What is the function of sebaceous glands?
Sebaceous, or oil, glands, are attached to hair follicles and can be found everywhere on the body except for the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. These glands secrete oil that helps keep the skin smooth and supple.
Which layer of the skin protects the body from the environment?
The Epidermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin, and protects the body from the environment.
What makes the skin waterproof?
These fatty molecules can be found in between the outermost layer of skin known as the stratum corneum. This fatty structure makes it to where water cannot pass in either direction of the skin, essentially, making the skin waterproof and not just water resistant.
What is the function of the sweat glands?
Eccrine glands are the true sweat glands. Found over the entire body, these glands regulate body temperature by bringing water via the pores to the surface of the skin, where it evaporates and reduces skin temperature. These glands can produce up to two liters of sweat an hour, however, they secrete mostly water,...

Which of the following helps to waterproof the skin?
- 1 - the keratinocytes: compose most of the epidermis. They produce a protein: the keratin that helps waterproof the skin and that protects the skin and the underlying tissues from heat, microbes, abrasion and chemicals.
What protects the skin's surface?
The outer layer (epidermis) The outermost layer of skin which you can see is called the epidermis. It is mostly made up of cells that produce keratin (keratinocytes). These cells are gradually pushed to the surface of the skin by newer cells, where they harden and then eventually die off.
What gland protects skin from drying out?
Sebaceous glandsSebaceous glands are oil producing glands which help inhibit bacteria, keep us waterproof and prevent our hair and skin from drying out.
What protein makes the skin tough and waterproof?
Keratinocytes produce keratin, a tough, protective protein that makes up the majority of the structure of the skin, hair, and nails. The squamous cell layer is the thickest layer of the epidermis, and is involved in the transfer of certain substances in and out of the body.
What is the function of dermis?
The dermis is a fibrous structure composed of collagen, elastic tissue, and other extracellular components that includes vasculature, nerve endings, hair follicles, and glands. The role of the dermis is to support and protect the skin and deeper layers, assist in thermoregulation, and aid in sensation.
What is the sebaceous gland responsible for?
The normal function of sebaceous glands is to produce and secrete sebum, a group of complex oils including triglycerides and fatty acid breakdown products, wax esters, squalene, cholesterol esters and cholesterol. Sebum lubricates the skin to protect against friction and makes it more impervious to moisture.
What are sebaceous glands also known as?
Sebaceous glands are the oil secreting glands of your body. This is why they are also called the oil glands. They are a type of holocrine simple saccular (alveolar) gland. Their function is to secrete a substance called sebum, a mixture of fatty substances, entire sebum-producing cells, and epithelial cell debris.
What does the sweat gland do?
The primary function of sweat glands is to keep the core body temperature at approximately 37 °C by releasing sweat in a hot environment or during physical activity [189,195]. Sweat glands are innervated by neurons, so the process of sweating is controlled by the central nervous system.
What does the skin protect against quizlet?
The skin protects against abrasion and ultraviolet light. It also keeps microorganisms from entering the body and prevents dehydration by reducing water loss from the body. Sensation. The integumentary system has sensory receptors that can detect heat, cold, touch, pressure, and pain.
How does the epidermis protect the body?
The epidermis acts as a barrier that protects the body from ultraviolet (UV) radiation, harmful chemicals, and pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Historically, it was thought that the function of the epidermis was to regulate fluid and protect the body from mechanical injury.
How can you protect your integumentary system?
Cover your skin with tightly woven long-sleeved shirts, long pants and wide-brimmed hats. Also consider laundry additives, which give clothing an additional layer of ultraviolet protection for a certain number of washings, or special sun-protective clothing — which is specifically designed to block ultraviolet rays.
How does the skin protect us from infection?
Skin is a barrier that serves as one of the body's first lines of defense against harmful microbes. Specialized immune cells within skin tissue help to fight invading organisms. Yet the skin hosts diverse communities of beneficial bacteria, collectively known as the skin microbiota.
What glands excrete lipids?
The sebaceous glands excrete lipids by disintegration of entire cells, a process known as holocrine secretion. Human sebum, as it leaves the sebaceous gland , contains squalene, cholesterol, cholesterol esters, wax esters, and triglycerides.
What is a sebaceous gland?
AT-A-GLANCE. Sebaceous glands are multilobular structures that consist of acini connected to a common excretory duct and are usually associated with a hair follicle. Sebaceous glands vary considerably in size, even in the same individual and in the same anatomic area.
