Full Answer
What is the structure of the peripheral nervous system Quizlet?
Structure. The peripheral nervous system is itself classified into two systems: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. Each system contains afferent and efferent components. The afferent arm consists of sensory (or afferent) neurons running from receptors for stimuli to the CNS.
What is the difference between the Central and peripheral nervous system?
The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system includes all of the nerves that branch out from the brain and spinal cord and extend to other parts of the body including muscles and organs.
What are the sensory receptors of the peripheral nervous system?
The PNS includes all neural structures outside of the brain and spinal cord—that is, the sensory receptors, peripheral nerves and their associated ganglia, and efferent motor endings. Match the following sensory receptors to the stimuli they detect. 1) Mechanoreceptors - C) stretch 2) Thermoreceptors - A) temperature
What is the difference between peripheral and CNS nerve axons?
Unlike axons of peripheral nerves, axons of CNS (brain and spinal cord) neurons do not regenerate following injury. Thus, damage to the brain or spinal cord is typically considered irreversible. A nerve that carries autonomic signals away from the central nervous system is classified as a __________.

Which structure is not a part of the peripheral nervous system?
Answer and Explanation: The b. brain is NOT a part of the peripheral nervous system. The brain, brain stem and spinal cord are all components of the central nervous system...
Which type of muscle is not dependent on the nervous system?
Cardiac (heart) muscleThe Nervous System The body is now in a state of paralysis. This is known as quadriplegia. The only organ that is not directly dependent upon the nervous system is the Cardiac (heart) muscle.
Which of the following is not part of the peripheral nervous system quizlet?
Which of the following is NOT part of the peripheral nervous system? spinal cord The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system, not the peripheral.
Which structures are connected to the peripheral nervous system?
The PNS is made up of cranial nerves that connect directly with the brain and spinal nerves that connect with the spinal cord.
Which muscle is not under direct control of nervous system?
Solution : The activities of the visceral muscles are not under the voluntary control of the nervous system and are therefore known as involuntary muscles.
Is skeletal muscle controlled by the autonomic nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is divided into the somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Skeletal muscles are controlled by the SNS, while cardiac and smooth muscles are controlled by the ANS.
What is not part of the nervous system?
Intermedin regulates skin pigmentation. On the other hand, Cyton and axon are the parts of a nerve cell (or neuron), and myelin is a fatty substance surrounding neurons. Hence all three cytons, axons, and myelin are the part of the nervous system & intermedin is not a part of nervous system.
Which of the following is are not part of the central nervous system?
Neuronal cell body of a sensory afferent is not part of the central nervous system.
What is not part of the central nervous system?
The cerebrum is responsible for processing information and higher thought. These structures are also part of the central nervous system. The cranial nerves attach directly to the spinal cord, but branch out into the periphery. They are not considered part of the central nervous system.
What are the 3 parts of the peripheral nervous system?
Nerves In the Peripheral Nervous System Sensory: Connects the brain and spinal cord to your skin and allow you to feel pain and other sensations. Autonomic: Controls involuntary function (e.g., blood pressure, digestion, heart rate). Motor: Connects the brain and spinal cord to muscles to stimulate movement.
Which of the following is not a function of the central nervous system CNS )?
Nervous system cellsQuestionAnswerInterneurons reside in the:CNS only.Which of the following is not a function of the central nervous system (CNS)?Integrating sensory information, Evaluating the information, and Initiating an outgoing responseNerves that contain mostly afferent fibers are called _____ nerves.Sensory27 more rows
Is the cerebellum part of the peripheral nervous system?
Traditionally, the nervous system is divided into central and peripheral components. The brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem) and spinal cord form the central nervous system (CNS). The peripheral nervous system (PNS) connects the CNS to the different tissues and organs of the body.
Which neuron is responsible for transferring information from the brain to the muscles?
Sensory neurons carry stimuli information to the brain; motor neurons carry processed information to muscles and glands. Sensory neurons carry stimuli information to the brain; motor neurons carry processed information to muscles and glands. sympathetic nervous system.
When did scientists believe that new neurons could not be generated in adult brains?
