
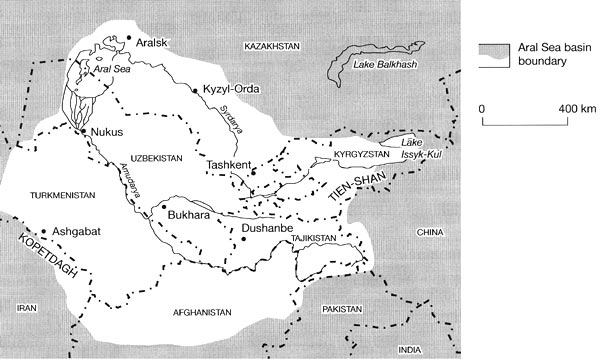
The water supply to the Aral Sea is mainly from two rivers, the Amu Darya and Syr Darya, which carry snow melt from mountainous areas. In the early 1960s, the then-Soviet Union diverted the Amu Darya and Syr Darya Rivers for irrigation of one of the driest parts of Asia to produce rice, melons, cereals, and especially cotton.
Which rivers mainly supply the Aral Sea?
- Similar- problems have been caused by humans, increase in salinity and toxins. ...
- Different- Salton Sea has been shrinking because of Soviet Union diverting the two main
- sources, Salton sea is increased in salinity because there is no way for the water to flow out. ...
What are the two rivers that flow into the Aral Sea?
The water supply to the Aral Sea is mainly from two rivers, the Amu Darya and Syr Darya , which carry snow melt from mountainous areas. In the early 1960s, the then-Soviet Union diverted the Amu Darya and Syr Darya Rivers for irrigation of one of the driest parts of Asia to produce rice, melons, cereals, and especially cotton.
What rivers that flow into Aral Sea have been diverted?
- Improving the quality of irrigation canals
- Using alternative cotton species that require less water
- Promoting non-agricultural economic development in upstream countries
- Using fewer chemicals on the cotton
- Cultivating crops other than cotton
Where does the Aral Sea get its water?
The water level in the Aral Sea started drastically decreasing from the 1960s onward. In normal conditions, the Aral Sea gets approximately one fifth of its water supply through rainfall, while the rest is delivered to it by the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers.

What rivers feed the Aral Sea?
The two rivers that feed it are the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers, respectively reaching the Sea through the South and the North.
How many rivers supply the Aral Sea?
two riversThe water supply to the Aral Sea is mainly from two rivers, the Amu Darya and Syr Darya, which carry snowmelt from mountainous areas.
What resources did the Aral Sea supply to the local people?
What resources did the Aral Sea supply to the local inhabitants? Source of fish, commerce, transportation, and recreation.
What has the diversion of water from the Aral Sea led to?
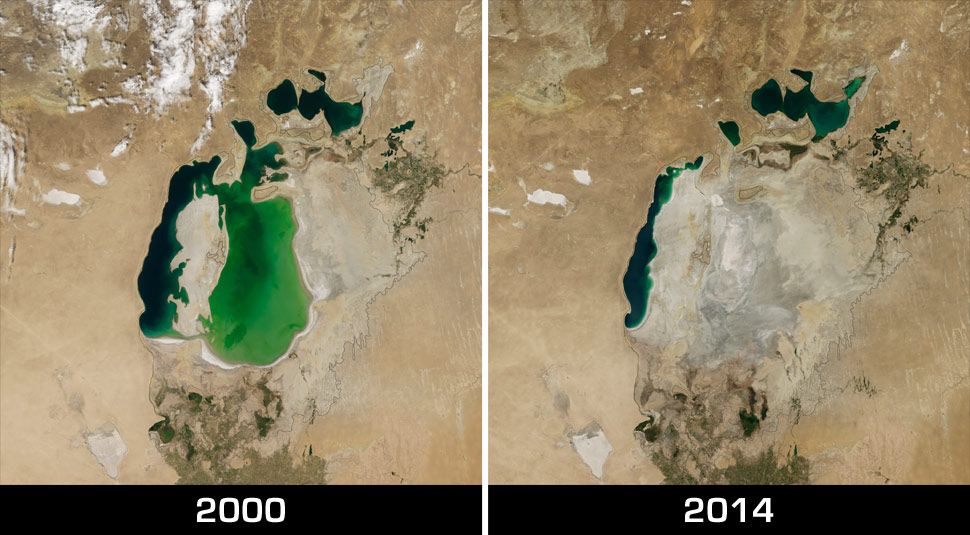
Diversion of water sources has caused the Aral Sea in Central Asia to decline significantly over the past five decades. It has broken into several smaller seas, leaving behind a vast desert and a multitude of environmental, economic and social problems.
