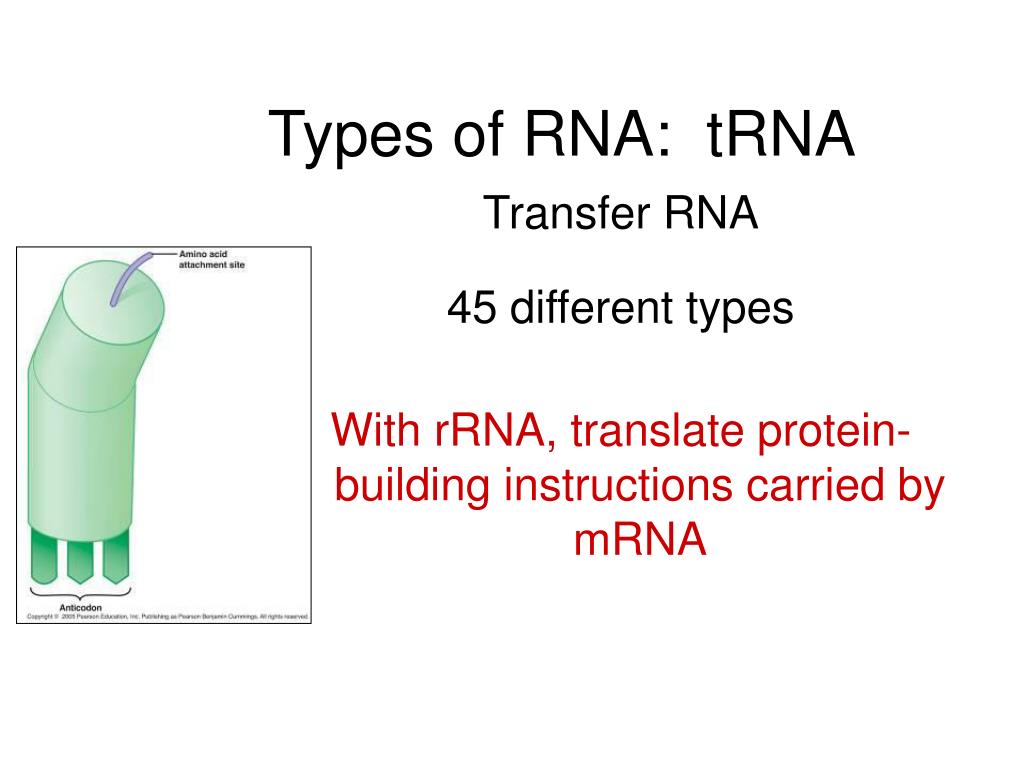
What is the tRNA that carries the amino acid for its anticodon?
How does rRNA work?
What type of RNA is responsible for delivering amino acids to the translation site?
What is the function of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
How many tRNAs are there for each type of amino acid?
What is the function of ribosomal RNA?
What is the mRNA strand made of?
See 2 more
About this website
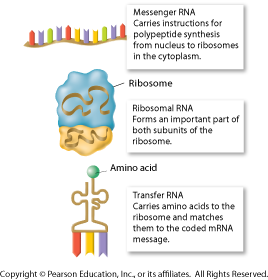
What type of RNA does translation?
messenger RNA (mRNA)Translation is the process by which a protein is synthesized from the information contained in a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA).
Is rRNA involved in translation?
Yes, ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is involved in translation because rRNA makes up the majority of a ribosome and it's the ribosomes that perform the translation of the data in an mRNA strand into a polypeptide chain.
Which type of RNA carries an amino acid and an anticodon used in translation?
The tRNA molecule has a distinctive folded structure with three hairpin loops that form the shape of a three-leafed clover. One of these hairpin loops contains a sequence called the anticodon, which can recognize and decode an mRNA codon. Each tRNA has its corresponding amino acid attached to its end.
Does translation require mRNA tRNA and rRNA?
Answer and Explanation: Translation requires mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. Translation is the process in which proteins are made from messenger RNA (mRNA).
Is tRNA used in translation?
Introduction. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are adaptor molecules that translate genetic information into protein sequence by delivering amino acids to the protein synthesis machinery during translation.
Does tRNA or mRNA carry amino acids?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules carry the coding sequences for protein synthesis and are called transcripts; ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules form the core of a cell's ribosomes (the structures in which protein synthesis takes place); and transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carry amino acids to the ribosomes during protein ...
Does rRNA carry amino acids?
