
What is the diaphragm in the respiratory system?
The diaphragm in the respiratory system is the dome-shaped sheet of muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen. It is also referred to the thoracic diaphragm because it’s located in the thoracic cavity, or chest. It is attached to the spine, ribs and sternum and is the main muscle of respiration,...
What is the diaphragm&respiratory muscle disorders program?
As part of the Temple Lung Center, our Diaphragm & Respiratory Muscle Disorders Program is the only one of its kind in the Philadelphia region. Conditions affecting the diaphragm — including diaphragm paralysis and respiratory muscle dysfunction — are not a common focus for many medical professionals.
What is the most important muscle in respiration?
It is attached to the spine, ribs and sternum and is the main muscle of respiration, playing a very important role in the breathing process. The lungs are enclosed in a kind of cage in which the ribs form the sides and the diaphragm, an upwardly arching sheet of muscle, Continue Scrolling To Read More Below...
What is the primary inspiratory muscle in the lungs?
Primary Muscles The primary inspiratory muscles are the diaphragm and external intercostals. Relaxed normal expiration is a passive process, happens because of the elastic recoil of the lungs and surface tension.

Which type of muscle is a diaphragm?
skeletal muscleThe diaphragm is a thin skeletal muscle that sits at the base of the chest and separates the abdomen from the chest. It contracts and flattens when you inhale. This creates a vacuum effect that pulls air into the lungs. When you exhale, the diaphragm relaxes and the air is pushed out of lungs.
What type of muscle is found in the respiratory system?
Airway smooth muscle (ASM), an important tissue involved in the regulation of bronchomotor tone, exists in the trachea and in the bronchial tree up to the terminal bronchioles.
Is diaphragm A involuntary muscle?
The diaphragm, located below the lungs, is the major muscle of respiration. It is a large, dome-shaped muscle that contracts rhythmically and continually, and most of the time, involuntarily. Upon inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens and the chest cavity enlarges.
Is the diaphragm made of smooth muscle?
The diaphragm has ONLY skeletal muscle, not smooth muscle - none.
Where is smooth muscle found?
Smooth muscle fibers are located in walls of hollow visceral organs (such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines), except the heart, appear spindle-shaped, and are also under involuntary control.
Is bronchi a smooth muscle?
Bronchial smooth muscle contraction induces airway narrowing. The smooth muscle also contributes to bronchial inflammation by secreting a range of inflammatory mediators, recruiting and activating inflammatory cells, such as mast cells or T-lymphocytes.
Is diaphragm skeletal muscle or smooth muscle?
CONTRACTILE PROTEINS The diaphragm muscle is of the skeletal or striated type and is the major muscle of ventilation.
What are the involuntary muscles?
Cardiac muscle and smooth muscle that line the internal organs like the intestinal tract, blood vessels, urogenital tract, respiratory tract, etc. are involuntary muscles.
Are respiratory muscles voluntary or involuntary?
The main respiratory muscles are under both voluntary and involuntary (automatic) control. These two control systems come from separate sites in the CNS and have separate descending pathways; the final integration of these outputs occurs at segmental levels in the cord.
Are respiratory muscles smooth or skeletal?
skeletal musclesSome of our respiratory muscles serve to pump air into and out of our lungs (ventilation). These pump muscles act on the thoracic and abdominal walls and are all skeletal muscles.
Is muscle of the lungs a skeletal muscle?
Abstract. Skeletal (striated) muscle is one of the four basic tissue types, together with the epithelium, connective and nervous tissues. Lungs, on the other hand, develop from the foregut and among various cell types contain smooth, but not skeletal muscle.
What are the 5 muscles of respiration?
Muscles of respirationThoracic muscles. External intercostal muscles. Musculi intercostales externi. ... Neck muscles. The external and internal intercostals do not work individually during breathing. ... Abdominal muscles. Serratus anterior muscle (ventral view)
How does the respiratory system work with the muscular system?
Muscles and bones help move the air you inhale into and out of your lungs. Some of the bones and muscles in the respiratory system include your: Diaphragm: Muscle that helps your lungs pull in air and push it out. Ribs: Bones that surround and protect your lungs and heart.
