Which lens in an electron microscope is used to focus the beam?
Which lens in an electron microscope is used to control and focus the beam of electrons. Hint: Glass lens like a concave and convex lens is used only in a light microscope.
What is the function of objective lens in microscope?
The electron beam coming out of the specimen passes down the second of magnetic coils called the objective lens, which has high power and forms the intermediate magnified image. The third set of magnetic lenses called projector (ocular) lenses produce the final further magnified image.
What are the components of an electron microscope?
2. Electromagnetic lenses 3. Specimen Holder 4. Image viewing and Recording System What is an Electron Microscope? An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination.
Which type of microscope is used in metallurgy?
It is also used in metallurgy. An electron microscope is defined as the type of microscope in which the source of illumination is the beam of accelerated electrons. It is a special type of microscope with a high resolution of images as the images can be magnified in nanometers.

What material is used as an objective lens in electron microscope?
Q.In electron microscope, what material isused as an objective lense?B.Superfine glassC.Aluminium foilsD.ElectronsAnswer» a. Magnetic coils1 more row
Which microscope uses glass lenses?
Optical microscopesThe most familiar type of microscope is the optical, or light, microscope, in which glass lenses are used to form the image. Optical microscopes can be simple, consisting of a single lens, or compound, consisting of several optical components in line. The hand magnifying glass can magnify about 3 to 20×.
Which lens is used in simple microscope?
double convex lensA simple microscope is a magnifying glass that has a double convex lens with a short focal length.
Which lens is used in telescope?
The telescope must have one convex lens as one of the two lenses since the convex lens is used to magnify the objects by bending the path of light.
What are the 3 types of lenses microscope?
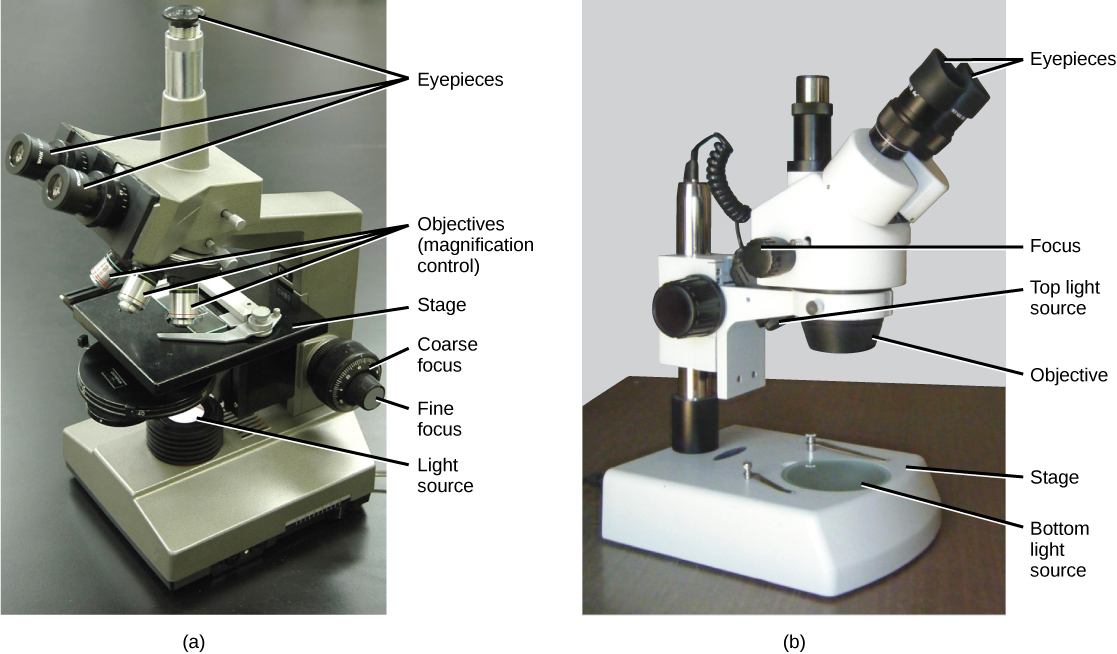
What Kind of Lens Is Used for a Microscope?Objective Lens. The objective lens is the lens closest to the slide or object you are viewing. ... Ocular Lens. The ocular lens, or eyepiece lens, is the one that you look through at the top of the microscope. ... Condenser Lens. ... Oil-Immersion Lens.
Which type of lens is used in magnifying glass?
Convex lensConvex lens is used in magnifying glass.
What type of lens is used in microscope and telescope?
The objective lens is a convex lens of short focal length (i.e., high power) with typical magnification from 5× to 100×. The eyepiece, also referred to as the ocular, is a convex lens of longer focal length.
What is microscopic glass?
Clear Image Microscope Glasses are two high powered, coated lenses “piggybacked” one behind the other. This “doublet” lens is designed to create a magnified, crystal clear, edge-to-edge image. The lens eliminates the aberrations and “pincushion” effect of a single high powered lens.
What is an electron microscope?
