
What is the name of the fracture in the legs and feet?
How to treat a pathological fracture?
How to treat transverse fracture?
What is a comminuted fracture?
What type of fracture requires surgery?
What happens when a bone is wrenched by the forceful rotation or twisting of a limb?
What is a stable fracture?
See 2 more
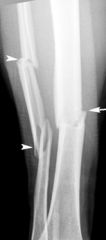
What is a Le Fort 1 fracture?
Le Fort I level fractures are essentially a separation of the hard palate from the upper maxilla due to a transverse fracture running through the maxilla and pterygoid plates at a level just above the floor of the nose.
Where is a maxillary fracture?
Maxilla (upper jaw) fracture occurs as a result of blunt trauma, car accidents, running into an object or assault. These fractures are also called jaw fractures or Le Fort I fracture.
What is the most common facial fracture?
Nasal bones (broken nose): Nasal bone fractures are the most common type of facial fracture. The nasal bone is made up of two thin bones. It takes less force to break the nasal bones than other facial bones because they are thin and prominent.
What are the types of mandibular fracture?
Few classifications of mandibular ramus fractures are found in the literature [5]. They are divided into vertical, horizontal, and combined fractures (Fig....6).Vertical fracture. ... Horizontal fracture. ... Combined fracture.
What do all LeFort fractures have in common?
All Le Fort fracture types involve the pterygoid processes of the sphenoid bones and therefore, disrupt the intrinsic buttress system to the midface-however further differentiation of Le Fort types I, II, and III depends on involvement of the maxillary, nasal, and zygomatic bones [3-5].
What is a Le Fort II fracture?
Le Fort Type II These fractures extend superiorly in the midface to include the nasal bridge, maxilla, lacrimal bones, orbital floor, and rim. They are pyramidal fractures with teeth at the base and nasal bone at the apex. These fractures are typically bilateral.
What is the 2nd most common facial fracture?
In patients who require surgery, the most commonly fractured bone is the mandible (41.6–75.2%) [1, 13, 15]. The second and third most commonly fractured bones vary with the series, being the maxilla and orbit (39.8% each) in one series [1] but the malar bone (15.2%) and maxilla (6.4%) in another [15].
What are 3 types of common fractures?
In this article we look at the three primary types of fractures: open, closed, and displaced fractures.
What are the 4 common fractures?
These are the main types of bone fractures:Simple or Closed Fracture. A bone fracture is classified as simple or closed if the broken bone remains within the body and does not push into or out of the skin. ... Compound or Open Fracture. ... Incomplete or Partial Fracture. ... Complete Fracture.
What is Lefort 4 fracture?
Le Fort fractures typically involve the pterygoid plates of the sphenoid bones, which form the base of the skull, extending behind the eye and below the front part of the brain. The pterygoid plates are projections of the sphenoid bones and connect the midface to the sphenoid bones.
What is the most common site of mandibular fracture?
The most common site of mandibular fractures in adult patients was the symphysis and parasymphysis, followed by the condyle, body and angle. However, the mandibular symphysis/ parasymphysis and condyle were determined to be most common sites in young patients.
What is the most common fracture of the mandible?
The most common mandible fractures in children involve the condyle (40–70%),77 78 which is considered a primary growth center of the jaw. Direct trauma to the anterior mandible can result in proximal transmission of force, leading to injury of the mandibular condyle.
Where is the maxillary sinus located?
There are two large maxillary sinuses, one in each of the maxillary bones, which are in the cheek area next to the nose. The maxillary sinuses are lined with cells that make mucus to keep the nose from drying out. Anatomy of the paranasal sinuses (spaces between the bones around the nose).
What is a maxillary sinus fracture?
Maxillary sinus fractures (MSFs) are most commonly caused by blunt force trauma to the face. Depending on the magnitude and location of the direct injury, MSFs can vary in appearance and symptomatology.
How do you fix a maxillary sinus fracture?
In the surgical treatment of an isolated anterior wall of the maxillary sinus fracture, open reduction and ridged fixation is required. Large fragments can be fixed with plates and screws and small fragments can either be positioned at the bony defect or removed.
How is a maxillary fracture treated?
Maxillary (Le Fort) fracture: Open reduction with internal fixation is the standard. If CSF rhinorrhea is present, a neurosurgeon should be consulted. Prophylactic antibiotics are warranted if the fracture extends through the tooth-bearing region or through the nasal or sinus mucosa.
17 Different Types of Bone Fractures | New Health Advisor
Having knowledge of different types of fractures is essential. Bone fractures can be a simple/compound fractures, complete/incomplete fractures or even pathological fracture.
The Most Common Types of Fractures, Their Causes, and Treatment
We offer COVID-19 Treatment. Click here to see if you are eligible. We have rapid COVID-19 testing with same day results. Patients with special circumstances may require a rapid PCR COVID-19 test .
What is the name of the fracture in the legs and feet?
6. Hairline Frac ture. A hairline fracture is also known as a stress fracture and occurs mostly on the legs and feet. It is a result of repetitive movement and occurs when athletes suddenly increase the frequency or intensity of workouts such as running or jogging.
