...
Equinoxes and solstices.
| ecliptic | equatorial | |
|---|---|---|
| December solstice | 270° | 18h |
What is the ecliptic plane?
The ecliptic plane is defined as the imaginary plane containing the Earth's orbit around the sun. In the course of a year, the sun's apparent path through the sky lies in this plane.
Which planets orbit the Sun in the ecliptic?
Top and side views of the plane of the ecliptic, showing planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Most of the planets orbit the Sun very nearly in the same plane in which Earth orbits, the ecliptic.
What is the ecliptic in geography?
The ecliptic is the mean plane of the apparent path in the Earth's sky that the Sun follows over the course of one year; it is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. This plane of reference is coplanar with Earth's orbit around the Sun (and hence the Sun's apparent path around Earth).
Why is the ecliptic the invariable plane of the Solar System?
Because of this, most Solar System bodies appear very close to the ecliptic in the sky. The invariable plane is defined by the angular momentum of the entire Solar System, essentially the vector sum of all of the orbital and rotational angular momenta of all the bodies of the system; more than 60% of the total comes from the orbit of Jupiter.
What determines the ecliptic line?
The ecliptic is defined by the plane of Earth's orbit around the sun. The major planets in our solar system and their moons, and some asteroids, orbit more or less in this same plane.
What is the ecliptic in astrology?
The linear path that the Sun describes across the sky is called the ecliptic. The constellations on that path are collectively called the zodiac and extend a few degrees above and below the ecliptic line.
Are all planets on the ecliptic?
Most major planets in our solar system stay within 3 degrees of the ecliptic. Mercury is the exception; its orbit is inclined to the ecliptic by 7 degrees. The dwarf planet Pluto is a widely known exception to this rule. Its orbit is inclined to the ecliptic by more than 17 degrees.
How do you find the ecliptic on a star chart?
The exact times appear at the top left of the map, but the sky doesn't change a lot within an hour or two of these times. The brownish line you see curving from southeast to northwest represents the ecliptic — the apparent path of the Sun across our sky.
Why are all the planets on the ecliptic?
The orbits of the planets are coplanar because during the Solar System's formation, the planets formed out of a disk of dust which surrounded the Sun. Because that disk of dust was a disk, all in a plane, all of the planets formed in a plane as well.
Is Venus always on the ecliptic?
At all times, Venus lies close to a line across the sky called the ecliptic. This line traces the path that the Sun takes through the zodiacal constellations every year, and shows the plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
Is the moon on the ecliptic?
The ecliptic is the path the sun, moon, and planets take across the sky as seen from Earth. It defines the plane of the Earth's orbit around the sun. The name "ecliptic" comes from the fact that eclipses take place along this line.
Is Venus on the ecliptic plane?
Viewed from a point above the solar system, the planet would appear directly in line with the sun and Earth. Actually Venus lies well north of the ecliptic plane at this time; we will see it 8.2-degrees north of the center of the sun's disk.
What is an ecliptic Why is it given that mean?
The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun throughout the course of a year. Because Earth takes one year to orbit the Sun, the apparent position of the Sun takes one year to make a complete circuit of the ecliptic. With slightly more than 365 days in one year, the Sun moves a little less than 1° eastward every day.
What is ecliptic used for?
Astronomers use the noun ecliptic to describe the sun's path as it's seen from the Earth. You're most likely to come across the word ecliptic in an astronomy class, since it's a technical term for the apparent path of the sun through the stars over the course of a year.
Why is it important to know where the ecliptic is?
Along with the celestial equator, the ecliptic is one of two important lines that astronomers use to divide up the night sky. From our planet, it looks as though the Sun moves around us over the course of a year.
What is the ecliptic Why does it go up and down?
If the sun's path is observed from the Earth's reference frame, it appears to move around the Earth in a path which is tilted with respect to the spin axis at 23.5°. This path is called the ecliptic. It tells us that the Earth's spin axis is tilted with respect to the plane of the Earth's solar orbit by 23.5°.
