
Types of signaling molecules
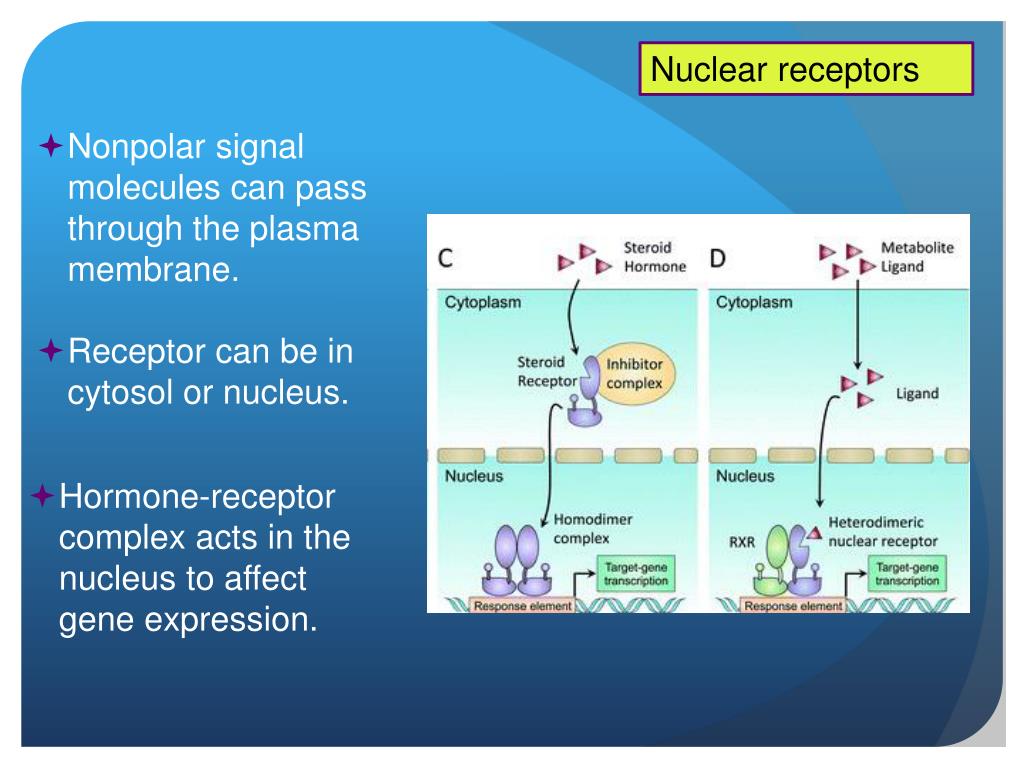
- Small Hydrophobic Ligands Small hydrophobic ligands can directly diffuse through the plasma membrane and interact with internal receptors. ...
- Water-Soluble Ligands Water-soluble ligands are polar and therefore cannot pass through the plasma membrane unaided; sometimes, they are too large to pass through the membrane at all. ...
- Other Ligands Nitric oxide (NO) is a gas that also acts as a ligand. ...
Which of the following molecules is involved in cell signaling?
The molecules involved in cell signaling are signaling molecules, such as hormones or local transmitters, their receptors, and the internal proteins of the cell that transduce the external signal to create internal changes in the cell.
What are the different types of signaling molecules?
Types of signaling molecules. Ligands are produced by signaling cells and act as chemical signals that travel to target cells to coordinate responses. The types of molecules that serve as ligands are incredibly varied and range from small proteins to small ions like calcium (Ca2+).
What is the difference between a signaling molecule and receptor?
The signaling molecule and receptor are specific to each other, so for a cell to respond to a signaling molecule, it must have the corresponding receptor. Typically, signaling molecules are unable to cross the cell membrane, or plasma membrane, although there are some exceptions.
How do signaling molecules cross the membrane?
Some signaling molecules are able to cross the plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus, whereas most bind to receptors expressed on the target cell surface. The sections that follow discuss the major types of signaling molecules and the receptors with which they interact.
What are hydrophobic ligands?
Which hormones are hydrophobic?
What is the role of nitric oxide in the body?
How are ligands produced?
Where do most ligands bind to?
Does NO cause blood vessels to dilate?