Read the passage below. Prior to the 1970s, scientists believed that new neurons could not be generated in adult brains. In the 1970s, Dr. Goldman and Dr. Nottbohm discovered that hormones injected in adult songbirds could cause female songbirds to develop new neurons.
What are the two parts of the peripheral nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system itself is divided into two parts: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system . Each of these components plays a critical role in how the peripheral nervous system operates.
Which part of the nervous system controls involuntary body functions?
The autonomic system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that's responsible for regulating involuntary body functions, such as blood flow, heartbeat, digestion, and breathing. In other words, it is the autonomic system that controls aspects of the body that are usually not under voluntary control. This system allows these functions ...
What is the somatic system?
The somatic system is the part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for carrying sensory and motor information to and from the central nervous system. The somatic nervous system derives its name from the Greek word soma, which means "body."
What are the two types of somatic neurons?
The somatic system is responsible for transmitting sensory information as well as for voluntary movement. This system contains two major types of neurons: 1 Motor neurons: Also called efferent neurons, motor neurons carry information from the brain and spinal cord to muscle fibers throughout the body. These motor neurons allow us to take physical action in response to stimuli in the environment. 2 Sensory neurons: Also called afferent neurons, sensory neurons carry information from the nerves to the central nervous system. It is these sensory neurons that allow us to take in sensory information and send it to the brain and spinal cord.
Which neuron is responsible for transferring sensory information from the brain to the spinal cord?
These motor neurons allow us to take physical action in response to stimuli in the environment. Sensory neurons: Also called afferent neurons, sensory neurons carry information from the nerves to the central nervous system. It is these sensory neurons that allow us to take in sensory information and send it to the brain and spinal cord.
Which part of the nervous system is responsible for communicating information?
The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system includes all of the nerves that branch out from the brain and spinal cord and extend to other parts of the body including muscles and organs. Each part of the system plays a vital role in how information is communicated throughout the body.
Which system is responsible for transmitting sensory information as well as for voluntary movement?
The somatic system is responsible for transmitting sensory information as well as for voluntary movement. This system contains two major types of neurons: Motor neurons: Also called efferent neurons, motor neurons carry information from the brain and spinal cord to muscle fibers throughout the body. These motor neurons allow us to take physical ...
What is the peripheral nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of all the nerves branching out of the brain and spinal cord ( the central nervous system, CNS). If you imagine the CNS as the main highway, then the PNS forms all the connecting secondary roads. These allow electrical impulses to travel to and from the furthest regions, or periphery, of the human body.
How many pairs of peripheral nerves are there?
The second set of peripheral nerves are spinal nerves, of which there are 31 pairs: eight cervical, twelve thoracic, five lumbar, five sacral, and one coccygeal. Their numbering relates to the vertebral column exit level; cervical spinal nerves are numbered according to the vertebra located below, while all the rest according to the vertebra situated above.
What nerves branch out after spinal nerve division?
Immediately after the division of the spinal nerve into the two rami, smaller communicating fibers branch out. These white and grey rami communicantes establish a connection between spinal nerves and the two sympathetic trunks of the autonomic nervous system that run along the length of the vertebral column.
What are the two main types of nerves?
There are two main types; spinal nerves and cranial nerves. Functionally, the PNS can be divided into the autonomic and somatic nervous systems. Both of these can be further subdivided; the former into sympathetic and parasympathetic arms and the latter into sensory and motor divisions.
What nerves innervate the head and neck?
Cranial nerves. Cranial nerves are peripheral nerves that mainly innervate anatomical structures of the head and neck. The exception to this is the vagus nerve, which also innervates various thoracic and abdominal organs. Cranial nerves originate from specific nuclei located in the brain.
Which nerves help you to pull away your hand when touching a hot object?
This helps you to instantly pull away your hand when touching a hot object. Both cranial and spinal nerves contribute to the somatic nervous system. Cranial nerves provide voluntary motor control and sensation to the head and face. Spinal nerves, as we mentioned previously, supply the trunk and limbs.
Where do the preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nerves travel?
The preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nerves leave the spinal cord through the T1 to L2 anterior roots, entering the corresponding spinal nerve. The fibers then travel through the white rami communicantes to paravertebral ganglia of the sympathetic trunks, located on either side of the vertebral column.
What are the two systems of the peripheral nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system is itself classified into two systems: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. Each system contains afferent and efferent components.
Where is the nervous system located?
This nervous system is embedded within the lining of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract so it can directly control the functions of the GI tract. It consists of two plexuses: Myenteric plexus. Located between the inner and outer layers of muscularis externa.
What is the PNS?
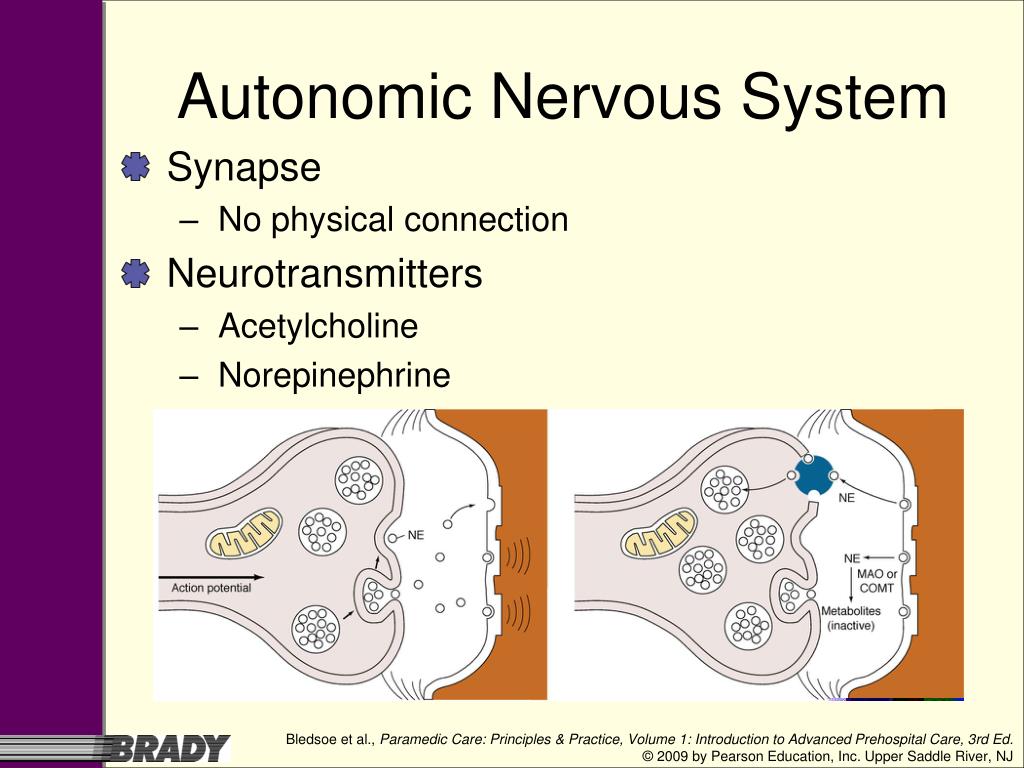
The PNS responsible for the rest and digest actions of the body and originates from craniosacral segments of the spinal cord. This system consists of long preganglionic neurones and short post ganglionic neurones. Both preganglion and postganglionic neurones use the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
What is the SNS and PNS?
The SNS and PNS are sub-divisions of the autonomic nervous system. The SNS is responsible for the fight or flight responses of the body and originates from thoracolumbar segments of the spinal cord. It uses short preganglionic neurones and long post ganglionic neurones.
What nerves detect external stimuli?
Afferent nerves detect the external environment via receptors for external stimuli such as sight, hearing, pressure, temperature etc. Afferent nerves exist in both the somatic and autonomic nervous systems as both can use sensory signals to alter their activity.
Which nerves control the visceral function of the body?
The efferent nerves of the autonomic (visceral) nervous system control the visceral functions of the body.
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is classified into the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord, leaving everything else in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What is the peripheral nervous system made of?
