
The critical path in the project – according to the CPM
Critical path method
The critical path method (CPM) is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. The critical path method (CPM) is a project modeling technique developed in the late 1950s by Morgan R. Walker of DuPont and James E. Kelley, Jr. of Remington Rand. Kelley and Walker related their …
Full Answer
How to create a critical path in Microsoft Project?
To maintain the critical path within Microsoft Project, the key steps involved include:
- Setting up the Options and non-working times for the project
- Maintain the start date of the project schedule
- Define resources (if they are used in the project schedule) and their non-working Times
- Entering the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Maintaining the tasks and their dependencies
How do I find critical path in MS Project?
- Press F9, and then click the Options button.
- Find the setting “Define Critical Activities as”. Choose Longest Path.
- Reschedule your Project.
- Notice the Gantt chart now. You should see a red Critical Path now.
How are project schedules tasks?
A project schedule is a tool used to help manage resources and tasks, and it will help to guide a project to a successful completion. The schedule lists the tasks to be completed during the project as well as identifying what resources – personnel and materials – are necessary to complete that task. This usually comes in the form of a Statement of Work (SOW) or Scope Statement, which is a detailed description of what will be accomplished during the life of the project.
How to calculate critical path in project management?
To calculate the critical path we will follow the following steps:
- Obtain the project data. Make a list of all the activities of the project along with their dependencies and their specific times.
- Elaborate the network diagram. We have written a post that explains how to elaborate the project network diagram step by step.
- Calculate the Early Start and Late Start Times. ...
- Calculate the Early Finish and Late Finish Times. ...

What is critical path?
The critical path refers to the sequence or order of schedule activities that will make up the entire duration of a project. It represents the longest path through the entirety of the project and typically this path consists of every single activity that must be concluded from the kickoff to the ultimate conclusion of the project.
How long does it take to install electricity and windows?
A house is being built, and windows and electricity are installed at the same time. Installing windows takes 1 day, installing electricity takes 3 days. If installing the windows takes 2 days, it will not affect the project duration.
Can a critical path terminate on a schedule milestone?
In some cases, a critical path can terminate on a particular schedule milestone that does not come at the conclusion of the project. In these cases, typically, the schedule milestone in question will have a finish that comes at a time no later than that of the imposed date schedule restraint in question. That said, in more cases than not the ...
Can a critical path terminate?
In some cases, a critical path can terminate on a particular schedule milestone that does not come at the conclusion of the project. In these cases, typically, the schedule milestone in question will have a finish that comes at a time no later than that of the imposed date schedule restraint in question. That said, in more cases than not the critical path does indeed run the entire life of a project. For more information, please see critical path method.
What are late constraints in MSP?
Late Constraints. Overall project completion priorities (and contractual requirements) often lead to the imposition of deadlines (in MSP), late-finish constraints (in MSP and P6), or project constraints (in P6). Such constraints can override the finish reflection and cause the late dates of some activities to be earlier or later than they would be in the absence of the constraints. As a result, total float can vary among the activities on the driving path to project completion. In a project with multiple constrained milestones, the driving path to only one of them (the most “urgent”) can be expected to have a constant total float value (i.e. the lowest total float.) Due to intersecting logic paths, total float can vary along the driving paths to other constrained milestones. Applying the “critical” flag to activities with total float less than or equal to the project’s lowest total float marks those activities that are on the driving path to the most urgent constrained milestone in the project. If a project constraint (in P6 only) is applied, the lowest total float value may be greater than zero; without a more urgent constraint, the marked activities then denote the driving path to the final activity in the project.
What is the P6 flag?
Unlike other project scheduling software, P6 allows the “critical” activity flag to be assigned on the basis of some criterion other than total float – called Longest Path. The name is misleading, as the method is based on driving logic rather than activity durations. Any activity that is found on the driving logic path to project completion is flagged as “critical.” (The algorithm tracks driving logic backward from the task (s) with the latest early finish in the project.) The Longest Path criterion ignores the total float impacts of multiple calendars and constraints. While it is effective in identifying the project’s critical (logic) path, Longest Path alone is not useful for identifying near-critical paths. MFP analysis (noted above) is useful for this purpose. “Longest path value ™,” a relative-float metric available in Schedule Analyzer Software (a P6 add-in) also helps to identify near-critical paths in these circumstances. For a more detailed review, see What is the Longest Path in a Project Schedule?
What is logic relationship?