What is the ecliptic?
The ecliptic is the plane of Earth's orbit around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system .
Why is the ecliptic used as the reference plane of the Solar System?
Because of the uncertainty regarding the exact location of the invariable plane, and because the ecliptic is well defined by the apparent motion of the Sun , the ecliptic is used as the reference plane of the Solar System both for precision and convenience.
What is the name of the two points that the Sun crosses the equator?
If the equator is projected outward to the celestial sphere, forming the celestial equator, it crosses the ecliptic at two points known as the equinoxes . The Sun, in its apparent motion along the ecliptic, crosses the celestial equator at these points, one from south to north, the other from north to south.
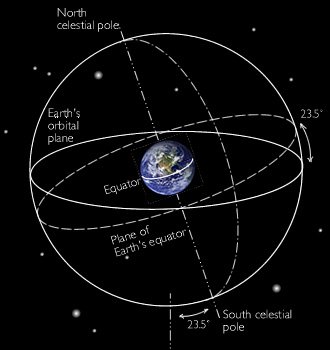
What is the plane of Earth's orbit?
The plane of Earth 's orbit projected in all directions forms the reference plane known as the ecliptic. Here, it is shown projected outward (gray) to the celestial sphere, along with Earth's equator and polar axis (green). The plane of the ecliptic intersects the celestial sphere along a great circle (black), the same circle on which the Sun seems to move as Earth orbits it. The intersections of the ecliptic and the equator on the celestial sphere are the vernal and autumnal equinoxes (red), where the Sun seems to cross the celestial equator.
Why is the equator not fixed?
The orientation of Earth's axis and equator are not fixed in space, but rotate about the poles of the ecliptic with a period of about 26,000 years, a process known as lunisolar precession, as it is due mostly to the gravitational effect of the Moon and Sun on Earth's equatorial bulge. Likewise, the ecliptic itself is not fixed. The gravitational perturbations of the other bodies of the Solar System cause a much smaller motion of the plane of Earth's orbit, and hence of the ecliptic, known as planetary precession. The combined action of these two motions is called general precession, and changes the position of the equinoxes by about 50 arc seconds (about 0.014°) per year.
Why do astronomers produce new fundamental ephemerides?
Astronomers produce new fundamental ephemerides as the accuracy of observation improves and as the understanding of the dynamics increases , and from these ephemerides various astronomical values, including the obliquity, are derived. Obliquity of the ecliptic for 20,000 years, from Laskar (1986).
What is the yearly path the Sun follows on the celestial sphere?
Ecliptic. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Jump to navigation Jump to search. Apparent path of the Sun on the celestial sphere. As seen from the orbiting Earth, the Sun appears to move with respect to the fixed stars, and the ecliptic is the yearly path the Sun follows on the celestial sphere.
Why is the ecliptic called the ecliptic?
The ecliptic got its name because the ancients saw that solar eclipses happen when the moon crosses the ecliptic during the new moon phase.
How to see the ecliptic?
If you’re able, keep an eye on the sun, the moon and the planets for a while. Watch for a few days, a few weeks, months, years, even. You’ll begin to get a feel for the ecliptic in your sky. You’ll notice the planets, sun and moon are always on or near the ecliptic, and you can use this line across your sky to help you find your way around, making your way between the constellations and stars . You’ll notice the sun’s path – the ecliptic – higher in the sky during the summer months and lower during the winter.
What is the imaginary track across our sky called?
The moon follows the sun’s path. And so do the major planets in our solar system. This imaginary track across our sky is called the ecliptic . Technically speaking, it’s a projection of the plane of Earth’s orbit around the sun, traced onto our sky. Practically speaking, the ecliptic forms a great circle around the sky and is a useful tool for stargazers.
Why do the moon and planets follow the Sun's path?
Why do the moon and planets follow the sun’s path? It’s mainly because, long ago – before there was a solar system as we know it today – there was a vast cloud of gas and dust in space. This cloud was spinning, and, as it spun, it flattened out. Our sun formed in the center of this cloud. The major planets, including Earth, and most other solar system objects formed in the flat disk surrounding the sun. The ecliptic is this flat disk of planets in our sun’s family – our solar system – translated onto our sky.