Where does the Syr Darya River start?
Kara DaryaNarynSyr Darya/Sources
What dried up the Aral Sea?
Once thriving, the vast Asian lake was drained for irrigation. Once the fourth largest lake in the world, Central Asia's shrinking Aral Sea has reached a new low, thanks to decades-old water diversions for irrigation and a more recent drought.
What is the source of the Colorado River?
La Poudre Pass LakeColorado River / SourceDENVER — The headwaters of the Colorado River are just a small stream in the mountains of northern Colorado. The water comes from a lake on the Poudre Pass in Rocky Mountain National Park and then flows out to Grand Lake and Lake Granby. It's in Granby where much of the water gets diverted.
For what purpose were the waters of the Syr Darya and the Amu Darya rivers both of which supply the Aral Sea diverted?
agricultural irrigationBeginning about 1960, the Aral Sea's water level was systematically and drastically reduced, because of the diversion of water from the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers for purposes of agricultural irrigation.
Why was the Colorado River diverted?
Much of the river's water is diverted for irrigated agriculture, including the Palo Verde, Imperial and Coachella valleys in California, in central Arizona and the Yuma region, and in Mexico.
What is the name of the river that flows into Aral?
During this period, the Amu Darya River, one of Aral’s main inlets, drained into the Caspian Sea. But some geographers, like Nick Middleton, believe the rivers started flowing into Aral in the current geological epoch (Holocene epoch). However, Syr Darya may have started flowing into the lake much earlier.
Where is the Aral Sea?
The Aral Sea, also known as Orol Dengizi (Uzbek) or Aral Tengizi (Kazakh) is a saline lake in Central Asia straddling the boundary between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan to the south and north. The lake once covered 68,000 square kilometers between the Kyzylorda and Aktobe regions in Kazakhstan and the Karakalpakstan region of Uzbekistan.
What did the Russians do to the Aral Sea?
Since the Aral Sea does not connect to any other water body, the Russians dissembled their vessels and transported them overland then reassembled them at Aralsk. One of the vessels was used by Butakov to survey the lake region in 1848. It took the Russians two years to explore the entire area.
How much water was diverted from the Aral Sea in the 1960s?
By 1960, the Soviet government had diverted close to 60 cubic kilometers of water from going to the Aral Sea.
What is the climate of the Aral Sea?
The area experiences a desert-continental climate, characterized by hot summers, cold winters, and varying diurnal air temperature. The Aral region receives sparse rainfall, with an average annual precipitation of 100 mm. Showers are frequent in autumn and spring. Northwesterly winds are common in winter and autumn, while southwesterly and westerly winds prevail in summer and spring.
How wide is the Aral Sea?
Before the 1960s, the Aral Sea had a maximum depth of 69 meters (western shores) and a surface area of 68,000 square kilometers. It has a maximum length of 435 kilometers from north to south and was 290 kilometers wide from west to east.
What is the average rainfall in Aral?
The Aral region receives sparse rainfall, with an average annual precipitation of 100 mm. Showers are frequent in autumn and spring. Northwesterly winds are common in winter and autumn, while southwesterly and westerly winds prevail in summer and spring.
Which river discharged into the Aral Sea?
That change resulted primarily because of the diversion (for purposes of irrigation) of the riverine waters of the Syr Darya (ancient Jaxartes River) in the north and the Amu Darya (ancient Oxus River) in the south, which discharged into the Aral Sea and were its main sources of inflowing water.
Where is the Aral Sea?