What are the two parts of the skin that release biochemical products?
INTRODUCTION. The human skin has several types of exocrine glands (Latin, glandulae cutis ), which release their biochemical products onto the skin surface. All skin glands consist by a secretory compartment, the gland or coil (tubulus), and an excretory part, the duct (ductus).
What are the three major types of skin glands?
Three major types of skin glands are recognized according to their product, the excretory function, and the location, where the excretory ducts release their products (diseases of these glands are listed in Table 6-1 ). Regarding their product, skin glands are classified into glands secreting sebum (sebaceous glands) and sweat (sweat glands).
What are the molecules that regulate the sebaceous gland?
Sebaceous glands are regulated by several molecules, among them androgens and retinoids.
Where do sweat glands release their products?
Regarding the location where their ducts release their product, the ducts of sebaceous glands, in most cases, and apocrine sweat glands excrete their products into the hair follicle canal, and the eccrine sweat glands excrete directly onto the skin surface.
What is the middle layer of the skin?
The dermis is the middle layer of the three layers of skin. It's located between the epidermis and the subcutaneous tissue. It contains connective tissue, blood capillaries, oil and sweat glands, nerve endings, and hair follicles.
What is the outermost layer of the epidermis?
Stratum corneum: This is the outermost or top layer of the epidermis. It's made of dead, flat keratinocytes that shed approximately every two weeks. The epidermis contains three specialized cells: Langerhans cells that act as the first line of defense in the skin's immune system.
What are the three types of cells in the epidermis?
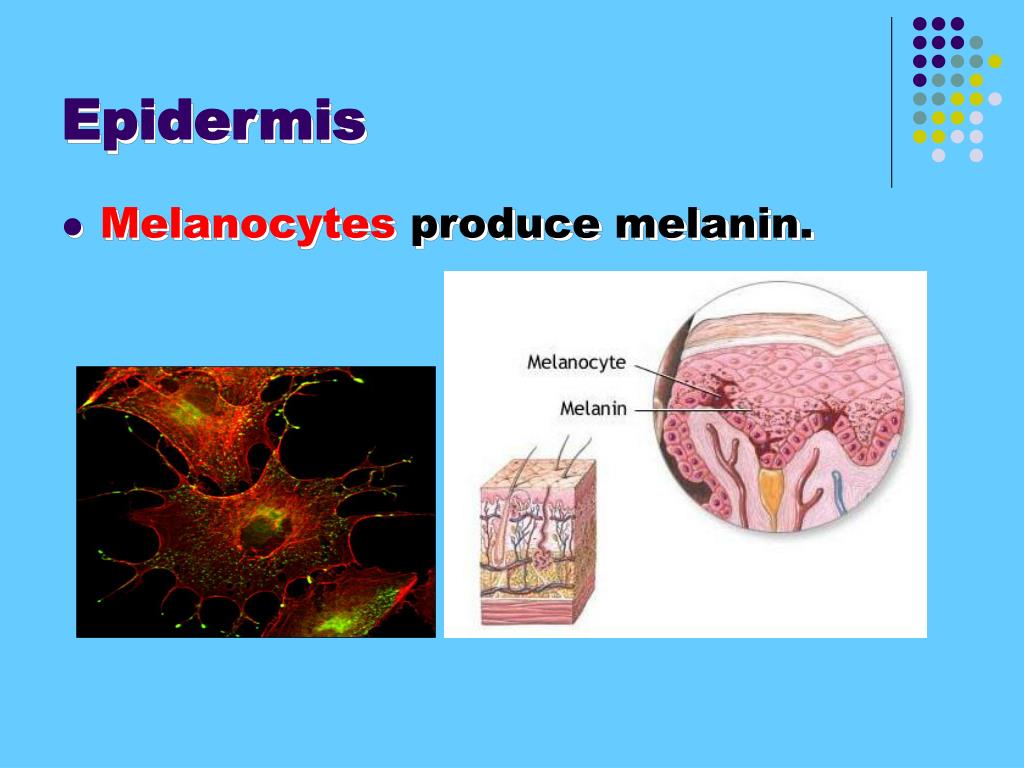
The epidermis contains three specialized cells: 1 Melanocytes that produce pigment (melanin) 2 Langerhans cells that act as the first line of defense in the skin's immune system 3 Merkel cells that have a function that is not yet fully understood. 4
How far down do tattoo needles go?