What are the muscles involved in inhalation and exhalation quizlet?
Inhalation and exhalation involve the respiratory system which includes the lungs, diaphragm and muscles like the internal and external intercostal muscles.
What are the accessory muscles of respiration?
Role of Muscle in Respiration Accessory muscles of ventilation include the scalene, the sternocleidomastoid, the pectoralis major, the trapezius, and the external intercostals. Smooth muscle is found in the trachea and in the pulmonary arteries and smaller vessels.
What is the diaphragm?
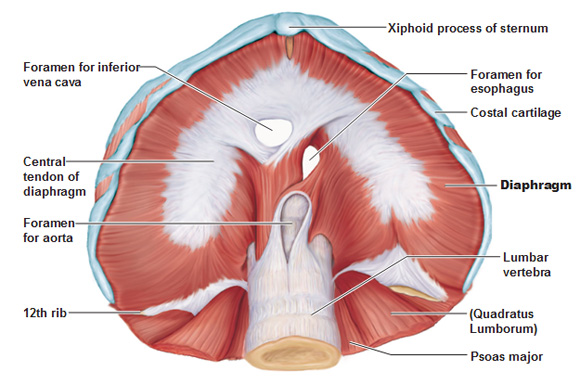
The diaphragm is a musculotendinous structure with a peripheral attachment to a number of bony structures. It is attached anteriorly to the xiphoid process and costal margin, laterally to the 11th and 12th ribs, and posteriorly to the lumbar vertebrae. The posterior attachment to the vertebrae is by tendinous bands called crura. The crura are attached to the anterior aspect of the bodies of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd lumbar vertebrae. The muscle fibres, extending from their bony attachments, converge on a central tendon.
Where does the diaphragm innervate?
Motor innervation of the diaphragm comes from the phrenic nerves (C3-C5). These nerves innervate the diaphragm from its abdominal surface after they penetrate it. Sensory innervation (pain and proprioception) at the central tendinous part is innervated by the phrenic nerves , while the peripheral muscular portions are innervated by 6th to 11th intercostal nerves .
How does the diaphragm separate the thoracic cavity?
It separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities from each other by closing the inferior thoracic aperture. The diaphragm is the primary muscle that is active in inspiration. Contraction of the muscle facilitates expansion of the thoracic cavity. This increases volume of the the cavity, which in turn decreases the intrathoracic pressure allowing ...
Why is the diaphragm shaped like a dome?
The diaphragm is shaped as two domes, with the right dome positioned slightly higher than the left because of the liver. The depression between the two domes is due to the pericardium slightly depressing the diaphragm. The diaphragm has two surfaces: thoracic and abdominal.
Which artery is associated with the diaphragm?
Inferior phrenic arteries are closely related to the diaphragm and give off a few branches to supply it. They are the main source of vascular supply to the diaphragm. The left inferior phrenic artery ascends toward the left diaphragmatic crus associated with the inferior surface of the diaphragm.
Which surface of the diaphragm passes through the right crus?
Abdominal surface of the diaphragm in a cadaver: The esophageal hiatus passes through the right crus of the diaphragm. The foramen of the inferior vena cava traverses through the central tendon, while the aortic hiatus passes behind the diaphragm.
How to remember the location of the diaphragm?
An easy way to remember the location and structures passing through the diaphragm is by using this mnemonic: 'I 8 10 EGG s AT 12' (read: I ate ten eggs at twelve).
What is the role of the diaphragm in breathing?
This movement creates a vacuum in your chest, allowing your chest to expand (get bigger) and pull in air. When you breathe out, your diaphragm relaxes and curves back up as your lungs push the air out.
What muscle is used to help you breathe?
The diaphragm is a muscle that helps you breathe. It sits under your lungs and separates your chest cavity from your abdomen. Many conditions, injuries and diseases can affect how the diaphragm works, causing symptoms such as trouble breathing and chest pain. Breathing exercises can strengthen your diaphragm and keep it working like it should.
What causes diaphragm to be weak?
The most common conditions include hernias and nerve damage from surgery or an accident. Neuromuscular disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) can also weaken the diaphragm. These conditions can cause difficulty breathing, heartburn and pain in the chest and belly.
