What is the rate of fermentation of glucose?
The rate of fermentation will be varied because of the sugars’ structure. Glucose solution have the fastest rate due to it simple structure. Starch have the slowest rate because of its complicate structure. Therefore, …show more content… Maltose is slower with 0.3 mL of CO2 release in 20 minutes. Starch is the lowest with 0 mL of gas produce.
Why does starch ferment faster than glucose?
The rate of fermentation will be varied because of the sugars’ structure. Glucose solution have the fastest rate due to it simple structure. Starch have the slowest rate because of its complicate structure. Therefore, …show more content…
Do disaccharides ferment more slowly than glucose and fructose?
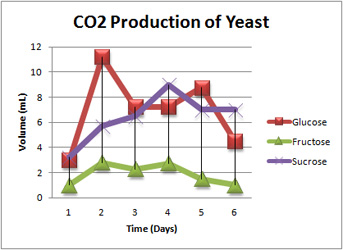
Each 20 g sugar sample was dissolved in 100 mL of water and then 7.0 g of yeast was added. Next we decided to compare the rate of fermentation of sucrose with that glucose and fructose, the two compounds that make up sucrose. We hypothesized that the disaccharide would ferment more slowly because it would first have to undergo hydrolysis.
What is an example of fermentation?
For example, sugars obtained from grapes are fermented to make wine, rum is produced from sugar cane, and grain starches are used for vodka, whiskey and beer. Fermentation is a process by which sugars are converted to alcohol and carbon dioxide by microorganisms such as yeast in the absence of air.

Which sugar is best for fermentation?
The white sugar had an average height of only 15.5 centimeters, the raw sugar had an average height of 17.5, and came close to the brown sugar, and the sugar substitute had an average growth of 10.5 centimeters. Therefore, brown sugar is the best sugar to use during fermentation.
Why does sucrose have the highest fermentation rate?
We hypothesize that sucrose and/or glucose will create a higher CO2 concentration over time in yeast fermentation because they have a simple chemical structure, making them easy to break down. Lactose is not as easily broken down in yeast fermentation due to yeast lacking the enzyme lactase which breaks lactose down.
Does glucose or fructose ferment faster?
As has been shown in multiple studies, and as many vintners and brewers can attest from firsthand experience, glucose does indeed ferment much more quickly than fructose. Grapes, which have a much higher fructose to glucose ratio, ferment into wine at a rate of approximately 2 to 3 weeks.
Which sugar has the highest rate of fermentation in yeast?
glucoseWe used the correlation statistical test to confirm there was a strong positive correlation between glucose concentrations and the rate of fermentation. Our results show that 80% glucose concentration in yeast fermentation produced the most amount of carbon dioxide.
Which ferments faster sucrose or glucose?
Of glucose, sucrose, and fructose, fermentation of glucose in yeast is the fastest and most efficient because glucose is a monosaccharide and does not need to be broken down. It can be used directly in the glycolysis cycle because it is already in a usable form. No energy use is required for this process.
Why does glucose have a higher rate of fermentation than starch?
Starch is the lowest with 0 mL of gas produce. Conclusion: The speed of fermentation depend on the structure of sugar. The simpler the structure the faster the speed will be, because there are less steps required to break down the polymer.
Is fructose easily fermented?
The slow fermentation of fructose appears to be a major cause of high residual sugar levels in finished wine and is often associated with sluggish and stuck wine fermentations. The results show that, for all wine yeast strains investigated, fermentation of fructose always lags behind that of glucose.
Which carbohydrate ferments the fastest?
The first one has the fastest fermented will be the glucose. The second is carbohydrate with the lowest gas production and slowest fermentation rate. And that is the starch and told his only water would walk as a negative control.
Why do simple sugars ferment faster?
This happens because glucose is a simple carbohydrate with less bonds than a more complex carbohydrate, such as lactose, that has a higher amount of bonds. We believe that because it has fewer bonds it has a higher rate of fermentation because it can be broken down faster.