Aral Sea, Kazakh Aral Tengizi, Uzbek Orol Dengizi, a once-large saltwater lake of Central Asia. It straddles the boundary between Kazakhstan to the north and Uzbekistan to the south. Shrinkage of the Aral Sea, 1960–2009. Animated map of the shrinking of the Aral Sea.
How high was the water level in the Aral Sea in 1960?
The water level had dropped to 125 feet (36 metres) above sea level, and the water volume was reduced by three-fourths of what it had been in 1960. Almost no water from the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya ever reached the Aral Sea anymore.
Why was the Aral Sea water level reduced?
Beginning about 1960, the Aral Sea’s water level was systematically and drastically reduced, because of the diversion of water from the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers for purposes of agricultural irrigation.
Why is the Aral Sea of great interest?
The Aral Sea and its demise are of great interest and increasing concern to scientists because of the remarkable shrinkage of its area and volume that began in the second half of the 20th century—when the region was part of the Soviet Union —and continued into the 21st.
Why did the Aral Sea shrink?
The Aral Sea began to quickly shrink because of the evaporation of its now unreplenished waters. By 1989 the Aral Sea had receded to form two separate parts, the “Greater Sea” in the south and the “Lesser Sea” in the north, each of which had a salinity almost triple that of the sea in the 1950s.
How many lakes did the Aral Sea have?
By the end of the century the Aral Sea had receded into three separate lakes: the Greater Sea had divided into a long, narrow, western lake and a larger, broader, eastern lake, with the remains of the Lesser Sea to the north.
What is the water supply to the Aral Sea?
The water supply to the Aral Sea is mainly from two rivers, the A mu Darya and Syr Darya, which carry snow melt from mountainous areas. In the early 1960s, the then-Soviet Union diverted the Amu Darya and Syr Darya Rivers for irrigation of one of the driest parts of Asia to produce rice, melons, cereals, and especially cotton.
Where is the Aral Sea?
The Aral Sea is a lake located east of the Caspian Sea between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan in central Asia. This area is part of the Turkestan desert, which is the fourth largest desert in the world; it is produced from a rain shadow effect by Afghanistan’s high mountains to the south.
How much of the Aral Sea was dissolved in 2007?
By 2007, the Aral Sea shrank to about 10% of its original size and its salinity increased from about 1% dissolved salt to about 10% dissolved salt, which is 3 times more saline than seawater. These changes caused an enormous environmental impact.
Why did the Aral Sea shrink?
Since then, it has progressively shrunk due to evaporation and lack of recharge by rivers.
What is another example of a massive lake that has nearly disappeared for the same reasons as the Aral Sea?
Lake Chad in Africa is another example of a massive lake that has nearly disappeared for the same reasons as the Aral Sea. Aral Sea and Lake Chad are the most extreme examples of large lakes destroyed by unsustainable diversions of river water.
Which lakes have shrunk?
Other lakes that have shrunk significantly due to human diversions of water include the Dead Sea in the Middle East, Lake Manchar in Pakistan, and Owens Lake and Mono Lake, both in California.
Is the Aral Sea dry?
The southern part of the Aral Sea has seen no relief and remains nearly completely dry. The destruction of the Aral Sea is one of the planet’s biggest environmental disasters and it is caused entirely by humans. Lake Chad in Africa is another example of a massive lake that has nearly disappeared for the same reasons as the Aral Sea.
What rivers feed the Aral Sea?
The two rivers that feed it are the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers, respectively reaching the Sea through the South and the North. The Soviet government decided in the 1960s to divert those rivers so that they could irrigate the desert region surrounding the Sea in order to favor agriculture rather than supply the Aral Sea basin.
Where is the Aral Sea?
The Aral Sea is situated in Central Asia, between the Southern part of Kazakhstan and Northern Uzbekistan. Up until the third quarter of the 20th century it was the world?s fourth largest saline lake, and contained 10grams of salt per liter. The two rivers that feed it are the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers, respectively reaching the Sea through the South and the North. The Soviet government decided in the 1960s to divert those rivers so that they could irrigate the desert region surrounding the Sea in order to favor agriculture rather than supply the Aral Sea basin. The reason why we decided to explore the implications up to today of this human alteration of the environment is precisely that certain characteristics of the region, from its geography to its population growth, account for dramatic consequences since the canals have been dug. Those consequences range from unexpected climate feedbacks to public health issues, affecting the lives of millions of people in and out of the region.