Logic Relationships. A logic relationship represents a simple (i.e. one-sided) schedule constraint that is imposed on the successor by the predecessor. Thus, a finish-to-start (FS) relationship between activities A and B dictates only that the start of activity B may NOT occur before the finish of activity A. (It does not REQUIRE that B start immediately after A finishes.) Other relationship types – SS, FF, SF, which were added as part of the precedence diagramming method (PDM) extension of traditional CPM – are similarly interpreted. E.g. A–> (SS)–>B dictates only that the start of B may not occur before the start of A. Activities with multiple predecessor relationships must be scheduled to satisfy ALL of them.
What is a CPM schedule?
A CPM project schedule is comprised of all the activities necessary to complete the project’s scope of work.
What is the CPM method?
The “critical path method” (CPM) – a ~60-year-old algorithm of fairly straightforward arithmetic – lies at the core of most modern project scheduling tools, and most project managers worthy of the name have been exposed to at least the basic CPM concepts. Any discussion of the critical path must address the underlying conceptual basis:
What is considered critical float?
When an activity is automatically marked “critical” based on total float/slack, the primary conclusion to be drawn is simply, “this activity has total float/slack that is at or below the threshold value. That is, there is insufficient working time available between the early- and late- start/finish dates.” If total float/slack is less than zero, then one might also conclude, “this activity is scheduled too late to meet one or more of the project’s deadlines/constraints.” [If automatic resource leveling has been applied, then even these simple conclusions are probably incorrect.] These are important facts, but a useful management response still requires knowledge of the driving logic path (s) to the specific activities/milestones whose deadlines/constraints are violated – knowledge that total float/slack and its associated “critical” flag do not always provide.
What is a logic path?
Logic Paths. A continuous route through the activities and relationships of the network – connecting an earlier activity to a later one – is called a “logic path.” Logic paths can be displayed – together or in isolation – to show the sequential plans for executing selected portions of the project. The simple network shown has only two logic paths between the start and finish milestones: Path 1 = (StartProject) <<A><B>> (FinishProject); and Path 2 = (StartProject) <<C><D>> (FinishProject). [Experimenting with some shorthand logic notation: “<” = logic connection to activity’s Start; “>” = logic connection to activity’s Finish.]
Is there overlap between Longest Path and Critical Path?
Let me say it this way – the Longest Path is a Critical Path, but not all Critical Paths are the Longest.
What Do You Think?
The Critical Path vs Longest Path debate is long from over. What are your thoughts about which one to use and why? Let us know in the comment section.
How do constraints affect total float?
Constraints affect an activity’s Total Float value. Constrained activities can show negative Total Float and can drive negative float to their successors or predecessors. Applying contraints throughout a project will affect what activities are Critical. And so, again the path of 0-total float through the project eludes you.
What is a critical path in a project?
You may have activities that have positive Total Float but are Critical in the client’s eyes. You may want to track a specific path of activities through a project. This is called real-world project controls. “Critical Path is a path through your project which has activities YOU consider critical.”.
Which path has the longest total duration?
If you start with a baseline schedule that has no actuals, no constraints and no deadline, and you perform some CPM scheduling on it, the path of 0 Total Float will be the Longest Path. If you add up the durations of all activities on that 0-float path, it will have the longest Total Duration.
What is the longest path?
The Longest Path is the path through a project network from start to finish where the Total Duration is longer than any other path.
Can actuals affect 0 float?
A project with actuals may not show a path of 0-float either. The actuals and the order of execution can affect the activities’ Total Float as well.
What is project control?
Project controls mean comparing the baseline schedule with actual work done at the site. The difference between monitoring and control is corrective action. Monitoring includes observing and reporting, and perhaps analyzing. Control adds corrective action to this definition.
What degree did Seyar have?
Seyar has a Master of Science degree in Construction Management from New York University (NYU).
What is a CPM schedule?
CPM Schedule commonly used in mega projects to help managers to make effective and timely decisions. It has multi-functions and can be used as a single unit of different project phases such as initiation, planning, design, execution, close-out, etc. It helps the Project Manager to identify hurdles on the critical path, ensure precautionary measures, and take necessary action to maintain the progress of work. Furthermore, coordination among government agencies, procurement teams, different subcontractors, and stakeholders reduces the communication gaps and enhances the approval process of required items. It also provides a platform to keep all the concerned departments on one page to achieve a common objective/goal of the project.
How is forecasting done?
Forecasting is done mostly by extrapolating actual performance for the remaining portion of the project. When the “Performance %” is ahead or behind of “Planned %” from the approved baseline schedule. It gives an alarm to the project manager to take necessary action. Project Updates.
What is the difference between resource and cost loading?
Resources mean labor, equipment, and materials, whereas Cost loading means assigning the budgeted cost to their respective activity. The sum of all activities costs should equal the total budgeted cost of the project.
What is critical path method?