Tattoo needles penetrate the epidermis and place ink into the dermis, about 2 millimeters below the skin’s topmost layer. 10 Injecting the pigment this deeply prevents the ink from wearing away so it can remain permanently visible. Understanding the Subcutaneous Tissue.
How many layers of the epidermis are there?
There are five layers of the epidermis: 2 . Stratum basale: This bottom layer, which is also known as the basal cell layer, has column-shaped basal cells that divide and push older cells toward the surface of the skin. As the cells move up through the skin, they flatten and eventually die and shed. Stratum spinosum: This layer, which is also known ...
What is the role of subcutaneous tissue in body temperature?
It also acts as a cushion, so if you ever fall or hit something with your body, it protects your insides and makes the injury hurt less.
What are the two layers of the dermis?
The dermis is split into two parts—the papillary dermis, which is the thin, upper layer, and the reticular dermis, which is the thick, lower layer. 5
What is the function of skin?
Pathogens are more commonly known as germs. The skin is the largest organ in the body. So, it has many functions. These functions include body temperature regulations, waterproof protection, and skin tone creation.
Why is skin water resistant?
Your skin is designed to specifically keep water out, not to keep it in. This is why regardless of how much it rains or how soaked your clothes get; your skin will always prevent the water from entering your body.
What makes skin impermeable?
An arrangement of fatty bilayer lipid molecules makes the skin impermeable. These fatty molecules can be found in between the outermost layer of skin known as the stratum corneum. This fatty structure makes it to where water cannot pass in either direction of the skin, essentially, making the skin waterproof and not just water resistant.
What is the substance that is made up of a mixture of cell debris and fats?
Sebaceous glands are generally attached to the follicles of the hair. These glands generate a substance known as sebum, which is made up of a mixture of cell debris and fats. Sebum has a greasy texture, which is utilized to keep skin hydrated and flexible.
What are the three layers of the skin?
There are three main layers of the skin – epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous (adipose) tissue. The only part of the skin that is not waterproof or water resistant is the pores.
Why does my skin keep getting waterlogged?
This is because your skin absorbed so much water. It’s the fact that your skin was specifically made to hold in water in the right amounts, while also keeping it out, this prevents you from becoming waterlogged after sitting in water for hours on in.
Why is my skin pruned up?
If you have ever spent a long time in the pool, ocean, or bathtub, you probably noticed that when you got out your skin was all pruned up. This is because your skin absorbed so much water.
What are the layers of the epidermis?
The epidermis is composed of five sublayers: 1 Stratum corneum: The top layer of dead, extremely flat cells. Cell nuclei are not visible. 2 Stratum lucidum: A thin, flattened layer of dead cells. Not visible in thin skin. 3 Stratum granulosum: A layer of rectangular cells that become increasingly flattened as they move to the surface of the epidermis. 4 Stratum spinosum: A layer of polyhedral-shaped cells that flatten as they get closer to the stratum granulosum. 5 Stratum basale: The innermost layer of elongated column-shaped cells. It consists of basal cells that produce new skin cells.
What is the innermost layer of the epidermis?
The innermost layer of the epidermis contains keratinocytes called basal cells. These cells constantly divide to produce new cells that are pushed upward to the layers above. Basal cells become new keratinocytes, which replace the older ones that die and are shed. Within the basal layer are melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanin is a pigment that helps protect the skin from harmful ultraviolet solar radiation by giving it a brown hue. Also found in the basal layer of the skin are touch receptor cells called Merkel cells.
What is the cell that is shed and replaced by cells from beneath?
Keratinocytes on the surface of the epidermis are dead and are continually shed and replaced by cells from beneath. This layer also contains specialized cells called Langerhans cells that signal to the immune system when there is an infection. This aids in the development of antigen immunity.
What is the body's first line of defense against bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens?
The integumentary system is the body's first line of defense against bacteria , viruses, and other pathogens. It also helps provide protection from harmful ultraviolet radiation. The skin is a sensory organ, too, with receptors for detecting heat and cold, touch, pressure, and pain.
What is the outermost layer of the skin?
The outermost layer of the skin, composed of epithelial tissue , is known as the epidermis. It contains squamous cells, or keratinocytes, which synthesize a tough protein called keratin. Keratin is a major component of skin, hair, and nails. Keratinocytes on the surface of the epidermis are dead and are continually shed and replaced by cells from beneath. This layer also contains specialized cells called Langerhans cells that signal to the immune system when there is an infection. This aids in the development of antigen immunity.