How does the Aral Sea get its water?
In normal conditions, the Aral Sea gets approximately one fifth of its water supply through rainfall, while the rest is delivered to it by the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers. Evaporation causes the water level to decrease by the same amount that flows into the Sea, making it sustainable as long as inflow is equal to evaporation on average.
What did the Soviet government do to the Aral Sea?
By establishing a program to promote agriculture and especially that of cotton, Soviet government led by Khrouchtchev in the 1950s deliberately deprived the Aral Sea of its two main sources of water income, which almost immediately led to less water arriving to the sea.
Why do small lakes in the Aral Sea have higher salinity?
Smaller lakes within the Aral Sea that have stopped being fed by river flows tend to have higher salinity due to evaporation, causing some or all fishes that either survived or had been reintroduced in the 1990s to die. Even re-watering those lakes does not compensate for the increased salinity over the years.
When did the water level in the Aral Sea decrease?
The water level in the Aral Sea started drastically decreasing from the 1960s onward.
How do dams affect salinity?
Dams also affect salinity, notably by reducing its variability with the seasons.
What is the importance of the Aral Sea?
The sea played an important role in the development of the region’s economy. Aral Sea was among the richest fishing ground in the world with annual catch of fish 30-35 thousand tonnes. More than 80 percent of inhabitants of the sea coast were engaged in production, processing and transportation of fish and fish products.
Where is the Aral Sea located?
Bilal Afridi. Aral Sea is located in Central Asia between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan, which serves as natural boundary of the two countries. It was the fourth largest inland lake in the world till 1960s. The major sour of filling the reservoir of the sea were two major rivers, Syr Darya and Amu Dasrya.
What was the purpose of the water flow in the 1960s?
In 1960s, government of former Soviet Union had decided to divert bulk of the water flow from Amu Darya and Syr Darya for irrigating the arid regions surrounding the Aral Sea for mainly growing cotton crop. The implementation of lopsided programme of agriculture development deprived Aral Sea from its two major sources of water inflow, ...
What are the two major rivers that fill the reservoir of the sea?
The major sour of filling the reservoir of the sea were two major rivers, Syr Darya and Amu Dasrya. Water from melting snow and glaciers on the southern Pamir Mountain in Tajikistan and the Tien Shan Mountain that border Kirgizstan and China are the contributory sources of water supply to these rivers.
What is the consequence of desiccation of the Aral Sea?
As a consequence of desiccation of Aral the Sea the unprecedented environmental change is felt not only in the Central Asia but other regions of the world as well. On the back part of the Aral Sea, a new salt desert with an area of 5.5 million hectare has appeared. Every year for 90 days dust storm rages over the salt desert ...
How much water was in the Aral Sea in 1998?
In 1998, water level dropped by 20 meters with a total volume of 210 cubic meters as compared to 1,063 cubic meters in 1960s. The Aral Sea region had a wide variety of flora and fauna with 38 species of fish and a number of species of rare animals that inhabited the sea basin.
Why did the Aral Sea have small lakes?
As the flow of water from rivers substantially decreased and the supply from rainfall was evaporating, small lakes appeared in the Aral Sea, which contained high density of salinity, confronting all types of fish and other creatures with survival threat. Even the reintroduced varieties of fish in 1990s could not survive.
Overview
Solution
Many different solutions to the problems have been suggested over the years, varying in feasibility and cost, including:
• Improving the quality of irrigation canals
• Using alternative cotton species that require less water
Formation
The Amu Darya river flowed into the Caspian Sea via the Uzboy channel until the Holocene. Geographer Nick Middleton believes it did not begin to flow into the Aral Sea until that time.
