line interconnects the left ends of the superior and inferior borders of the heart.
What is the sound of auscultation?
The sound heard during auscultation is caused by the closing of the valves, when they audibly snap shut due to a sudden change of pressure. The normal heartbeat heard with a stethoscope sounds something like: “lub-dub, lub-dub”. The “lub” corresponds to the closure of the atrioventricular valves at the beginning of ventricular systole. It is called the first heart sound (S1). On the other hand, the “dub” is associated with the closure of the aortic and pulmonary valves at the end of the ventricular systole. This is called the second heart sound (S2) and it is best auscultated at the Erb’s point. This landmark is located on the left third intercostal space, parasternally, between the pulmonic and tricuspid areas.
What is the difference between lub and dub?
The “lub” corresponds to the closure of the atrioventricular valves at the beginning of ventricular systole. It is called the first heart sound (S1). On the other hand, the “dub” is associated with the closure of the aortic and pulmonary valves at the end of the ventricular systole.
What are the surface projections of the heart?
The surface projections of the heart represent points on the thoracic wall that map out the outline and valves of the heart. These include four borders (superior, right, inferior, left) and four valves (left atrioventricular, right atrioventricular, aortic, pulmonary). The main reference points used for the surface projections of the heart are the borders of the sternum and costal cartilages, the clavicle and intercostal spaces. The latter favour sound transmission, facilitating clinical maneuvers such as percussion, auscultation and palpation to pinpoint the cardiac location.
What are the four heart valves?
There are four existing heart valves: The left atrioventricular (mitral) valve between the left atrium and left ventricle. It projects posteriorly to the left side of the sternum, at the level of the left fourth costal cartilage. The right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve between the right atrium and right ventricle.
What are the S3 and S4 sounds?
These include splits, third (S3) and fourth (S4) heart sounds, as well as murmurs . S3 and S4 are associated with diastole and the cycle of the atria. They are usually physiological in children and skinny adults, but pathological in the general adult population. On the other hand, murmurs are always a sign of cardiovascular dysfunction.
Where is the inferior border?
The inferior border is marked by a line that joins the inferior end of the right border (six right costal cartilage) to the point where the fifth left intercostal space and midclavicular line intersect. Also, this point of intersection marks the apex of the heart.
Why are the cusps pushed open?
The cusps are pushed open to allow blood flow in one direction, and then closed to seal the orifices and prevent the backflow of blood. Backward prolapse of the cusps is prevented by the chordae tendineae –also known as the heart strings–fibrous cords that connect the papillary muscles of the ventricular wall to the atrioventricular valves.
What are the semilunar valves in a cadaver?
Heart valves in a cadaver. Semilunar valves prevent backflow from the great vessels to the ventricles. The pulmonary semilunar valve is between the right ventricle and the opening of the pulmonary trunk. It has three semilunar cusps/leaflets: anterior/non-adjacent, left/left adjacent, and right/right adjacent.
What are the two leaflets that separate the atria from the ventricles?
Heart valves. Heart valves separate atria from ventricles, and ventricles from great vessels. The valves incorporate two or three leaflets (cusps) around the atrioventricular orifices and the roots of great vessels.
What is the margin of the right atrium?
The right margin is the small section of the right atrium that extends between the superior and inferior vena cava . The left margin is formed by the left ventricle and left auricle. The superior margin in the anterior view is formed by both atria and their auricles. The Inferior margin is marked by the right ventricle.
How many cusps does the right tricuspid valve have?
The right atrioventricular/tricuspid valve is between the right atrium and right ventricle. It has three cusps/leaflets: anterior/anterosuperior, septal, and posterior/inferior. The left atrioventricular/bicuspid valve is also called the mitral valve since it only has two cusps and resembles a miter in shape.
How big is the ascending aorta?
Because they are large in size; the diameter of the ascending aorta is 2.1 centimeters, which is like the size of an American nickel (five-cent coin), and they all carry blood to and from the heart. Oh, not to mention that the aorta gives off branches which supply the entire body with oxygenated blood.
Why does angina hurt?
Stable angina is the most common form and occurs because of the severe narrowing of the coronary arteries. Pain is felt upon exertion and is treated with nitroglycerin. Infective endocarditis is a bacterial or fungal infection of the heart and can include but is not limited to the cardiac valves.
Why is the right atrial lateral wall important?
Importance in cardiovascular diseases: The right atrial lateral wall is considered by some to have a role in the genesis of several atrial arrhythmias, including atrial reentry and focal atrial tachycardia. Importance in device delivery: The lateral wall is sometimes used to place right atrial pacing leads.
What is the lateral wall?
The lateral wall is generally considered to include the wall of the right atrium from the ostia of the superior and inferior vena cava anteriorly to the ostium of the right appendage or auricle. The endocardial surface of the lateral wall includes both smooth muscle, in the posterior region between the vena cava and the crista terminalis, ...