Ribosomal RNA The rRNA also carries the enzymes required to bond the amino acids together. The rRNA attaches to the strand of mRNA, moving along like a zipper as it binds the amino acids together.
How is each type of RNA mRNA tRNA and rRNA used in translation?
The mRNA (messenger RNA) carries the info regarding what protein is to be made. Which amino acid is supposed to be where is written in here. The tRNA (transport RNA) carries the amino acid to the rRNA. The rRNA (ribosomal RNA) makes up the ribosome.
What is the role of rRNA in translation process?
The primary function of rRNA is in protein synthesis – in binding to messenger RNA and transfer RNA to ensure that the codon sequence of the mRNA is translated accurately into amino acid sequence in proteins.
What is rRNA and what is its role in translation?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) rRNAs combine with proteins and enzymes in the cytoplasm to form ribosomes, which act as the site of protein synthesis. These complex structures travel along the mRNA molecule during translation and facilitate the assembly of amino acids to form a polypeptide chain.
Is rRNA involved in transcription?
These results indicate that the rate of rRNA gene transcription and cell growth are positively correlated with the expression level of genes involved in rRNA gene transcription, including B23.
What do tRNA and rRNA do during translation?
During translation, these tRNAs carry amino acids to the ribosome and join with their complementary codons. Then, the assembled amino acids are joined together as the ribosome, with its resident rRNAs, moves along the mRNA molecule in a ratchet-like motion.
Why is rRNA important in translation?
Since rRNA is the main building block of ribosomes, it has a very large and important role in translation. It basically holds the single stranded mRNA in place so the tRNA can match up its anticodon with the mRNA codon that codes for a specific amino acid.
What is the tRNA anticodon?
The tRNA anticodon is a complementary sequence of the mRNA codon. The tRNA is therefore ensured to match up with the correct part of the mRNA and the amino acids will then be in the right order for the protein.
What is the role of miRNA in gene expression?
miRNA is thought to be a control mechanism leftover from evolution. (Getty/MOLEKUUL) Also involved in gene expression is micro RNA (or miRNA). miRNA is a non-coding region of mRNA that is believed to be important in the either promotion or inhibition of gene expression.
What is the role of tRNA in translation?
Transfer RNA (or tRNA) has the important job of making sure the correct amino acids are put into the polypeptide chain in the correct order during the process of translation. It is a highly folded structure that holds an amino acid on one end and has what is called an anticodon on the other end. The tRNA anticodon is a complementary sequence of the mRNA codon. The tRNA is therefore ensured to match up with the correct part of the mRNA and the amino acids will then be in the right order for the protein. More than one tRNA can bind to mRNA at the same time and the amino acids can then form a peptide bond between themselves before breaking off from the tRNA to become a polypeptide chain that will be used to eventually form a fully functioning protein.
What is the process of mRNA?
Before mRNA can move on to the next step of gene expression, it first must undergo some processing. There many regions of DNA that do not code for any genetic information. These non-coding regions are still transcribed by mRNA. This means the mRNA must first cut out these sequences, called introns, before it can be coded into a functioning protein. The parts of mRNA that do code for amino acids are called exons. The introns are cut out by enzymes and only the exons are left. This now single strand of genetic information is able to move out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm to begin the second part of gene expression called translation.
What is the part of mRNA that codes for amino acids called?
This means the mRNA must first cut out these sequences, called introns , before it can be coded into a functioning protein. The parts of mRNA that do code for amino acids are called exons . The introns are cut out by enzymes and only the exons are left.
What are the nitrogen bases in mRNA?
Three adjacent nitrogen bases in the mRNA sequence is called a codon and they each code for a specific amino acid that will then be linked with other amino acids in the correct order to make a protein. Before mRNA can move on to the next step of gene expression, it first must undergo some processing.
What is the function of RNA polymerase?
RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA from DNA that is functionally for protein-coding (messenger RNA, mRNA) or non-coding (RNA genes). Because of these functions, RNA molecules are of following types: messenger RNA (mRNA) – It is the RNA that carries information from DNA to the ribosomes (site of protein synthesis) in the cell.
How many nucleotides are in ribosomal proteins?
The small subunit along with ribosomal proteins has a sedimentation rate of the 30S. This is paired with the larger subunit, having two RNA molecules – one that is nearly 3000 nucleotides (23S) in length and the other is a short sequence of 120 nucleotides (5S).
What type of mRNA is found in RBCs?