What type of yeast ferments the fastest?
Save Time By Fermenting with Kveik Yeast Really fast. As Garshol says, brewers using kveik yeasts have cut their fermentation time in half — from two weeks down to one — and he reports watching a dried and dormant strain start visibly fermenting within 30 minutes.
What is the best sugar source for yeast?
Clearly, maltose is the best for yeast metabolism. Remember, yeast is made of two glucose molecules. Glucose (aka dextrose) is a close second. Fructose is in third place.
Why is maltose good for fermentation?
Contents. Maltose is important in the fermentation of alcohol, as starch is converted to carbohydrates and is readily broken down into glucose molecules with the maltase enzyme present in yeast.
Why is sucrose important in fermentation?
Sucrose is the major carbon source used by Saccharomyces cerevisiae during production of baker's yeast, fuel ethanol and several distilled beverages.
How does sucrose affect fermentation?
disaccharides such as sucrose must be digested prior to being fermented by yeast. yeast cells. concentration of sugar, for example in bread, may affect the production rate of carbon dioxide, and consequently the rate of the fermentation reaction.
Why is sucrose necessary for fermentation?
The addition of sucrose significantly improved yeast growth and alcohol production, altered the color qualities, and slightly decreased titratable acidity during fermentation. The highest tested proportion of added sucrose resulted in the highest maximum yeast counts and final ethanol concentrations.
How does concentration of sucrose affect fermentation?
We tested our hypothesis and the results showed that the 4% concentration of sucrose was the most effective concentration to produce the greatest production of yeast. Therefore, 4% of sucrose concentration would be the best concentration to use for the most effective fermentation of alcohol and baking.
What is fermentation sugar?
Fermentation is a process by which sugars are converted to alcohol and carbon dioxide by microorganisms such as yeast in the absence of air. The sugar could be a simple sugar such as glucose or fructose, or a more complex sugar such as sucrose.
How does sugar affect alcohol production?
Increasing the amount of sugar increases the amount of alcohol produced. The type of sugar being used can change the flavor of the alcohol. In any chemical reaction, including fermentation, the amount of products formed is determined by the amount of reactants used. Thus, increasing the amount of sugar used increases the amount ...
What happens to glucose in anaerobic conditions?
But under anaerobic conditions, fermentation occurs, and the sugars are converted to alcohol. ADVERTISEMENT.
What determines the flavor of alcohol?
The source of the sugar can determine the flavor of the alcohol produced. For example, sugars obtained from grapes are fermented to make wine, rum is produced from sugar cane, and grain starches are used for vodka, whiskey and beer.
Is sucrose a dimer?
Sucrose is a dimer, which means it is made up of one molecule of glucose linked to one molecule of fructose. When sucrose is used in the fermentation process, the first step has to be the breakage of the link between the two simple sugars by an enzyme.
Why is fermentation faster?
The simpler the structure the faster the speed will be, because there are less steps required to break down the polymer.
Which solution has the fastest rate?
Glucose solution have the fastest rate due to it simple structure. Starch have the slowest rate because of its complicate structure. Therefore, …show more content…. Maltose is slower with 0.3 mL of CO2 release in 20 minutes. Starch is the lowest with 0 mL of gas produce.
What is the slowest substance to break down?
On the other hand, starch, is a polymer, which required multiple steps to be broken down, is the slowest substance with 0 mL of accountable gas formation. There is a change color (lighter brown the tail of the tube) at 20 minutes.
Why does sugar melt in the mouth?
By entering your mouth, complex carbohydrates into sugar melt due to the action of the digestive enzyme alpha-amylase present in the saliva. Chewing a slice of white bread transformed up to 50% of the starch to glucose, even before it reaches the stomach.
What is added sugar?
Added sugar is the extra sugar in processed foods and drinks when it is being made. This would increases our sugar intake in just one meal. Nordqvist wrote in his article stating that American Heart Association said “Added sugars contribute zero nutrients and are just empty calories that lead to obesity”.