Why do the moon and planets trace out a line across our sky?
The moon and planets trace out a line across our sky because they all orbit the sun, more or less, in a single plane. And – as seen from Earth – we look edgewise into that flat plane of the solar system.
How many times does the Moon cross the solar system?
It crosses it twice each orbit; once going upward and once downward from our point of view. We usually see the moon close to, but not exactly alongside the other solar system objects. On the other hand, the moon sometimes passes right in front of other solar system objects, in an event called an occultation.
What would happen if we could see the solar system from far above the Earth's north pole?
If we could watch the solar system from far above the Earth’s north pole, we’d see the planets, moons, asteroids, and some of the comets (but not all of them) rushing around the sun counterclockwise in this plane, like marbles rolling around a dish. Actually, the major planets are more within the dish than on it.
Which planets line up on the ecliptic?
The planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, and Saturn lined up along the ecliptic (red line) shortly after sunset. Image via Jia Hao/Wikipedia
What is the ecliptic of the zodiac?
What is the zodiac? Besides define the path of the sun, the ecliptic marks the line along which eclipses occur, the moon and planets and asteroids wander, the Zodiac constellations live.
How do eclipses happen?
The ecliptic – the line across our sky defined by the sun’s path – gets its name from the fact that eclipses can only occur along it. A lunar eclipse happens when the moon passes through Earth’s shadow, when it is directly opposite the sun on the sky. During a solar eclipse the moon passes between Earth and the sun momentarily blocking out its light and warmth. Though the moon circles Earth roughly once a month, eclipses don’t happen nearly that frequently because the moon’s orbit is slightly tilted relative to that of our planet. Our satellite actually spends most of its time either above or below the plane of Earth’s orbit and therefore is usually not nicely aligned with us and the sun. Twice a month it crosses the ecliptic – but an eclipse will only occur when that passage happens during either a full moon for a lunar eclipse or a new moon for a solar one. The need for this precise alignment is why eclipses happen only a couple of times a year at most.
What constellation is on the other side of the Sun?
For example, if we could see the stars during the day, we would notice that in late March and early April, the constellation Pisces (the Fish) is on the other side of the sun. As the days and weeks went by, the sun would appear to drift eastward across Pisces until moving in front of Aries, the Ram, in the second half of April. One month later, the sun would be flanked by the stars in Taurus, then Gemini, Cancer, Leo, and so on. Roughly every month or so, as Earth moes in orbit, a different constellation sits behind the sun.
What happens when the Earth orbits the Sun?
As Earth orbits the sun, the sun appears to drift across the background stars. The ecliptic marks out the path of this motion on the sky. Credit: Wikipedia
Which planets are stretched out from the west to the east?
To put that another way, the planets allow you to actually trace out the ecliptic on any clear night yourself. Right now (April 1, 2012), the moon, Jupiter, Venus, and Mars are stretched out from west to east across the sky shortly after sun set. Go out tonight and try to find them.
How many degrees does the Moon's orbit tip?
The moon's orbit is tipped five degrees relative to Earth's. Eclipses only occur when the moon crosses the ecliptic during a full or new moon.
What is the plane of the ecliptic?
A basic definition is that the plane of the ecliptic is the plane of the Earth’s orbit, but that does not mean much to most people. Space is a three-dimensional vacuum, which you can think of as a kind of pool with the planets suspended in it.
How does the ecliptic plane get its name?
The ecliptic plane got its name from the fact that a solar eclipse can only happen when the Moon crosses this plane to block out the Sun. Our Moon crosses the ecliptic about twice a month. A solar e clipse occurs when a new Moon crosses the ecliptic, and a lunar eclipse occurs when a full Moon cross es it. Seasons on Earth are caused by our planet’s ...
Why is the solar system flat?