Electron microscope definition. An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. It is a special type of microscope having a high resolution of images, able to magnify objects in nanometres, which are formed by controlled use of electrons in vacuum captured on a phosphorescent screen.
Why is a scanning electron microscope called a scanning electron microscope?
It is termed a scanning electron microscope because the image is formed by scanning a focused electron beam onto the surface of the specimen in a raster pattern.
Why is an electron beam ultra thin?
As the penetration power of the electron beam is very low, the object should be ultra-thin. For this, the specimen is dried and cut into ultra-thin sections before observation.
How many sets of condenser lenses are there?
Two sets of condenser lenses focus the electron beam on the specimen and then into a thin tight beam.
Why do electrons appear darker in a specimen?
The denser regions in the specimen scatter more electrons and therefore appear darker in the image since fewer electrons strike that area of the screen. In contrast, transparent regions are brighter.
Which lens focuses the electron beam on the specimen?
Electromagnetic lenses. Condenser lens focuses the electron beam on the specimen. A second condenser lens forms the electrons into a thin tight beam. The electron beam coming out of the specimen passes down the second of magnetic coils called the objective lens, which has high power and forms the intermediate magnified image.
How many types of electron microscopes are there?
There are two types of electron microscopes, with different operating styles:
How do electrons hit a fluorescence screen?
After the sample, the electrons hit a fluorescence screen that forms an image with the electrons that were transmitted. You can better understand this process by imagining how a movie projector works. In a projector, you have a film that has the negative image that will be projected. The projector shines white light on the negative and the light transmitted forms the image contained in the negative.
What are the different types of electron microscopes?
The main types of electron microscopes are the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) and the Scanning Transmission Microscope (STEM). Electron microscopes have a wide range of applications in science and technology. Main Types of Electron Microscopes.
How do electrons interact with a sample?
The electrons interact with the material in a way that triggers the emission of secondary electrons. These secondary electrons are captured by a detector, which forms an image of the surface of the sample. The direction of the emission of the secondary electrons depends on the orientation of the features of the surface. There, the image formed will reflect the characteristic feature of the region of the surface that was exposed to the electron beam.
Why do we use microscopes in school?
You've probably used a microscope in school -- maybe to observe the wings of an insect or to get a closer look at a leaf. If so, then you know microscopes are used in the classroom to illuminate the surface of your subject of study. These microscopes use transparent glass lenses to magnify the image of whatever you are observing.
What can we observe with an electron microscope?
Uses of the Electron Microscope. With electron microscopes we can observe the small scale world that makes up most of the things around us. Before the development of the electron microscope we did not know how all these things looked (shape, size, etc.).
How small can a microscope see?
Visible light, which is the one our eyes are sensitive to, ranges between 390 and 700 nanometers (one nanometer is one billionth of a meter). This means that we cannot observe things that are smaller than a few hundred nanometers using our eyes and visible light.
Why do electrons have a wavelength?
An electron beam allows us to see at very small scales because electrons can also behave as light. It has the properties of a wave with a wavelength that is much smaller than visible light (a few trillionths of a meter!). With this wavelength we can distinguish features down to a fraction of a nanometer.
What is the difference between an electron microscope and a light microscope?
As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a higher resolving power than light microscopes and can reveal the structure of smaller objects. A scanning transmission electron microscope has achieved better than 50 pm resolution in annular dark-field imaging mode and magnifications of up to about 10,000,000× whereas most light microscopes are limited by diffraction to about 200 nm resolution and useful magnifications below 2000×.
Why is SEM better than TEM?
Generally, the image resolution of an SEM is lower than that of a TEM. However, because the SEM images the surface of a sample rather than its interior , the electrons do not have to travel through the sample. This reduces the need for extensive sample preparation to thin the specimen to electron transparency. The SEM is able to image bulk samples that can fit on its stage and still be maneuvered, including a height less than the working distance being used, often 4 millimeters for high-resolution images. The SEM also has a great depth of field, and so can produce images that are good representations of the three-dimensional surface shape of the sample. Another advantage of SEMs comes with environmental scanning electron microscopes (ESEM) that can produce images of good quality and resolution with hydrated samples or in low, rather than high, vacuum or under chamber gases. This facilitates imaging unfixed biological samples that are unstable in the high vacuum of conventional electron microscopes.
What type of microscope uses a magnetic field?
Electron microscopes use shaped magnetic fields to form electron optical lens systems that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope.
How does a SEM work?
The SEM produces images by probing the specimen with a focused electron beam that is scanned across a rectangular area of the specimen ( raster scanning ). When the electron beam interacts with the specimen, it loses energy by a variety of mechanisms. The lost energy is converted into alternative forms such as heat, emission of low-energy secondary electrons and high-energy backscattered electrons, light emission ( cathodoluminescence) or X-ray emission, all of which provide signals carrying information about the properties of the specimen surface, such as its topography and composition. The image displayed by an SEM maps the varying intensity of any of these signals into the image in a position corresponding to the position of the beam on the specimen when the signal was generated. In the SEM image of an ant shown below and to the right, the image was constructed from signals produced by a secondary electron detector, the normal or conventional imaging mode in most SEMs.