What is the pigment that protects skin from ultraviolet radiation?
Melanin is a pigment that helps protect the skin from harmful ultraviolet solar radiation by giving it a brown hue. Also found in the basal layer of the skin are touch receptor cells called Merkel cells. The epidermis is composed of five sublayers: Stratum corneum: The top layer of dead, extremely flat cells.
What are the components of the dermis?
Components of the dermis include: Blood vessels: Transport oxygen and nutrients to the skin and remove waste products. These vessels also transport vitamin D from the skin to the body. Lymph vessels : Supply lymph (milky fluid containing white blood cells of the immune system) to skin tissue to fight microbes.
What is the epidermis made of?
The epidermis contains the melanocytes (the cells in which melanoma develops), the Langerhans' cells ( involved in the immune system in the skin), Merkel cells and sensory nerves. The epidermis layer itself is made up of five sublayers that work together to continually rebuild the surface of the skin:
What is the process of keratinocytes moving up the skin?
This process results in the cells fusing together into layers of tough, durable material, which continue to migrate up to the surface of the skin.
How long does it take for the stratum corneum to slough off?
Complete cell turnover occurs every 28 to 30 days in young adults, while the same process takes 45 to 50 days in elderly adults.
What is the squamous layer?
The squamous cell layer is located above the basal layer, and is also known as the stratum spinosum or "spiny layer" due to the fact that the cells are held together with spiny projections. Within this layer are the basal cells that have been pushed upward, however these maturing cells are now called squamous cells, or keratinocytes. Keratinocytes produce keratin, a tough, protective protein that makes up the majority of the structure of the skin, hair, and nails.
What is the function of the dermis?
The main functions of the dermis are to regulate temperature and to supply the epidermis with nutrient -saturated blood.
What is the outermost layer of the skin?
The Epidermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin, and protects the body from the environment. The thickness of the epidermis varies in different types of skin; it is only .05 mm thick on the eyelids, and is 1.5 mm thick on the palms and the soles of the feet. The epidermis contains the melanocytes (the cells in which melanoma ...
Why do melanocytes produce freckles?
Sun exposure causes melanocytes to increase production of melanin in order to protect the skin from damaging ultraviolet rays, producing a suntan. Patches of melanin in the skin cause birthmarks, freckles and age spots. Melanoma develops when melanocytes undergo malignant transformation. Merkel cells, which are tactile cells ...
How many layers of skin are there?
The skin has three layers. Beneath the surface of the skin are nerves, nerve endings, glands, hair follicles, and blood vessels. Sweat is produced by glands in the dermis and reaches the surface of the skin through tiny ducts.
Why does sweat make your body smell?
As sweat evaporates off the skin, it helps cool the body. Specialized sweat glands in the armpits and the genital region (apocrine sweat glands) secrete a thick, oily sweat that produces a characteristic body odor when the sweat is digested by the skin bacteria in those areas.
Why do sweat glands produce sweat?
The sweat glands produce sweat in response to heat and stress. Sweat is composed of water, salt, and other chemicals. As sweat evaporates off the skin, it helps cool the body. Specialized sweat glands in the armpits and the genital region (apocrine sweat glands) secrete a thick, oily sweat that produces a characteristic body odor when the sweat is digested by the skin bacteria in those areas.
How does the dermis help the body?
The blood vessels of the dermis provide nutrients to the skin and help regulate body temperature. Heat makes the blood vessels enlarge (dilate), allowing large amounts of blood to circulate near the skin surface, where the heat can be released. Cold makes the blood vessels narrow (constrict), retaining the body's heat.
What is the epidermis?
The epidermis is the relatively thin, tough, outer layer of the skin. Most of the cells in the epidermis are keratinocytes. They originate from cells in the deepest layer of the epidermis called the basal layer. New keratinocytes slowly migrate up toward the surface of the epidermis.
What is the function of melanin?
Melanin's primary function, however, is to filter out ultraviolet radiation from sunlight (see Overview of Sunlight and Skin Damage ), which damages DNA, resulting in numerous harmful effects, including skin cancer .
What is the role of skin in vitamin D synthesis?
The skin keeps vital chemicals and nutrients in the body while providing a barrier against dangerous substances from entering the body and provides a shield from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation emitted by the sun. In addition, skin color, texture, and folds (see Descriptions of Skin Marks, Growths, ...