Full Answer
What is Durbin Watson test in regression analysis?
1 The Durbin Watson statistic is a test statistic used in statistics to detect autocorrelation in the residuals from a regression analysis. 2 The Durbin Watson statistic will always assume a value between 0 and 4. ... 3 One important way of using the test is to predict the price movement of a particular stock based on historical data.
What is the'Durbin Watson statistic'?
What is the 'Durbin Watson Statistic'. The Durbin Watson statistic is a number that tests for autocorrelation in the residuals from a statistical regression analysis. The Durbin-Watson statistic is always between 0 and 4.
What is the Durbin Watson statistic for autocorrelation?
Updated Jul 18, 2019. The Durbin Watson (DW) statistic is a test for autocorrelation in the residuals from a statistical regression analysis. The Durbin-Watson statistic will always have a value between 0 and 4. A value of 2.0 means that there is no autocorrelation detected in the sample.
How to perform a Durbin-Watson test in Excel?
Real Statistics Data Analysis Tool: The Linear Regression data analysis tool provided by the Real Statistics Resource Pack also supports the Durbin-Watson Test as described next. To conduct the test in Example 1, press Ctrl-m and double click on the Linear Regression data analysis tool. Now fill in the dialog box that appears as shown in Figure 2.

For which regression assumptions does the Durbin-Watson statistic test?
The Durbin Watson statistic is a test for autocorrelation in a regression model's output. The DW statistic ranges from zero to four, with a value of 2.0 indicating zero autocorrelation. Values below 2.0 mean there is positive autocorrelation and above 2.0 indicates negative autocorrelation.
What is the purpose of Durbin-Watson test?
The Durbin Watson (DW) statistic is used as a test for checking auto correlation in the residuals of a statistical regression analysis. If auto correlation exists, it undervalues the standard error and may cause us to believe that predictors are significant when in reality they are not.
What is the alternative hypothesis for the Durbin-Watson test?
The alternative hypothesis is that there is autocorrelation among the residuals. p = dwtest( r , x , Name,Value ) returns the p-value for the Durbin-Watson test with additional options specified by one or more name-value pair arguments.
How do you test for autocorrelation in linear regression?
A common method of testing for autocorrelation is the Durbin-Watson test. Statistical software such as SPSS may include the option of running the Durbin-Watson test when conducting a regression analysis. The Durbin-Watson tests produces a test statistic that ranges from 0 to 4.
What are the assumptions of linear regression?
There are four assumptions associated with a linear regression model: Linearity: The relationship between X and the mean of Y is linear. Homoscedasticity: The variance of residual is the same for any value of X. Independence: Observations are independent of each other.
How do you test for multicollinearity in regression?
How to check whether Multi-Collinearity occurs?The first simple method is to plot the correlation matrix of all the independent variables.The second method to check multi-collinearity is to use the Variance Inflation Factor(VIF) for each independent variable.More items...•
What are the limitations of Durbin-Watson test?
Limitations or Shortcoming of Durbin-Watson Test Statistics Durbin-Watson test is inconclusive if computed value lies between and . It is inappropriate for testing higher-order serial correlation or for other forms of autocorrelation.
What is autocorrelation in regression analysis?
What is Autocorrelation? Autocorrelation refers to the degree of correlation of the same variables between two successive time intervals. It measures how the lagged version of the value of a variable is related to the original version of it in a time series.
What is multicollinearity in regression?
Multicollinearity occurs when two or more independent variables are highly correlated with one another in a regression model. This means that an independent variable can be predicted from another independent variable in a regression model.
What is the difference between multicollinearity and autocorrelation?
Autocorrelation is the correlation of the signal with a delayed copy of itself. Multicollinearity, which should be checked during MLR, is a phenomenon in which at least two independent variables are linearly correlated (one can be predicted from the other).
Why autocorrelation is a problem in linear regression?
PROBLEM OF AUTOCORRELATION IN LINEAR REGRESSION DETECTION AND REMEDIES. In the classical linear regression model we assume that successive values of the disturbance term are temporarily independent when observations are taken over time. But when this assumption is violated then the problem is known as Autocorrelation.
What is the difference between correlation and autocorrelation?