Which wall is used for right atrial pacing?
The lateral wall is sometimes used to place right atrial pacing leads. The anterior aspect of the lateral wall is one of the thinnest walls of the heart, resulting in a higher than usual risk for perforation when extracting a lead from this location.
What is the cardiac silhouette?
Cardiac silhouette refers to the outline of the heart as seen on frontal and lateral chest radiographs and forms part of the cardiomediastinal contour . The size and shape of the cardiac silhouette provide useful clues for underlying disease.
What is considered enlarged cardiac silhouette?
The cardiac silhouette is considered enlarged if the cardiothoracic ratio is greater than 50% on a PA view of the chest 1. See main article: enlargement of the cardiac silhouette for more information.
Which artery forms the left border?
the left border is formed by the left ventricle and left atrial appendage. . the pulmonary artery, aortopulmonary window and aortic notch extend superiorly. On the lateral projection the cardiac silhouette is formed by 1: the anterior border by right ventricle.
Which border is formed by the right atrium?
From the frontal projection, the cardiac silhouette can be divided into right and left borders: the right border is formed by the right atrium. . the superior vena cava entering superiorly and the inferior vena cava often seen at its lower margin.
Which sinus separates the pulmonary trunk and aorta?from teachmeanatomy.info
Superior to the left atrium. In this position, the transverse pericardial sinus separates the arterial vessels (aorta, pulmonary trunk) and the venous vessels (superior vena cava, pulmonary veins) of the heart.
Where is the oblique pericardial sinus located?from teachmeanatomy.info
The oblique pericardial sinus is a blind ending passageway located on the posterior surface of the heart. The transverse pericardial sinus is found superiorly on the heart.
What are the four main borders of the heart?from teachmeanatomy.info
Borders. Separating the surfaces of the heart are its borders. There are four main borders of the heart: Right border - Right atrium. Inferior border - Left ventricle and right ventricle. Left border - Left ventricle (and some of the left atrium) Superior border - Right and left atrium and the great vessels.
Is the pericardial sinus the same as the paranasal sinus?from teachmeanatomy.info
The pericardial sinuses are not the same as ‘anatomical sinuses’ (such as the paranasal sinuses). They are passageways formed the unique way in which the pericardium folds around the great vessels. The oblique pericardial sinus is a blind ending passageway located on the posterior surface of the heart.
How many chambers does the heart have?from teachmeanatomy.info
The heart is a hollow structure. On the interior, it is divided into four chambers. These divisions create grooves on the surface of the heart – these are known as sulci.
What is the heart a pyramid?from teachmeanatomy.info
The heart has been described by many texts as “a pyramid which has fallen over”. The apex of this pyramid pointing in an anterior-inferior direction.
Where is the oblique sinus?from teachmeanatomy.info
The oblique pericardial sinus is a blind ending passageway located on the posterior surface of the heart. The transverse pericardial sinus is found superiorly on the heart. It can be used in coronary artery bypass grafting – see below.
How are the atria separated from the ventricles?
The atria are separated from the ventricles by the coronary sulcus (atrioventricular groove); this contains the trunks of the nutrient vessels of the heart and is deficient in front, where it is crossed by the root of the pulmonary artery. The interatrial groove, separating the two atria, is scarcely marked on the posterior surface while anteriorly it is hidden by the pulmonary trunk and ascending aorta.
What is the heart positioned on the left side of the body?
It is positioned posteriorly to the body of the sternum with one-third situated on the right and two-thirds on the left of the midline. Its left-sided orientation is formally known as levocardia (cf. dextrocardia ).
What is arterial supply?
Arterial supply. Arterial supply is from the coronary arteries with coronary arterial dominance describing the dominant vessel supplying the interventricular septum. The vascular territories of the myocardium are divided into 17 myocardial segments according to the AHA nomenclature.
What are the valves in the heart?
Heart valves. The outflow of each chamber is guarded by a heart valve: atrioventricular valves between the atria and ventricles. tricuspid valve. mitral valve (bicuspid valve) semilunar valves which are located in the outflow tracts of the ventricles. aortic valve. pulmonary valve.
How many chambers does the heart have?
The heart, therefore, consists of four chambers: right atrium. left atrium. right ventricle. left ventricle.
Which valves are in the right atrium?
pulmonary valve. It is best to remember the four chambers and four valves in order of the series that blood travels through the heart: venous blood returning from the body drains into the right atrium via the SVC , IVC and coronary sinus.
Where is the interatrial groove located?
The interatrial groove, separating the two atria, is scarcely marked on the posterior surface while anteriorly it is hidden by the pulmonary trunk and ascending aorta. The ventricles are separated by two grooves, one of which, the anterior longitudinal sulcus, is situated on the sternocostal surface of the heart, close to its left margin, ...