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is the commonly used method by Project Managers for its simplicity and effectiveness. It is used for tracking/monitoring and control of a project. The critical path in construction schedule derives the project duration and there can be multiple critical paths in schedule depending upon the constraints ...
What is early start?
Early Start (ES): The earliest date on which an activity can start within available constraints. Early Finish (EF): The earliest date on which an activity can finish within available constraints. Late Start (LS): The latest date on which an activity can start without delaying project duration.
What is summary path?
Summary path is a variant of critical path which shows you a more refined critical path of subtasks that you select, as opposed to showing you the critical path of an entire sheet. Summary path will look at all child tasks in the summary path’s hierarchy.
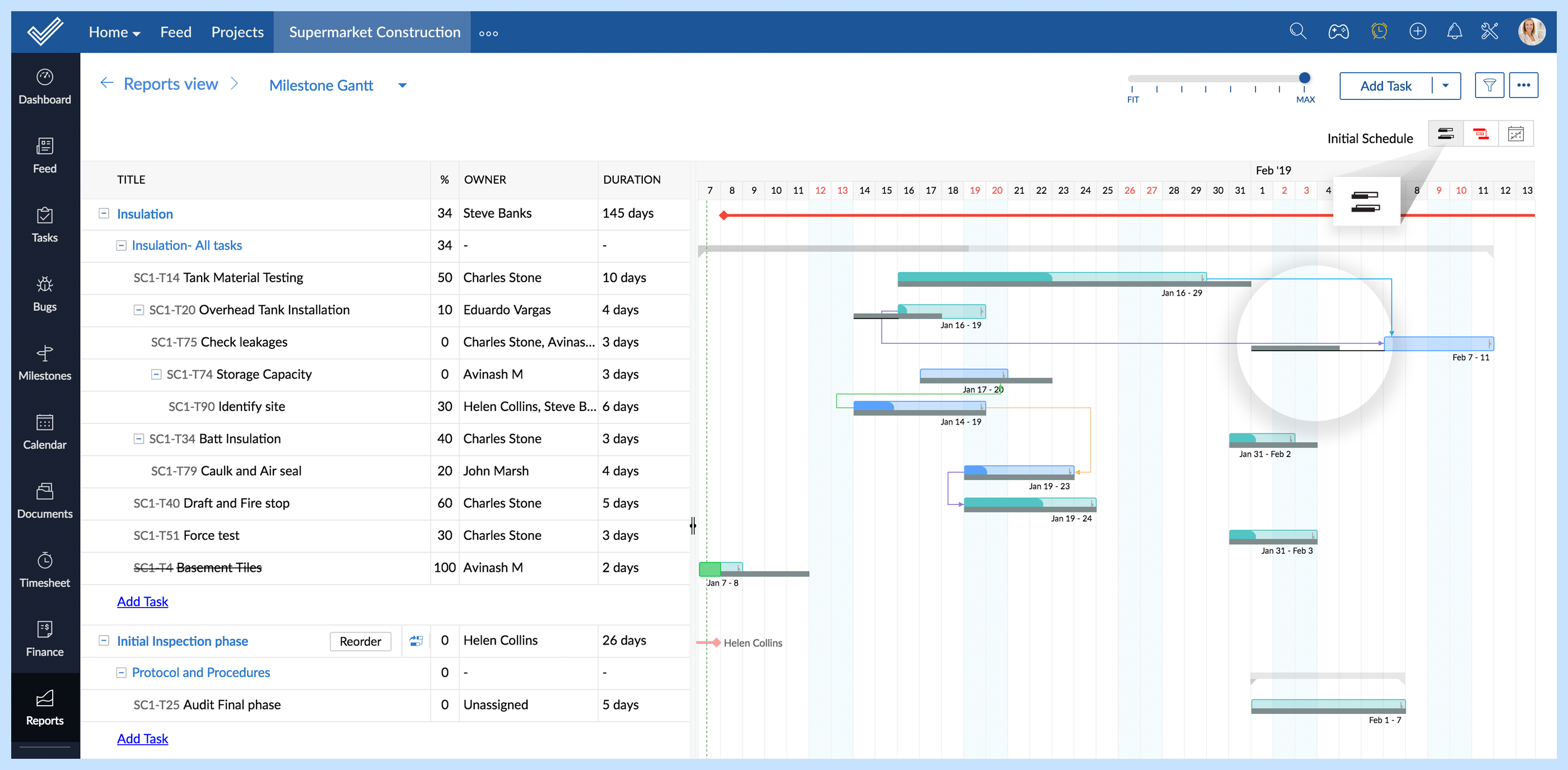
What color is the critical path in Gantt chart?
All tasks and milestones that make up the project's critical path will be highlighted in red in the Gantt chart.
What color are summary path task bars?