What is the least expensive milk?
The second least expensive product was the powdered milk . The lower costs of 100g of protein, the higher protein content the product had per…
Which is more effective in delaying gelatinization: sugar or protein?
Sugar was found more effective in delaying gelatinization than the water and protein. In water-limited systems the effects of sugar and protein on the gelatinization of starch were very effective.
Which has the highest sugar content?
Graph 1 shows the data from table 1 in a better form to compare and analyze the result. Coke has the highest sugar content than other solutions. The two peaks of orange juice and rice punch are almost produce the same amount of carbon dioxide.
What is the only pathway to obtain energy in fermentation?
Fermentation is an anaerobic pathway for breaking down a glucose. Glycolysis is the only pathway to obtain energy in fermentation. Because of lacking the presence of oxygen, the pyruvate cannot continue to go the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain. In fermentation, the electron transport chain isn’t functional, the NADH made in glycolysis cannot drop its electrons off, then it turns back into NAD + and regenerates.
How does yeast produce energy?
All living thing on earth can uptake energy from the environment to do biological work by cellular respiration and fermentation. Yeast breaks down glucose to conduct fermentation, release energy, and produce alcohol or other organic acid and carbon dioxide. This experiment is conducted to study the effective various forms of sugar that substitute to produce energy and influence the metabolic activities of yeast. Using five Ziploc bags with yeast and each with different solutions from varying sugar content, and one bag as the control analyzes the speed increase of fermentation of yeast and compare to each other. Throughout the experiment, the amount of CO 2 bubbles measures the bag thickness by a ruler, and measure the acidic of yeast production by pH indicator. From the experiment, the data gathered show that the higher sugar in a solution, the faster in the rate of fermentation. This means the amount of gas production and the acidic of the solution will be raised up.
How does sugar affect carbon dioxide?
After looking at the experiment’s result, from table 1 and graph 1, we are able to determine that the relationship between the amount of sugar and the amount of carbon dioxide produced is directly proportional. Sugar increases the rate of fermentation, and it releases the higher gas produced. As we expect, Coke has 39g of sugar, in which the highest per serving size compared to other solution, produce the highest number of carbon dioxide. While berry drink contains the lowest amount of sugar, its rate of fermentation is lowest. From table 2, the fermentation does not occur in the water without sugar which is the control. Meanwhile, the fermentation had been occurred in other liquid food sources that make it more acidic by ten times, but only rice punch drink is hundred times more acidic from the initiation liquid. Therefore, our hypotheses were accepted and supported by the data.
What is the process of lactic acid fermentation?
After glycolysis, NADH transfers its electrons to pyruvate to generate lactate as a product. Lactate is the deprotonated form of lactic acid. Muscle cell also carries out lactic acid fermentation. Then, lactic acid is transported through the bloodstream to the liver that converted back to pyruvate and processed in the remaining reactions of cellular respiration.
What is the process of releasing energy from glucose?
Cellular respiration is the process of releasing energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from the glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6) in the food. Cells need these energies for cellular work, all the activities of life. Cellular respiration occurs partially in the cytoplasm, and most of the steps occurs in the mitochondria. Cellular respiration involves four stages process: glycolysis, intermediate stage, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain. Glycolysis occurs in the presence or absence of oxygen called anaerobic pathway. But the other stage requires the presence of oxygen called aerobic pathway. Substrate level phosphorylation includes glycolysis and Krebs cycle stage. Oxidative phosphorylation is the electron transport chain stage that produces ATP with oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor. The overall chemical reaction is
How Does Sugar Affect Yeast Growth?