See 1 more
Which molecule is used for cell signaling?
The binding of adrenaline to an adrenergic receptor initiates a cascade of reactions inside the cell. The signal transduction cascade begins when adenylyl cyclase, a membrane- bound enzyme, is activated by G-protein molecules associated with the adrenergic receptor.
Are proteins used as signaling molecules?
Another major class of signaling enzymes is guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins, also called G proteins, a large family of signaling proteins that control a wide array of cellular functions, including motility, hormone responses, sensory perception, and neurotransmission. G proteins function as molecular switches.
What are the 5 types of cell signaling?
What are the different types of cell signalling?Paracrine signalling.Autocrine signalling.Endocrine signalling.Direct Contact.
What is an example of signal molecule?
The steroid hormones are the classic examples of this group of signaling molecules, which also includes thyroid hormone, vitamin D3, and retinoic acid (Figure 13.2).
What are the four types of cell signaling?
Depending on the ligand's origin (from the same cell, from the neighbour cell or from far distance), recptor-ligand interaction and signaling pathway activation is classified into four different types: autocrine, endocrine, paracrine and juxtacrine.
What are some examples of cell signaling?
An example is the conduction of an electric signal from one nerve cell to another or to a muscle cell. In this case the signaling molecule is a neurotransmitter. In autocrine signaling cells respond to molecules they produce themselves.
What is cell cell signaling?
Cell signaling is the fundamental process by which specific information is transferred from the cell surface to the cytosol and ultimately to the nucleus, leading to changes in gene expression.
What is molecular signalling?
Molecular signaling includes the molecules which perform by transmitting information between cells in the body. However the molecular characteristics of signaling molecules can differ highly. Some the molecules transmit signals for a short distance however some of them carry over long distances.
What is the role of the protein molecules classified as enzymes?
Enzymes are proteins that act upon substrate molecules and decrease the activation energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur by stabilizing the transition state. This stabilization speeds up reaction rates and makes them happen at physiologically significant rates.
Which of the following signal molecules is not used for extracellular signaling?
Which of the following signal molecules is not used for extracellular signaling? Which of the following signal molecules does not interact with cell surface receptors? Sol: (d) Testosterone.
What is an example of endocrine signaling?
In endocrine signaling hormones are produce by an endocrine gland and sent through the blood stream to distant cells. Hormones can be: small lipophilic molecules that diffuse through the cell membrane to reach cytosolic or nuclear receptors. Examples are progesterone and testosterone, as well as thyroid hormones.
Can proteins function as structural molecules?
Figure 2 : Proteins can have a structural role in a cell. Actin filaments (red) and microtubules (green) are two different kinds of proteins that provide structure to cells.
Cell Signaling | 5 Types Explained with Suitable Examples - Study Read
Example: Endocrine gland cells secrete hormones to affect the distant cell.. Synaptic signaling. This is a signal which occurs between two nerve cells. It is specific and occurs only at the nervous tissue.. Here the signal is passed from one nerve cells to another through the neurotransmitter.. The nerve cell secretes acetylcholine, dopamine, and other neurotransmitters at its nerve ending ...
Signaling Molecules Overview & Types - Study.com
Explore signaling molecules. Learn the definition of a signaling molecule and understand its different types. Find the steps of the process of cell...
Signaling Molecules: Definition & Concept - Study.com
Signaling molecules are used to carry messages with instructions for how to perform a variety of cellular functions. Learn the definition of this concept, the process of these molecules, and the ...
Signaling Molecules and Their Receptors - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf
Many different kinds of molecules transmit information between the cells of multicellular organisms. Although all these molecules act as ligands that bind to receptors expressed by their target cells, there is considerable variation in the structure and function of the different types of molecules that serve as signal transmitters. Structurally, the signaling molecules used by plants and ...
What are hydrophobic ligands?
Important members of this class of ligands are the steroid hormones.
Which hormones are hydrophobic?
Other hydrophobic hormones include thyroid hormones and vitamin D. Figure 1 Steroid hormones have similar chemical structures to their precursor, cholesterol. Because these molecules are small and hydrophobic, they can diffuse directly across the plasma membrane into the cell, where they interact with internal receptors.
What is the role of nitric oxide in the body?