What is the advantage of electron diffraction over X-ray crystallography?
The advantages of electron diffraction over X-ray crystallography are that the specimen need not be a single crystal or even a polycrystalline powder, and also that the Fourier transform reconstruction of the object's magnified structure occurs physically and thus avoids the need for solving the phase problem faced by the X-ray crystallographers after obtaining their X-ray diffraction patterns.
How does an electron microscope work?
The original form of the electron microscope, the transmission electron microscope (TEM), uses a high voltage electron beam to illuminate the specimen and create an image. The electron beam is produced by an electron gun, commonly fitted with a tungsten filament cathode as the electron source. The electron beam is accelerated by an anode typically at +100 k eV (40 to 400 keV) with respect to the cathode, focused by electrostatic and electromagnetic lenses, and transmitted through the specimen that is in part transparent to electrons and in part scatters them out of the beam. When it emerges from the specimen, the electron beam carries information about the structure of the specimen that is magnified by the objective lens system of the microscope. The spatial variation in this information (the "image") may be viewed by projecting the magnified electron image onto a fluorescent viewing screen coated with a phosphor or scintillator material such as zinc sulfide. Alternatively, the image can be photographically recorded by exposing a photographic film or plate directly to the electron beam, or a high-resolution phosphor may be coupled by means of a lens optical system or a fibre optic light-guide to the sensor of a digital camera. The image detected by the digital camera may be displayed on a monitor or computer.
What is a microscope with electrons?
Type of microscope with electrons as a source of illumination. A modern transmission electron microscope. Diagram of a transmission electron microscope. Electron microscope constructed by Ernst Ruska in 1933. An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination.
What are the Different Types of Microscopes?
There are different types of microscopes and each of these has different purposes of use. Some are suitable for biological applications , while others are used in educational institutions. There are also microscope types that find application in metallurgy and studying three-dimensional samples.
What is a simple microscope?
A simple microscope is defined as the type of microscope that uses a single lens for the magnification of the sample. A simple microscope is a convex lens with a small focal length. The magnifying power of the simple microscope is given as:
What is the difference between a high powered microscope and a low powered microscope?
The basic difference between low-powered and high-powered microscopes is that a high power microscope is used for resolving smaller features as the objective lenses have great magnification. However, the depth of focus is greatest for low powered objectives. As the power is switched to higher, the depth of focus reduces.
How many types of microscopes are there?
In this article, there are 5 such microscope types that are discussed along with their diagram, working principle and applications. These five types of microscopes are:
What metal is used in electron microscopes?
The metal used in an electron microscope is tungsten. A high voltage current is applied which results in the excitation of the electrons in the form of a continuous stream that is used as a beam of light. The lenses used in the electron microscope are magnetic coils. These magnetic coils are capable of focusing the electron beam on the sample such that the sample gets illuminated. As the flow of current increases, the strength of the magnetic lens increases. The electron beam flow is designed such that it cannot pass through the glass lens.
What is an electron microscope?
An electron microscope is defined as the type of microscope in which the source of illumination is the beam of accelerated electrons. It is a special type of microscope with a high resolution of images as the images can be magnified in nanometers.
What is the working principle of a simple microscope?
The working principle of a simple microscope is that when a sample is placed within the focus of the microscope, a virtual, erect and magnified image is obtained at the least distance of distinct vision from the eye that is held at the lens.
What is an electron microscope?
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM): In this microscope, electron beam is transmitted through an ultra-thin section of the object and the image is magnified by the electromagnetic fields.
How much greater is the resolving power of an electron microscope than that of a light microscope?
The resolving power of electron microscopes is 200 times greater than that of light microscopes. They can produce useful magnifications up to X 400,000, as compared to X 2000 in light microscopes. Thus, the useful magnification is 200 times greater in electron microscopes than in light microscopes. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What are the different types of microscopes?
Types of Microscope: Optical and Electron Microscope (With Figure)! Microorganisms are usually not visible to naked human eye. They can be made visible, only when they are magnified under microscopes. Microscopes are instruments, which can produce enlarged images of very small objects, making it possible to view them, which, otherwise, ...
What is a microscope used for?
Microscopes are instruments, which can produce enlarged images of very small objects, making it possible to view them, which, otherwise, cannot be seen distinctly by naked human eye. Different types of microscopes are used by the microbiologists for specific purposes. Microscopes are of the following types (Figure 4.1).
What is phase contrast microscope?
Phase-contrast Microscope: With a phase-contrast microscope, the differences among various cells with different refractive indices or thickness can be seen in unstained condition. Unstained structures within cells, not discernible by most other microscopes can also be observed, due to the slight differences in their refractive indices or thickness. ...
How does a microscope work?
This microscope uses an electron beam to scan the surface of the object, thereby inducing it to release a shower of electrons, which are collected by a detector to generate the image . It is used to observe the surface structure of microscopic objects.
What is a simple microscope?
A simple microscope is used to obtain small magnifications. A single biconvex lens magnifies the size of the object to get an enlarged virtual image.