Yeast can use oxygen to release the energy from sugar (like you can) in the process called "respiration". So, the more sugar there is, the more active the yeast will be and the faster its growth (up to a certain point - even yeast cannot grow in very strong sugar - such as honey). However, if oxygen is short (like in the middle of a ball of dough), then yeast can still release energy from sugar, but in these conditions, its byproducts are alcohol and carbon dioxide. It is this carbon dioxide gas which makes the bubbles in dough (and therefore in bread), causing the dough to rise. Alcohol is a poison (for yeast as well as for people) and so the yeast is not able to grow when the alcohol content gets too high. This is why wine is never more than about 12% alcohol. WHY does an excess of sugar inhibit the yeast? My guess would be that the osmotic concentration of the sugar gets so great that the yeast is unable to get enough water for growth. As fresh yeast is more than 90% water, the single substance most needed for growth is water. As osmotic concentration increases, the water potential of the sugar solution gets more and more negative until it reaches a point where is lower than the water potential of the yeast cell contents and water tends to move OUT of the cell rather than IN. I do not know whether yeast cells are able to take up water actively, by expenditure of metabolic energy to pump the water against the water potential gradient. I imagine that up to a certain concentration, the limiting factor is the amount of sugar available for respiration and synthesis of cell materials with the yeas Continue reading >>
What is the most common trisaccharide in beer?
The most common trisaccharide that exists in brewing sugars is maltotriose, which is made up of three glucose molecules. When monosaccharides join in structures of 4 or more the resulting structures are called dextrin, which is not fermentable by beer yeast.
What is the name of the sugar that is made up of two monosaccharides?
When two monosaccharides join they form another sugar structure called a disaccharide. Common disaccharides that exist in brewing sugars are sucrose and maltose. Sucrose is made up of a glucose molecule and fructose molecule, while maltose is made up of two glucose molecules.
What is sucrose made of?
Best Answer: Sucrose is a disaccharide made of glucose and fructose. Before the yeast can utilize sucrose it must split it into its two sub sugars. Glucose will enter the the process of glycolysis and be changed into glucose 6 phosphate and then be changed to fructose 6 phosphate (2 steps).
What is the process of brewing sugar?
Grains are soaked in approx. 150 degree water to extract these sugars, this is called mashing. Next the fermentation process uses yeast to convert these sugars in the wort into alcohol and CO2. The common sugars associated with brewing, there prevalence in wort, and how yeast breaks them down are described below. Building Blocks Here are the very basic things to know about the sugars extracted from grains during brewing. Sugar is basically a ringed structure made up of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen A sugar ring is named by how many carbon atoms are attached to it. Common brewing sugars, such as glucose and fructose are made up of a single hexose (6 carbon atoms, chemical formula C6H12O6) A single hexose is called a monosaccharide. Common monosaccharides that existing in brewing sugars are glucose, fructose, and galactose. When two monosaccharides join they form another sugar structure called a disaccharide. Common disaccharides that exist in brewing sugars are sucrose and maltose. Sucrose is made up of a glucose molecule and fructose molecule, while maltose is made up of two glucose molecules. When three monosaccharides join they form another sugar structure called a trisaccharide. The most common trisaccharide that exists in brewing sugars is maltotriose, which is made up of three glucose molecules. When monosaccharides join in structures of 4 or more the resulting structures are called dextrin, which is not fermentable by beer yeast. Pure dextrin is actually added to some beers during the boil to increase body in the final product, our Northern English Brown ale is a good example. Common Brewing Sugars Breakdown Monosaccharides � Continue reading >>
What is the name of the monosaccharide in brewing sugar?
Common brewing sugars, such as glucose and fructose are made up of a single hexose (6 carbon atoms, chemical formula C6H12O6) A single hexose is called a monosaccharide. Common monosaccharides that existing in brewing sugars are glucose, fructose, and galactose.
Is sucrose a common sugar?
Glucose, Fructose, and Sucrose were capable of being fermented by yeast. Because Sucrose (disaccharide) was a common sugar and made of Glucose (monosaccharide) and Fructose (monosaccharide), these three carbohydrates were fermented by yeast whereas other typescannot. Therefore, disaccharide and monosaccharide of same sugar could be fermented.