How to treat a pathological fracture?
Treatment for a Pathological Fracture: Treatment will depend on the underlying condition that caused the fracture. If the illness doesn’t affect the bone’s ability to heal, the patient will only need to wear a cast to immobilize the limb. If an illness has compromised the body’s ability to heal, surgery will be necessary.
How to treat transverse fracture?
Treatment for a Transverse Fracture: The medical provider will realign the bones through an open reduction internal fixation (ORIF). Once the bone fragments are aligned, a traditional cast or splint will be used to immobilize the bone.
What is a comminuted fracture?
A comminuted fracture leaves the bone in fragments. It is most common after severe trauma, such as a car accident, and is more likely to occur in the hands or feet.
What type of fracture requires surgery?
4. Oblique Fracture. An oblique fracture occurs when the bone breaks at an angle.
What happens when a bone is wrenched by the forceful rotation or twisting of a limb?
This happens when a bone is wrenched by the forceful rotation or twisting of a limb. It results in a clean break where the bone completely breaks into two fragments.
What is a stable fracture?
This is the type of fracture that occurs when an injury causes the bone to break clean, with its parts in alignment. This means that the bone maintains its original position. Treatment for a Stable Fracture: Since this type of fracture doesn’t require realignment, the doctor will simply immobilize the bone with a cast.
Where do spiral fractures occur?
Spiral fractures occur in long bones in the body, usually in the femur, tibia, or fibula in the legs. However, they can occur in the long bones of the arms.
What are the different types of fractures?
There are several types of bone fractures, and each type can have slight variations. Many of the types of fractures we’ll talk about later may also be described by one of the following terms: 1 Open Fracture: A fracture in which the bone breaks through the skin and can be seen outside the leg. Or there is a deep wound that exposes the bone through the skin. This is also called a compound fracture. 2 Closed Fracture: A fracture that does not break the skin. This is also called a simple fracture. 3 Partial Fracture: An incomplete break of the bone 4 Complete Fracture: A complete break of the bone causing it to be separated into two or more pieces 5 Stable Fracture: The broken ends of the bone line up and have not moved out of place. 6 Displaced Fracture: There is a gap between the broken ends of the bone. Repairing a displaced fracture may require surgery.
What is a comminuted fracture?
A comminuted fracture is one in which the bone is broken into 3 or more pieces. There are also bone fragments present at the fracture site. These types of bone fractures occur when there is a high-impact trauma, such as an automobile accident. 10. Avulsion Fracture.
What is a fracture in which the bone breaks through the skin and can be seen outside the leg?
Many of the types of fractures we’ll talk about later may also be described by one of the following terms: Open Fracture: A fracture in which the bone breaks through the skin and can be seen outside the leg. Or there is a deep wound that exposes the bone through the skin. This is also called a compound fracture.
What is a fracture that does not break the skin called?
This is also called a compound fracture. Closed Fracture: A fracture that does not break the skin. This is also called a simple fracture. Partial Fracture: An incomplete break of the bone. Complete Fracture: A complete break of the bone causing it to be separated into two or more pieces.
What causes bone fractures?
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), the most common causes of bone fractures are trauma, osteoporosis, and overuse. Let’s take a closer look at the different types of bone fractures and how they occur.
Why do children have partial fractures?
Children are most likely to experience this type of fracture because their bones are softer and more flexible.
What is the name of the fracture in the legs and feet?
6. Hairline Frac ture. A hairline fracture is also known as a stress fracture and occurs mostly on the legs and feet. It is a result of repetitive movement and occurs when athletes suddenly increase the frequency or intensity of workouts such as running or jogging.
How to treat a pathological fracture?
Treatment for a Pathological Fracture: Treatment will depend on the underlying condition that caused the fracture. If the illness doesn’t affect the bone’s ability to heal, the patient will only need to wear a cast to immobilize the limb. If an illness has compromised the body’s ability to heal, surgery will be necessary.
How to treat transverse fracture?
Treatment for a Transverse Fracture: The medical provider will realign the bones through an open reduction internal fixation (ORIF). Once the bone fragments are aligned, a traditional cast or splint will be used to immobilize the bone.
What is a comminuted fracture?
A comminuted fracture leaves the bone in fragments. It is most common after severe trauma, such as a car accident, and is more likely to occur in the hands or feet.
What type of fracture requires surgery?
4. Oblique Fracture. An oblique fracture occurs when the bone breaks at an angle.
What happens when a bone is wrenched by the forceful rotation or twisting of a limb?
This happens when a bone is wrenched by the forceful rotation or twisting of a limb. It results in a clean break where the bone completely breaks into two fragments.
What is a stable fracture?
This is the type of fracture that occurs when an injury causes the bone to break clean, with its parts in alignment. This means that the bone maintains its original position. Treatment for a Stable Fracture: Since this type of fracture doesn’t require realignment, the doctor will simply immobilize the bone with a cast.
