What are 4 similarities between mitosis and meiosis?
- Mitosis and meiosis take place in the cell nuclei.
- Both involve cell division.
- Both the processes occur in the M-phase of the cell cycle.
- In both cycles, the stages are common – metaphase, anaphase, telophase and prophase.
- Synthesis of DNA occurs in both.
Full Answer
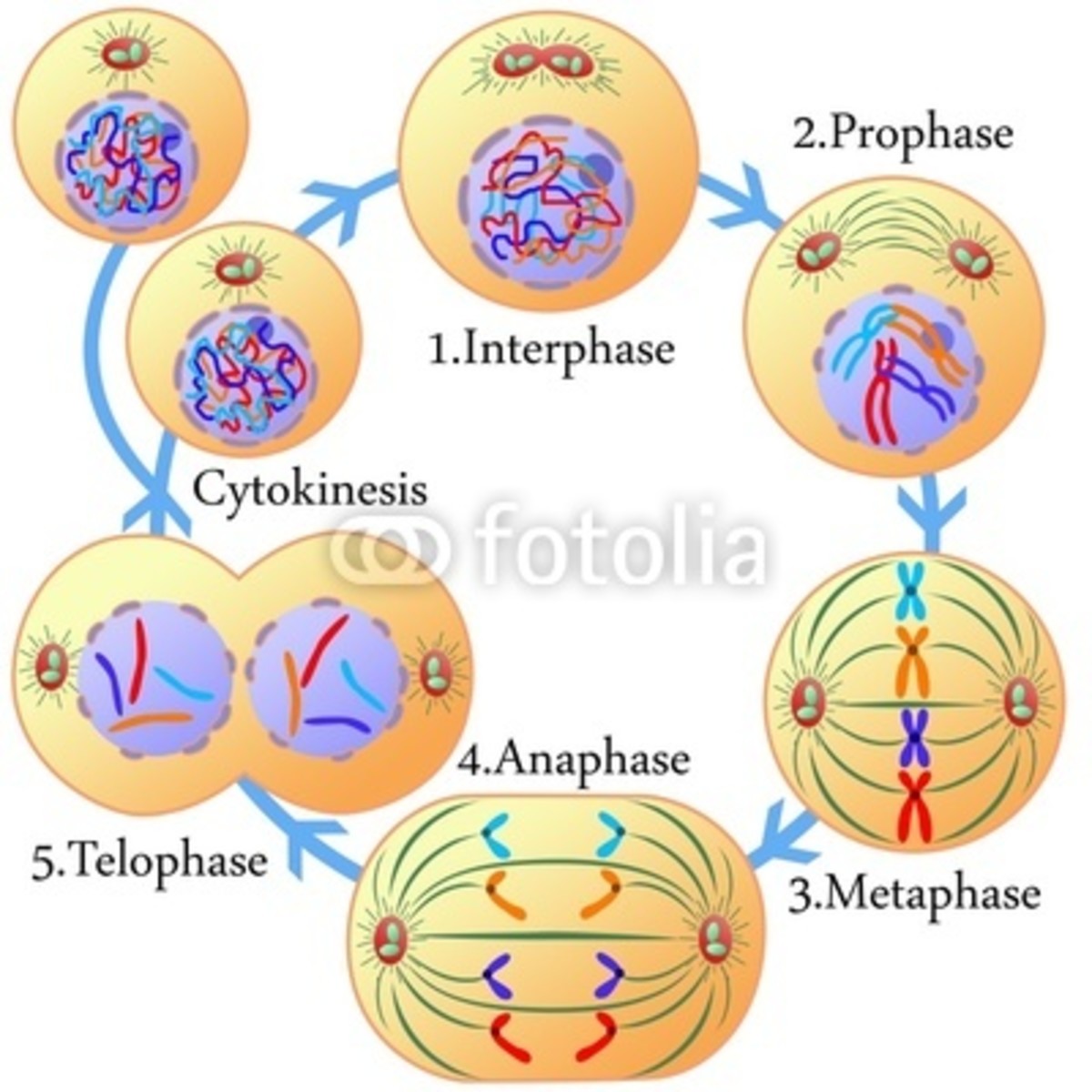
What are the 7 stages of mitosis in order?