Actually our entire Solar System can be thought of as flat because all of the planets’ orbits are near or on this plane. The ecliptic plane is used as the main reference when describing the position of other celestial objects in our Solar System.
What is the shape of the Earth's orbit?
The Earth orbits the Sun on a particular angle and its orbit is elliptical in shape. The orbit is often shown as an ellipse made of dotted lines with the Sun at its center. If you made this ellipse a solid surface and extended it infinitively, then you would have the plane of the ecliptic.
Which planet has the highest inclination?
Until it was stripped of its status as a planet, Pluto was the planet with the most extreme inclination – 17°. Mercury is the only other planet with a significant inclination of 7°. There is also a 7° inclination between the plane of the Sun’s equator and the ecliptic plane. There are other celestial bodies that have a much greater inclination ...
What causes seasons on Earth?
Seasons on Earth are caused by our planet’s axial tilt of 23.5°, which causes variations in the amount of sunlight different parts of the Earth receive. This goes for all the other planets too. For example, Uranus rotates on its side with an axial tilt of 97.8°, which results in extreme variations in its seasons.
Need more help understanding the ecliptic?
oblem 4.45 - Enhanced - with Feedback Part A Find the s- and y-components of the vector d = (7.0 km, 29° left of +y-axis). 2- Express your answers in kilometers. Enter the x and y components of the vector separated ...
Get the most out of Chegg Study
In science there are many key concepts and terms that are crucial for students to know and understand. Often it can be hard to determine what the most important science concepts and terms are, and even once you’ve identified them you still need to understand what they mean.

Overview
Plane of the Solar System
Most of the major bodies of the Solar System orbit the Sun in nearly the same plane. This is likely due to the way in which the Solar System formed from a protoplanetary disk. Probably the closest current representation of the disk is known as the invariable plane of the Solar System. Earth's orbit, and hence, the ecliptic, is inclined a little more than 1° to the invariable plane, Jupiter's orbit is within a little more than ½° of it, and the other major planets are all within about 6°. Because o…
Sun's apparent motion
The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun throughout the course of a year.
Because Earth takes one year to orbit the Sun, the apparent position of the Sun takes one year to make a complete circuit of the ecliptic. With slightly more than 365 days in one year, the Sun moves a little less than 1° eastward every day. This small difference in the Sun's position against the stars causes any particular spot on Earth's surface to catch up with (and stand directly nort…
Relationship to the celestial equator
Because Earth's rotational axis is not perpendicular to its orbital plane, Earth's equatorial plane is not coplanar with the ecliptic plane, but is inclined to it by an angle of about 23.4°, which is known as the obliquity of the ecliptic. If the equator is projected outward to the celestial sphere, forming the celestial equator, it crosses the ecliptic at two points known as the equinoxes. The Sun…
Obliquity of the ecliptic
Obliquity of the ecliptic is the term used by astronomers for the inclination of Earth's equator with respect to the ecliptic, or of Earth's rotation axis to a perpendicular to the ecliptic. It is about 23.4° and is currently decreasing 0.013 degrees (47 arcseconds) per hundred years because of planetary perturbations.
The angular value of the obliquity is found by observation of the motions of Ea…
Celestial reference plane
The ecliptic forms one of the two fundamental planes used as reference for positions on the celestial sphere, the other being the celestial equator. Perpendicular to the ecliptic are the ecliptic poles, the north ecliptic pole being the pole north of the equator. Of the two fundamental planes, the ecliptic is closer to unmoving against the background stars, its motion due to planetary p…
Eclipses
Because the orbit of the Moon is inclined only about 5.145° to the ecliptic and the Sun is always very near the ecliptic, eclipses always occur on or near it. Because of the inclination of the Moon's orbit, eclipses do not occur at every conjunction and opposition of the Sun and Moon, but only when the Moon is near an ascending or descending node at the same time it is at conjunction (new) or opposition (full). The ecliptic is so named because the ancients noted that eclipses only occur w…
In the constellations
The ecliptic currently passes through the following constellations:
• Pisces
• Aries
• Taurus
• Gemini