That’s it! Your summary path task bars are outlined in orange.
How to track key tasks in a project?
Track the key tasks in your project by setting it up to display the critical path. As task dates or predecessor relationships change, this can impact the project's critical path. Smartsheet will update automatically and always highlight the tasks on the current critical path.
How to enable dependencies on a sheet?
Enable dependencies on the sheet by right-clicking any column header and selecting Edit Project Settings.
What is critical path?
Your Critical Path is the longest distance between the start and the finish of your project, including all the tasks and their duration, which gives you a clear picture of the project’s actual schedule.
Can you filter critical path?
TIP: After you’ve set up the critical path using the steps below, you’ll be able to apply a filter to your sheet to only display tasks in the critical path. Information on how to filter on your project’s critical path tasks can be found in Using Filters to Show or Hide Sheet Data.
How to view critical activities in Primavera P6?
Another way to view the critical activities in Primavera P6 is to right-click on the schedule and select “Columns…”: Select “Critical” under the General heading on the left side of the Columns screen and use the arrow in the middle to bring that selection to the Selected Options box. Select “OK”:
Why is CPM important?
The CPM is especially important in the construction industry, where delays in even small tasks can translate into catastrophic and costly project delays. The CPM and its visualization is important and is used in a wide variety of industries. Before demystifying the critical path, the project team must ensure that the execution project schedule is ...
What does the red bar on a project schedule mean?
The red bars represent the critical path in the Gantt portion of the project schedule:
What is the CPM method?
The Critical Path Method, or CPM, is a scheduling technique that identifies the longest path of logically dependent and connected activities that it takes to reach the end of the project or the end project deliverable. Although there can be more than one critical path, otherwise known as secondary or tertiary critical paths, there is only one primary critical path. Any delay in the project’s critical path will prevent the project from completing and delivering on time.
What is a finish to start relationship?
The majority of the task relationships will contain finish-to-start relationships, which means that a task cannot start until its predecessor task (s) have been completed. Project resources in a resource-loaded schedule should be properly defined and assigned.
What is a project schedule?
A solid project schedule will contain a detailed breakdown of activities in the form of tasks to define the scope of work in a project to drive to an end delivery or goal. These tasks should contain realistic durations and sufficient descriptions of the required work scope, and they should be logically linked. All tasks in a project schedule with exception of the first task (often a start milestone) and the final task (often a finish or delivery milestone) should contain both a predecessor and a successor task relationship. The majority of the task relationships will contain finish-to-start relationships, which means that a task cannot start until its predecessor task (s) have been completed.
How to make float less than or equal to in Schedule?
Once the Schedule Options box launches, select the option “Total Float less than or equal to” under “Define critical activities as”. Ensure that it is set to zero and then select the Close button (activities with zero float are considered critical):
Basic CPM Concepts (in General)
Software – The Critical Activities / Critical Tasks
- The basic element of modern project schedules is the activity or task. In most scheduling tools, logic paths are not explicitly defined. Nevertheless, the obvious importance of the critical path dictates that software packages attempt to identify it – indirectly– by marking activities that meet certain criteria with the “critical” flag. Activities with the “critical” flag are called “critical activities…
Definitions and Recommended Practices
- Defense Contract Management Agency
DCMA’s in-house training course, Integrated Master Plan/Integrated Master Schedule Basic Analysis (Rev 21Nov09)is the source of the “14-Point Assessment” that – because its explicit “trigger” values are easily converted to pass/fail thresholds and red/yellow/green dashboards – i… - AACE International
AACE International (formerly the Association for the Advancement of Cost Engineering) maintains and regularly updates its Recommended Practice No. 10S-90: Cost Engineering Terminology. The most recent issue of RP 10S-90 (June 2018) includes the following definitions: CRITICAL PATH …
Recap
- A full understanding of driving and non-driving schedule logic paths for major schedule activities is useful for managing and communicating a project execution plan.
- The most important logic path in the project schedule is the “critical path,” i.e. the driving path to project completion. Overall acceleration (or recovery) of a project is only made possible by...
- Some traditional notions of critical path path attributes – e.g. critical path activities possess …
- A full understanding of driving and non-driving schedule logic paths for major schedule activities is useful for managing and communicating a project execution plan.
- The most important logic path in the project schedule is the “critical path,” i.e. the driving path to project completion. Overall acceleration (or recovery) of a project is only made possible by...
- Some traditional notions of critical path path attributes – e.g. critical path activities possess no float; slippage or acceleration of critical path activities always translates directly to projec...
- Total float remains a valuable indicator of an activity’s scheduling flexibility with respect to completion constraints of the project. An activity with TF=0 may not be allowed to slip if all proj...