What are the 7 stages of mitosis in order?
- Interphase. Cell performs normal functions, Cell growth (G1 and g2), Synthesizes new molecules and organelles.
- Prophase.
- Prometaphase.
- Metaphase.
- Anaphase.
- Telophase.
- Cytokinesis.
What are the stages of meiosis 1 and 2?
- Prophase I. The chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase I. Pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase I.
- Telophase I and Cytokinesis.
- Prophase II.
- Metaphase II.
- Anaphase II.
- Telophase II and Cytokinesis.
What are the similarities and differences between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two cells from one parent using one division event. But meiosis produces four new child cells with two divisions, each of which has half the genetic material of its parent. Mitosis takes place all over the body, while meiosis only takes place in the sex organs and produces sex cells.
What are the two divisions of meiosis?
Overview of the Stages of Meiosis
- Interphase. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: meiosis I and meiosis II. ...
- Prophase I. Chromosomes condense and attach to the nuclear envelope. ...
- Metaphase I. Tetrads align at the metaphase plate. ...
- Anaphase I. Chromosomes move to the opposite cell poles. ...
- Telophase I. ...
- Prophase II. ...
- Metaphase II. ...
- Anaphase II. ...
- Telophase II. ...
- Stages of Meiosis: Daughter Cells. ...

How many steps are there in meiosis?
Meiosis includes two steps of division, compared to the single step of Mitosis. During the process of meiosis,the number of chromosomes is reduced by half, while in mitosis, they remain the same. Also, mitosis produces 2 diploid cells, while meiosis produces 4 haploid cells.
How many chromosomes are processed in meiosis 2?
Actually, meiosis 2 is just like mitosis except the chromosome number is half of the original cell. For humans, that would be 23 chromosomes are processed where the duplicates are separated.
When does crossing over occur in meiosis?
In meiosis, crossing over occurs during (the pachytene stage of) prophase I. Here, corresponding regions of NON -sister chromosomes get exchanged. so after crossing over has occurred, the sister chromatids are no longer identical.
Why do sister chromatids always start off identical?
Sister chromatids always start off identical, because they result from DNA replication; the DNA of both of the two sister chromatids is identical to the DNA molecule that was replicated, and so the two chromatids are also identical to each other.
Why are sister chromatids not identical in meiosis?
In mitosis, sister chromatids are identical. In meiosis, they are not identical because crossing over has occurred.
Which phase do homologous chromosomes separate?
2) In anaphase, homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis I, not sister chromatids.
Can crossing over occur during mitosis?
PS: Crossing over can occur during mitosis, but that is the exception, not the rule. Also, crossing over can sometimes not occur during meiosis, but that is the exception, not the rule. Also, crossing over can occur between sister chromatids (called SCE, for sister chromatid exchange), but since they are identical, there is no meaningful difference after crossing over.
How are mitosis and meiosis similar?
Although mitosis and meiosis have very different results, the processes are similar, with just a few changes within the stages of each. Both processes start out after a cell goes through interphase and copies its DNA exactly in the synthesis phase, or S phase. At this point, each chromosome is made up of sister chromatids held together by a centromere. The sister chromatids are identical to each other. During mitosis, the cell undergoes the mitotic phase, or M phase, only once, ending with two identical diploid cells. In meiosis, there are two rounds of the M phase, resulting in four haploid cells that aren't identical.
What is the first stage of mitosis?