It's conceptually similar to the correlation between two different time series, but autocorrelation uses the same time series twice: once in its original form and once lagged one or more time periods. For example, if it's rainy today, the data suggests that it's more likely to rain tomorrow than if it's clear today.
How autocorrelation can be detected?
Autocorrelation is diagnosed using a correlogram (ACF plot) and can be tested using the Durbin-Watson test. The auto part of autocorrelation is from the Greek word for self, and autocorrelation means data that is correlated with itself, as opposed to being correlated with some other data.
How do you find autocorrelation?
The number of autocorrelations calculated is equal to the effective length of the time series divided by 2, where the effective length of a time series is the number of data points in the series without the pre-data gaps. The number of autocorrelations calculated ranges between a minimum of 2 and a maximum of 400.
How do you manually calculate autocorrelation?
1:1510:00Autocorrelation by Hand ,autocorrelation in excel - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt would be basically a sum of YT minus y bar or the mean of Y multiplied by Y t minus K minus y barMoreIt would be basically a sum of YT minus y bar or the mean of Y multiplied by Y t minus K minus y bar or mean of Y. And which are going to divide by YT minus y bar and square it square.
How do you know if autocorrelation is significant?
The lag 1 autocorrelation, which is generally the one of greatest interest, is 0.281. The critical values at the 5 % significance level are -0.140 and 0.140. This indicates that the lag 1 autocorrelation is statistically significant, so there is evidence of non-randomness. A common test for randomness is the runs test.
What happens if the absolute value of the Durbin-Watson test statistic is greater than the value found in?
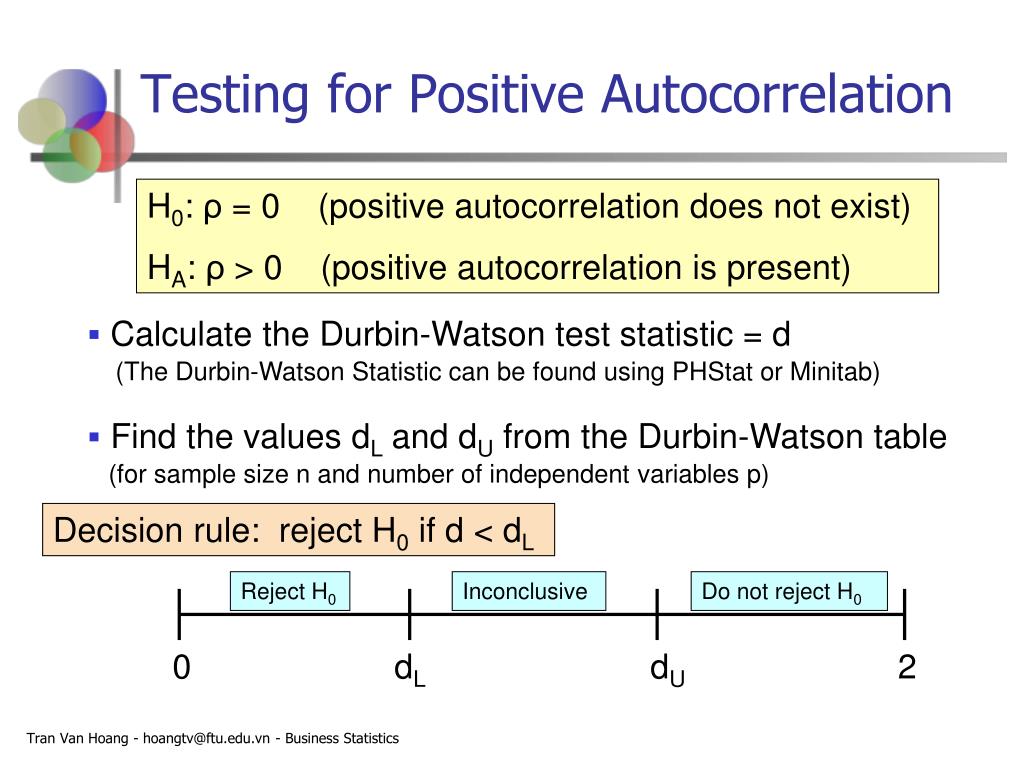
If the absolute value of the Durbin-Watson test statistic is greater than the value found in the table, then you can reject the null hypothesis of the test and conclude that autocorrelation is present.