The peripheral nervous system is made up of thick bundles of axons, called nerves, carrying messages back and forth between the CNS and the muscles, organs, and senses in the periphery of the body (i.e., everything outside the CNS).
What are the two parts of the nervous system?
The nervous system of the body is split into two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made up of the brain and the spinal cord components. The PNS is all the nerves that branch out from the CNS components and extend to other parts of the body – to the sense organs, muscles, and glands.
What are the two parts of the PNS?
Parts of the PNS. The PNS can be divided into two components: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are both part of the peripheral nervous system. The SNS controls voluntary actions such as walking. The ANS is responsible for the control ...
How does the brain send signals to the muscles?
The brain can then send signals through the nerves to the muscles, resulting in the muscles to move in response. Therefore, there is always a stream of incoming and outgoing information between the PNS, CNS, and the body through the form of nerve impulses.
Which nerves carry signals from receptors around the body to the spinal cord?
The spinal nerves carry signals from receptors around the body to the spinal cord.
What are the functions of the PNS?
The main functions of the PNS are voluntary movements such as chewing food, walking, and facial expressions . The PNS also regulates autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and digesting – the unconscious bodily behaviors. The PNS is thus especially important for humans to survive.
What is the function of nerve cells?
The nerve cells (or neurons) are the information processing units of the brain that are responsible for sending, receiving, and transmitting signals throughout the body. The neurons are essentially the cells which make up the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The structure of neurons allows it to receive ...
Which nerve is responsible for pinching?
median nerve. The pinching motion that is important for picking up small objects is highly dependent upon the median nerve. The median nerve descends through the arm to the anterior forearm. It then branches off to innervate the skin and flexor muscles of this region.
What is the difference between a visceral and efferent nerve?
visceral efferent. Visceral refers to autonomic nervous system fibers. Afferent (sensory) means toward the CNS, while efferent (motor) means away from the CNS. Thus, a nerve that carries autonomic signals away from the CNS is classified as a visceral efferent nerve.
What is the PNS?
The PNS includes all neural structures outside of the brain and spinal cord—that is, the sensory receptors, peripheral nerves and their associated ganglia, and efferent motor endings. Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆. Match the following sensory receptors to the stimuli they detect.
What do proprioceptors do?
Proprioceptors advise the brain of our body movements by monitoring how much the organs containing these receptors (skeletal muscles, tendons, joints, and ligaments and in connective tissue coverings of bones and muscles) are stretched.
Which receptors are fast adapting?
Many sensory receptors exhibit adaptation. Adaptation is a change in sensitivity (and nerve impulse generation) in response to a constant stimulus. Phasic receptors are fast-adapting receptors. Tonic receptors provide a sustained response with little or no adaptation.
Do axons of the central nervous system regenerate?
Most central nervous system axons are able to regenerate following injury. Unlike axons of peripheral nerves, axons of CNS (brain and spinal cord) neurons do not regenerate following injury.
Which system regulates the body's physiological functions?
The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary responses that are essential for maintaining normal physiological functions and homeostasis, such as heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, peristalsis, urinary bladder muscle control, pupil dilation/constriction, and salivary gland secretion. The autonomic nervous system within the gastrointestinal system is also called the enteric nervous system and regulates peristalsis. The autonomic nervous system is always active but depending on the physiological state of the animal either the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system dominates.
Which nerves are involved in sensory and somatosensory information?
The somatic nervous system includes sensory and somatosensory nerves, as well as some that have both functions. Cranial nerves provide somatosensory information. There are twelve cranial nerves, of which 10 originate from the brain stem. The vagal nerve (CN X) receives sensory information as well from the thorax and abdomen.
What are the components of the PNS?
General components of the PNS are: 1 Ganglia, sensory (or also called dorsal root ganglia) and autonomic 2 Myelinated nerve fibers 3 Unmyelinated nerve fibers
What is the PNS?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes ganglia and nerves located outside the brain and spinal cord, which are considered the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS is divided into the autonomic and somatic nervous systems. Ten of the twelve cranial nerves may also be considered part of the PNS.