It is able to diffuse directly across the plasma membrane, and one of its roles is to interact with receptors in smooth muscle and induce relaxation of the tissue. NO has a very short half-life and therefore only functions over short distances.
How are ligands produced?
Ligands are produced by signaling cells and act as chemical signals that travel to target cells to coordinate responses. The types of molecules that serve as ligands are incredibly varied and range from small proteins to small ions like calcium (Ca 2+ ).
Where do most ligands bind to?
Instead, most water-soluble ligands bind to the portion of a cell-surface receptor which is on the outside of the cell. This group of ligands is quite diverse and includes small molecules, peptides (short chains of amino acids), and proteins.
Does NO cause blood vessels to dilate?
NO has a very short half-life and therefore only functions over short distances. Nitroglycerin, a treatment for heart disease, acts by triggering the release of NO, which causes blood vessels to dilate (expand), thus restoring blood flow to the heart.
How do signaling molecules affect the behavior of nearby cells?
In contrast to hormones, some signaling molecules act locally to affect the behavior of nearby cells. In paracrine signaling, a molecule released by one cell acts on neighboring target cells. An example is provided by the action of neurotransmitters in carrying signals between nerve cells at a synapse. Finally, some cells respond to signaling molecules that they themselves produce. One important example of such autocrine signalingis the response of cells of the vertebrate immune system to foreign antigens. Certain types of T lymphocytes respond to antigenic stimulation by synthesizing a growth factor that drives their own proliferation, thereby increasing the number of responsive T lymphocytes and amplifying the immune response. It is also noteworthy that abnormal autocrine signalingfrequently contributes to the uncontrolled growth of cancercells (see Chapter 15). In this situation, a cancer cell produces a growth factor to which it also responds, thereby continuously driving its own unregulated proliferation.
How do signaling molecules work?
Many different kinds of molecules transmit information between the cells of multicellular organisms. Although all these molecules act as ligands that bind to receptors expressed by their target cells, there is considerable variation in the structure and function of the different types of molecules that serve as signal transmitters. Structurally, the signaling molecules used by plants and animals range in complexity from simple gases to proteins. Some of these molecules carry signals over long distances, whereas others act locally to convey information between neighboring cells. In addition, signaling molecules differ in their mode of action on their target cells. Some signaling molecules are able to cross the plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus, whereas most bind to receptors expressed on the target cell surface. The sections that follow discuss the major types of signaling molecules and the receptors with which they interact. Subsequent discussion in this chapter focuses on the mechanisms by which cell surface receptors then function to regulate cell behavior.
What is the action of steroid hormones?
The steroid hormones diffuse across the plasma membrane and bind to nuclear receptors, which directly stimulate transcription of their target genes. The steroid hormone receptors bind DNA as dimers.
What are the signaling molecules in animals?
The widest variety of signaling molecules in animals are peptides, ranging in size from only a few to more than a hundred amino acids . This group of signaling molecules includes peptide hormones, neuropeptides, and a diverse array of polypeptidegrowth factors(Table 13.1). Well-known examples of peptide hormonesinclude insulin, glucagon, and the hormones produced by the pituitary gland (growth hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, prolactin, and others).
How does nitric oxide work?
Nitric oxide is synthesized from the amino acidarginine by the enzyme nitric oxide synthase (Figure 13.5). Once synthesized, NO diffuses out of the cell and can act locally to affect nearby cells. Its action is restricted to such local effects because NO is extremely unstable, with a half-life of only a few seconds. One well-characterized example of NO action is signaling the dilation of blood vessels. The first step in this process is the release of neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, from the terminus of nerve cells in the blood vessel wall. These neurotransmitters act on endothelial cells to stimulate NO synthesis. NO then diffuses to neighboring smooth muscle cells where it reacts with iron bound to the active siteof the enzyme guanylyl cyclase. This increases enzymatic activity, resulting in synthesis of the second messengercyclic GMP (discussed later in this chapter), which induces muscle cell relaxation and blood vessel dilation. For example, NO is responsible for signaling the dilation of blood vessels that leads to penile erection. It is also interesting to note that the medical use of nitroglycerin in treatment of heart disease is based on its conversion to NO, which dilates coronary blood vessels and increases blood flow to the heart.