What are the symptoms of a diaphragm problem?
Some signs of diaphragm problems are similar to symptoms of a heart attack. If you have shortness of breath, chest tightness or chest pain, get immediate medical help.
Which nerve controls the diaphragm's movement?
Phrenic nerve, which controls the diaphragm’s movement.
Which artery carries blood away from the heart to the rest of the body?
Aorta, a big artery that carries your blood away from your heart to the rest of your body.
Can diaphragm problems be a sign of other conditions?
Symptoms of diaphragm problems may also be signs of other conditions. It’s essential to see your provider for an evaluation.
Which muscles contract with the diaphragm?
The external intercostal muscles or rib cage muscles (located between the ribs) contract together with the diaphragm, lifting and expanding the rib cage to provide even more space [21].
Where is the diaphragm located?
The diaphragm is located between the thoracic and abdominal cavities [3], with important organs like the lungs and heart located superior to it, and the liver (proximal position), kidney and stomach being inferior to it. The curved muscle is inserted into the lower part of the rib cage. Diaphragm Muscle Location Picture.
What is the thoracic diaphragm?
The thoracic diaphragm is a large, flat muscle that plays a vital role in the respiratory system, and is located just beneath the two lungs, dividing the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity [1]. With its characteristic dome shape, it is the primary respiratory muscle, also supporting the lungs and heart [2]. Diaphragm.
What happens to the diaphragm during exhalation?
The diaphragm then relaxes and comes back to its natural dome shape, reducing the space within the chest cavity, thus putting pressure on the lungs so the air can be pushed out [3].
How long do diaphragm spasms last?
Diaphragm Spasms: Sometimes, the diaphragm spasms causing harmless hiccups may last for days or weeks, indicating some underlying health condition. Sometimes, this abnormally contracted muscle may make it difficult to breathe deeply, leading to other problems [24].
Which arteries supply the diaphragm?
Blood Supply to the Diaphragm Muscle. Its central part gets arterial supply from the phrenic arteries [3], while the 5 lower intercostal and subcostal arteries provide arterial supply to the costal margins. All these blood vessels connect and open into each other (anastomose) to ensure proper blood supply to the diaphragm [5].
Which side of the diaphragm is innervated?
The left side of the diaphragm is innervated by the left phrenic nerve and the right side by the right phrenic nerve [3]. Due to this reason, the two halves are capable of working independently [16]. Both the phrenic nerves provide innervation to the right crus [5]. The outer or peripheral regions of the diaphragm are innervated by ...
What Is The Diaphragm: Definition
Where Is The Diaphragm Located
- The diaphragm is located between the thoracic and abdominal cavities , with important organs like the lungs and heart located superior to it, and the liver (proximal position), kidney and stomach being inferior to it. The curved muscle is inserted into the lower part of the rib cage.
Diaphragm Anatomy
- Diaphragm Openings
Since it is located between the abdominal and chest cavities, any structure that needs to pass into the abdominal cavity from above has to go through the diaphragm . The three primary openings are: Caval opening (vena caval hiatus) at the 8th vertebral level: Allows the inferior vena cava an… - What Nerves Innervate the Diaphragm
The phrenic nerve, originating at the C3-C5 vertebral level, provides motor supply to the diaphragm , and controls its movement . The medullary inspiratory neuron (responsible for regulating breathing) sends information to the diaphragm via this nerve, enabling us to breathe in. The left …
Diaphragm Function – What Does It Do
- Despite being a skeletal muscle, the diaphragm is unique as it can work both as a voluntary and involuntary muscle . Humans do have some control over it, as we can increase or decrease the rate of inhalation, or hold our breath . However, it functions on its own most of the time.
Associated Conditions
- Diaphragm Spasms: Sometimes, the diaphragm spasms causing harmless hiccups may last for days or weeks, indicating some underlying health condition. Sometimes, this abnormally contracted muscle may make it difficult to breathe deeply, leading to other problems . Paralyzed Diaphragm: A trauma to the phrenic nerves, lung or lymph node cancer, injury or surgical trauma …