The first stage is called prophase in mitosis and prophase I or prophase II in meiosis I and meiosis II. During prophase, the nucleus is getting ready to divide. This means the nuclear envelope has to disappear and the chromosomes start to condense. Also, the spindle starts to form within the centriole of the cell that will help with the division of chromosomes during a later stage. These things all happen in mitotic prophase , prophase I and usually in prophase II. Sometimes there is no nuclear envelope at the beginning of prophase II and most of the time the chromosomes are already condensed from meiosis I.
What is the final stage of telophase?
The final stage is called telophase. In mitotic telophase and telophase II, most of what was done during prophase will be undone. The spindle begins to break down and disappear, a nuclear envelope begins to reappear, chromosomes start to unravel, and the cell prepares to split during cytokinesis. At this point, mitotic telophase will go into cytokinesis that will create two identical diploid cells. Telophase II has already gone one division at the end of meiosis I, so it will go into cytokinesis to make a total of four haploid cells.
Why do sister chromatids cross over?
Actual pieces of one of the sister chromatids break off and reattach to the other homolog. The purpose of crossing over is to further increase genetic diversity, since alleles for those genes are now on different chromosomes and can be placed into different gametes at the end of meiosis II.
How many identical cells are there in the M phase?
The sister chromatids are identical to each other. During mitosis, the cell undergoes the mitotic phase, or M phase, only once, ending with two identical diploid cells. In meiosis, there are two rounds of the M phase, resulting in four haploid cells that aren't identical.
What is the process of dividing a somatic cell into two identical diploid cells?
Updated August 11, 2019. Mitosis (along with the step of cytokinesis) is the process of how a eukaryotic somatic cell, or body cell, divides into two identical diploid cells. Meiosis is a different type of cell division that begins with one cell that has the proper number of chromosomes and ends with four cells—haploid cells—that have half ...
How does metaphase affect chromosomes?
Since the spindles attached at the centromere on both sides of the same chromosome during metaphase, it essentially rips apart the chromosome into two individual chromatids. Mitotic anaphase pulls apart the identical sister chromatids, so identical genetics will be in each cell.
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis involves the replication of somatic cells (i.e. any cells of the body that aren’t gametes), whereas meiosis is the process by which sperm and egg cells are produced.
What are Mitosis and Meiosis?
Mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division. Though there are similarities between mitosis and meiosis, there are some key differences between these two processes.
What is the process of cell division?
Mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division. Mitosis is the process by which most cells in the body divide, involves a single round of cell division, and produces two identical, diploid daughter cells.
How many cells are involved in meiosis II?
Meiosis II is very similar to the process of mitosis, except it involves two haploid cells rather than one diploid cell.
What type of cell divides in meiosis?
Meiosis. Almost all of your body’s cells divide by mitosis. Meiosis is used to produce only one type of cell, and those are the gametes. During meiosis, a diploid cell divides to produce four, non-identical haploid daughter cells, each containing a single set of chromosomes. In humans, these are sperm and egg cells.
What is the process of mitosis?
Mitosis is how the cells of your body reproduce. During mitosis, a diploid parent cell (i.e. a cell with two sets of chromosomes) makes a complete copy of its DNA before splitting in two. This process produces two genetically identical daughter cells and takes place across five phases. The phases of mitosis are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, ...
How many stages of meiosis are there?
These happen across two stages: Meiosis I, and Meiosis II. Each stage of meiosis can be further divided into five phases: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Egg and sperm cells.

Both Undergo Similar Processes
Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis
- There are four stages of mitosisand eight stages in meiosis. Since meiosis undergoes two rounds of splitting, it is divided into meiosis I and meiosis II. Each stage of mitosis and meiosis has many changes going on in the cell, but very similar, if not identical, important events mark that stage. Comparing mitosis and meiosis is fairly easy if thes...
Mitosis and Meiosis in Evolution
- Most of the time, mutations in the DNA of somatic cells that undergo mitosis will not be passed down to the offspring and therefore are not applicable to natural selection and do not contribute to the evolutionof the species. However, mistakes in meiosis and the random mixing of genes and chromosomes throughout the process contribute to genetic diversity and drive evolution. Crossi…