How does cell signaling take place?
Modes of cell-cell signaling. Cell signaling can take place either through direct cell-cell contacts or through the action of secreted signaling molecules. (A) In endocrine signaling, hormones are carried through the circulatory system to act on distant (more...)
How does signaling work in animal cells?
Signaling by direct cell-cell (or cell-matrix) interactions plays a critical role in regulating the behavior of cells in animal tissues. For example, the integrins and cadherins(which were discussed in the previous chapter) function not only as cell adhesion moleculesbut also as signaling molecules that regulate cell proliferation and survival in response to cell-cell and cell-matrix contacts. In addition, cells express a variety of cell surface receptors that interact with signaling molecules on the surface of neighboring cells. Signaling via such direct cell-cell interactions plays a critical role in regulating the many interactions between different types of cells that take place during embryonic development, as well as in the maintenance of adult tissues.
What happens when phosphorylation induces activation?
If phosphorylation induces activation, the longer a signalling protein is active, the more downstream signalling molecules it can activate (or the longer that second messengers are synthesized or released by an active signalling protein, the higher the concentrations that they achieve).
What is the phosphate derived from?
The phosphate is derived from the terminal (γ) phosphate of ATP, and added covalently to a tyrosine, serine or threonine residue by a protein kinase. Phosphorylation usually, but not necessarily, activates a protein. Sometimes, however, it may cause a conformational change that inactivates the protein.
How does a protein switch between active and inactive?
In both, the protein switches between the active and the inactive conformation by the addition/removal of a phosphate group. (a) In the case of proteins that are phosphorylated, the phosphate is derived from the terminal phosphate of ATP, and then added covalently to a tyrosine, serine or threonine residue by a kinase.
What is the function of second messengers?
With second messengers, it is easy to understand: they are produced or released in large quantities, diffuse to their target, to which they usually bind, bringing about a functional change , after which they are degraded or stored within a subcellular compartment (such as endoplasmic reticulum). With signalling proteins it is less obvious.
Why are proteins called molecular switches?
The reason why such molecules are sometimes referred to as molecular switches is because they are either ‘on’ or ‘off’. These proteins can be grouped according to how they are switched on/off, rather than their subsequent mode of action. As outlined above and in Figure 8. 63.
Can a molecular switch be a single on/off function?
Molecular switches can be a lot more sophisticated than a single on/off function. A protein can be phosphorylated at multiple sites, which may have different effects on its activity. Integrate many different signals such that the signalling outcome is determined by the summation of signalling inputs.
Is GTP a phosphate?
The GTP is hydrolysed back to GDP ( again, releasing Pi) by either intrinsic or accessory (via GTPase activating proteins, GAPs) GTPase activity. ). The phosphate is derived from the terminal (γ) phosphate of ATP, and added covalently to a tyrosine, serine or threonine residue by a protein kinase.
What are hydrophobic ligands?
Important members of this class of ligands are the steroid hormones.
Which hormones are hydrophobic?
Other hydrophobic hormones include thyroid hormones and vitamin D. Figure 1 Steroid hormones have similar chemical structures to their precursor, cholesterol. Because these molecules are small and hydrophobic, they can diffuse directly across the plasma membrane into the cell, where they interact with internal receptors.
What is the role of nitric oxide in the body?
It is able to diffuse directly across the plasma membrane, and one of its roles is to interact with receptors in smooth muscle and induce relaxation of the tissue. NO has a very short half-life and therefore only functions over short distances.
How are ligands produced?
Ligands are produced by signaling cells and act as chemical signals that travel to target cells to coordinate responses. The types of molecules that serve as ligands are incredibly varied and range from small proteins to small ions like calcium (Ca 2+ ).
Where do most ligands bind to?
Instead, most water-soluble ligands bind to the portion of a cell-surface receptor which is on the outside of the cell. This group of ligands is quite diverse and includes small molecules, peptides (short chains of amino acids), and proteins.
Does NO cause blood vessels to dilate?
NO has a very short half-life and therefore only functions over short distances. Nitroglycerin, a treatment for heart disease, acts by triggering the release of NO, which causes blood vessels to dilate (expand), thus restoring blood flow to the heart.