What is the assumption of linear regression?
One of the main assumptions in linear regression is that there is no correlation between consecutive residuals. In other words, it’s assumed that the residuals are independent. When this assumption is violated, the standard errors of the coefficients in a regression model are likely to be underestimated which means predictor variables are more ...
Is there a correlation between residuals of H0?
H0 (null hypothesis): There is no correlation among the residuals.
What Is the Durbin Watson Statistic?
The Durbin Watson (DW) statistic is a test for autocorrelation in the residuals from a statistical model or regression analysis. The Durbin-Watson statistic will always have a value ranging between 0 and 4. A value of 2.0 indicates there is no autocorrelation detected in the sample. Values from 0 to less than 2 point to positive autocorrelation and values from 2 to 4 means negative autocorrelation.
What is Durbin Watson?
The Durbin Watson statistic is a test for autocorrelation in a regression model's output.
What does autocorrelation show?
Autocorrelation can show if there is a momentum factor associated with a stock. For example, if you know that a stock historically has a high positive autocorrelation value and you witnessed the stock making solid gains over the past several days, then you might reasonably expect the movements over the upcoming several days (the leading time series) to match those of the lagging time series and to move upward.
Who is Durbin Watson named after?
The Durbin Watson statistic is named after statisticians James Durbin and Geoffrey Watson.
Will Kenton be an economist?
Will Kenton is an expert on the economy and investing laws and regulations. He previously held senior editorial roles at Investopedia and Kapitall Wire and holds a MA in Economics from The New School for Social Research and Doctor of Philosophy in English literature from NYU.
What is the key assumption in regression?
A key assumption in regression is that the error terms are independent of each other. On this webpage, we present a simple test to determine whether there is autocorrelation (aka serial correlation), i.e. where there is a (linear) correlation between the error term for one observation and the next. This is especially relevant with time series data where the data are sequenced by time.
What does a value of d mean?
d takes on values between 0 and 4. A value of d = 2 means there is no autocorrelation. A value substantially below 2 (and especially a value less than 1) means that the data is positively autocorrelated, i.e. on average, a data element is close to the subsequent data element. A value of d substantially above 2 means that the data is negatively autocorrelated, i.e. on average a data element is far from the subsequent data element.

Overview
In statistics, the Durbin–Watson statistic is a test statistic used to detect the presence of autocorrelation at lag 1 in the residuals (prediction errors) from a regression analysis. It is named after James Durbin and Geoffrey Watson. The small sample distribution of this ratio was derived by John von Neumann (von Neumann, 1941). Durbin and Watson (1950, 1951) applied this statistic to the residuals from least squares regressions, and developed bounds tests for the null hypothesis t…
Computing and interpreting the Durbin–Watson statistic
If et is the residual given by the Durbin-Watson test statistic is
where T is the number of observations. For large T, d is approximately equal to 2(1 − ), where is the sample autocorrelation of the residuals, d = 2 therefore indicates no autocorrelation. The value of d always lies between 0 and 4. If the Durbin–Watson statistic is substantially less than 2, there is evidence of positive serial correlation. As a rough rule of thumb, if Durbin–Watson is less than 1.…
Durbin h-statistic
The Durbin–Watson statistic is biased for autoregressive moving average models, so that autocorrelation is underestimated. But for large samples one can easily compute the unbiased normally distributed h-statistic:
using the Durbin–Watson statistic d and the estimated variance
of the regression coefficient of the lagged dependent variable, provided
Implementations in statistics packages
1. R: the dwtest function in the lmtest package, durbinWatsonTest (or dwt for short) function in the car package, and pdwtest and pbnftest for panel models in the plm package.
2. MATLAB: the dwtest function in the Statistics Toolbox.
3. Mathematica: the Durbin–Watson (d) statistic is included as an option in the LinearModelFit function.
See also
• Time-series regression
• ACF / PACF
• Correlation dimension
• Breusch–Godfrey test
• Ljung–Box test
External links
• Table for high n and k
• Econometrics lecture (topic: Durbin–Watson statistic) on YouTube by Mark Thoma