Ecology
Despite its former vast size, the Aral Sea had relatively low indigenous biodiversity. However, the Aral Sea basin had an exceptional array of endemic fish subspecies (as well as the three endemic sturgeon species). Most of these still survive in the North Aral Sea, but some, such as the sturgeons, have been decimated or even driven to extinction by the lake's shrinkage. Native fish spec…
History
Climate shifts have driven multiple phases of sea-level rise and fall. Inflow rates from the Amu Darya and Syr Darya are affected by glacial melt rates at the rivers' headwaters as well as precipitation within the river basins and cold, dry climates restrict both processes. Geologically driven shifts in the course of the Amu Darya between the Aral Sea and the Sarykamysh basins and anthropogen…
Impact on environment, economy, and public health
The Aral Sea is considered an example of ecosystem collapse. The ecosystems of the Aral Sea and the river deltas feeding into it have been nearly destroyed, largely because of the drastically higher salinity. The receding sea has left huge plains covered with salt and toxic chemicals from weapons testing, industrial projects, and pesticides and fertilizer runoff. Due to the shrinking water sourc…
Institutional bodies
The Interstate Commission for Water Coordination of Central Asia (ICWC) was formed on 18 February 1992 to formally unite Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan in the hopes of solving environmental, as well as socioeconomic problems in the Aral Sea region. The River Basin Organizations (the BVOs) of the Syr Darya and Amu Darya rivers were institutions called upon by the ICWC to help manage water resources. According to the ICWC, the main obje…
Vozrozhdeniya Island
Vozrozhdeniya (Russian for rebirth) Island is a former island of the Aral Sea or South Aral Sea. Due to the ongoing shrinkage of the Aral, it became first a peninsula in mid-2001 and finally part of the mainland. Other islands like Kokaral and Barsa-Kelmes shared a similar fate. Since the disappearance of the Southeast Aral in 2008, Vozrozhdeniya Island effectively no longer exists as a …
Contents
Location
- The Aral Sea, also known as Orol Dengizi (Uzbek) or Aral Tengizi (Kazakh) is a saline lake in Central Asia straddling the boundary between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan to the south and north. The lake once covered 68,000 square kilometers between the Kyzylorda and Aktobe regions in Kazakhstan and the Karakalpakstan region of Uzbekistan. The Caspian Seaon the west is the lak…
Geology and Formation
- The depression, later filled with water and became the Aral Sea, formed in the late Neogene Period, about 2.6 million years ago. During this period, the Amu Darya River, one of Aral’s main inlets, drained into the Caspian Sea. But some geographers, like Nick Middleton, believe the rivers started flowing into Aral in the current geological epoch (Ho...
Climate and Hydrology
- The Aral Sea is located within the harsh climate region of Central Asia. The area experiences a desert-continental climate, characterized by hot summers, cold winters, and varying diurnal air temperature. The Aral region receives sparse rainfall, with an average annual precipitation of 100 mm. Showers are frequent in autumn and spring. Northwesterly winds are common in winter an…
Brief History
- Desert nomads inhabited most of the areas around the lake. However, not much is known about them since they left few written records. Later, the Kwarazm of the Tang Dynasty occupied the Oxus delta in the south and established the Chinese western frontier in the region. Russian expedition, led by Alexey Butakov, conducted the first Aral Sea for exploration in 1848. Three yea…
The Diminishing Sea
- Before the 1960s, the Aral Sea had a maximum depth of 69 meters (western shores) and a surface area of 68,000 square kilometers. It has a maximum length of 435 kilometers from north to south and was 290 kilometers wide from west to east. However, the average depth was less than 16 meters. The northern shore had numerous bays and the eastern shore had a huge river …
Impact
- The disappearance of the Aral Sea did not surprise the Soviets since they expected it to happen at some point. However, not many people were prepared to deal with the environmental consequences that would follow. The lake’s rapid shrinkage has led to numerous problems in the region, chief of which is ecosystem collapse. The high mineral and salt content has made the w…
Restoration Strategies
- The Aral Sea's survival and future lie in the decisions made by five countries; Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Kyrgyzstan. The five countries adopted the Aral Sea Basin Program in 1994 as part of the restoration strategy. The program aimed to stabilize the basin’s environment, rehabilitate the areas around the sea, and improve the lake’s water management. T…