Some types of mRNA are specific for certain types of cells, which encode for the proteins that are needed for the function of that particular cell such as mRNA for hemoglobin is found in Red Blood Cells (RBCs). Figure: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Messenger RNA (mRNA). Image Source: ScienceDirect.
What is the mRNA code used for?
transfer RNA (tRNA) – It is used to transfer specific amino acids to growing polypeptide chains at the ribosomal site of protein synthesis during translation.
How many nucleotides are in the small subunit of RNA?
The small subunit is made up of two short rRNA molecules that are less than 200 nucleotides in length (5S and 5.8S), and the large subunit which is made up of two large molecules that are longer, one which has over 5kb (28S) and a second one with 2kilobases (18S).
How many nucleotides are in a prokaryotic subunit?
The small subunits of the prokaryotes are made of an RNA molecule of about 1500 nucleotides in length with a Svedberg coefficient of 16S.
Where is RNA synthesized?
The rRNA is synthesized or transcribed in the cell nucleus, specifically in the nucleoli. The nucleoli play a major role in the biogenesis of ribosomes via the sequestration of ribosomal proteins.
What is the start codon in mRNA?
Our cells use a very smart strategy to solve this problem – the “start codon”. Because the translation only begins at the start codon (AUG) and continues in successive groups of three, the position of the start codon ensures that the mRNA is read in the correct frame (in the example above, in Frame 3).
What is the name of the mRNA molecule that Nirenberg discovered?
Nirenberg started with an mRNA molecule consisting only of the nucleotide uracil (called poly-U). When he added poly-U mRNA to the cell-free system, he found that the polypeptides made consisted exclusively of the amino acid – Phenylalanine (Phe). Nirenberg concluded that UUU might code for phenylalanine. Using the same approach, he discovered that triplet CCC codes for Proline (Pro).
What is the relationship between amino acids and codons called?
The full set of relationships between codons and amino acids (or stop signals) is called the genetic code . The genetic code is often summarized in a codon chart (or codon table), where codons are translated to amino acids.
What is the order of the protein translation?
mRNA codons are read from 5′ end to 3′ end, and its order specifies the order of amino acids in a protein from N-terminus to C-terminus.
Why are codons used in natural selection?
Codon usage biases could be the consequence of natural selection (tRNA abundance ). For laboratories to produce certain proteins in a large quantity, researchers may perform “codon optimization” to resynthesize genes in such a way that their codons are more appropriate for the desired expression host (i.e., making human proteins in E coli. bacteria).
What did Nirenberg do in a test tube?
Nirenberg did so in a test tube of cytoplasm from burst E. coli bacteria, which contains all the ingredients needed for translation.
How many stop codons are there in a protein?
Three “ Stop ” codons mark the end of a protein and terminate the translation.
What is the tRNA that carries the amino acid for its anticodon?
The tRNA also carries the corresponding amino acid for its anticodon. The tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome (rRNA). The amino acid is then "dropped off" and is fused with the growing chain of amino acids based off of the mRNA sequence. This ultimately creates the protein coded for by the DNA.
How does rRNA work?
The rRNA attaches to the strand of mRNA, moving along like a zipper as it binds the amino acids together. Multiple mRNAs can be attached and working simultaneously at different points along the mRNA strand.
What type of RNA is responsible for delivering amino acids to the translation site?
To carry out this process, there are three types of RNA: messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA. It is the transfer RNA, also called tRNA, that is responsible for delivering the correct amino acids to the translation site. Amino acids are carried to the ribosomes by units of tRNA. 00:00. 00:00 12:50. GO LIVE.
What is the function of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
The ribosome serves as the stabilizing structure during the protein syntheses process. It essentially is the site of protein synthesis, almost like a protein factory. The rRNA also carries the enzymes required to bond the amino acids together. The rRNA attaches to the strand of mRNA, moving along like a zipper as it binds the amino acids together.
How many tRNAs are there for each type of amino acid?
There is at least one tRNA for each type of amino acid. The tRNA is relatively small and resembles the configuration of a clover leaf. Each tRNA has a nucleotide triplet, called an anticodon. This anticodon is the opposite match for one codon on the mRNA. The tRNA also carries the corresponding amino acid for its anticodon.
What is the function of ribosomal RNA?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) functions as the factory, providing the structure for the synthesis process and performing the bonding work. Transfer RNA (tRNA) functions as the delivery vehicle, collecting and dropping off the correct amino acids to the factory, or translation site.
What is the mRNA strand made of?
This mRNA strand is made up of triplets of nucleotides that are called codons. Each of these codons represents one amino acid.
