What is the exclusion zone?
What is the warm zone?
Why are safety zones established?
What is a support zone?
See 1 more
About this website

What is the zone of contamination called?
The Exclusion ZoneThe Exclusion Zone is the area where contamination does or could occur. The primary activities performed in the Exclusion Zone are: Site characterization, such as mapping. photographing, and sampling.
What are the 4 zones of a decontamination site?
OSHA HAZWOPER Work Zone ClassificationExclusion Zone. The Exclusion Zone is where the actual contamination occurs or could occur. ... Contamination Reduction Zone. ... Support Zone.
What are the 3 hazmat zones?
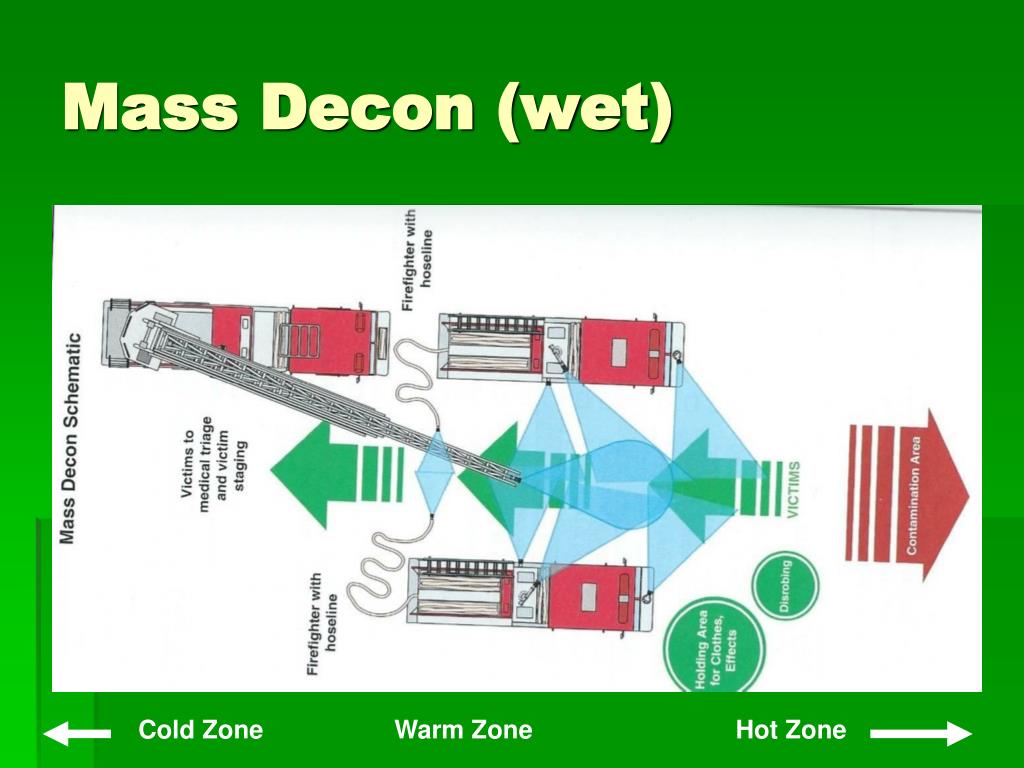
Most incident scenes will have at least three zones: Hot Zone (contaminated area), Warm Zone (the area where decontamination of personnel and equipment takes place) and the Cold Zone (the uncontaminated area where workers should not be exposed to hazardous conditions).
What zone is used for decontamination?
At a hazardous waste site, decontamination facilities should be located in the Contamination Reduction Zone (CRZ), i.e., the area between the Exclusion Zone (the contaminated area) and the Support Zone (the clean area) as shown in 3.
What is the cold zone?
The support zone (or cold zone) is the area of the site that is free from contamination and that may be safely used as a planning and staging area.
What occurs in the warm zone?
Warm Zone means the controlled transition zone between the Hot Zone and the Cold Zone, where Hot Zone support, medical management of patients (if required) and the decontamination of individuals and equipment takes place, and which requires the use of personal protective equipment.
What is hazard Zone A?
Hazard Zone A: More that one liter (1.08 quarts) per package of a "material poisonous by inhalation," as defined in 171.8 of 49 CFR, that meets the criteria for "hazard zone A," as specified in 173.116(a) or 173.133(a) of 49 CFR.
What are safety zones?
A safety zone is a location where a threatened firefighter can find adequate refuge from an approaching fire. What is the difference between a safety zone and a deployment site? In a safety zone, a firefighter can survive without using a fire shelter.
What are the hot warm and cold zones?
The terms hot, warm and cold zones (some jurisdictions may refer to these zones as red, yellow and green zones) describe the degree of hazard. The hot zone typically describes an IDLH environment; the warm and cold zones describe less-hazardous environments.
What are the 3 levels of decontamination?
There are three levels of decontamination, general cleaning, disinfection and sterilisation. Equipment used in health care may be designated as single use, single patient use or reusable multi-patient use.
Where can contaminants be found?
Most contaminants enter the environment from industrial and commercial facilities; oil and chemical spills; non-point sources such as roads, parking lots, and storm drains; and wastewater treatment plants and sewage systems.
What are the four decontamination stages?
The key stages of the decontamination process are: pre-sterilisation cleaning. disinfection. inspection.
What are safety zones?
A safety zone is a location where a threatened firefighter can find adequate refuge from an approaching fire. What is the difference between a safety zone and a deployment site? In a safety zone, a firefighter can survive without using a fire shelter.
What is the fourth step in all three levels of the decontamination line?
There are 4 main categories of physical and chemical means of decontamination: (1) heat; (2) liquid disinfection; (3) vapors and gases; and (4) radiation.
In which of the following zones are proper decontamination methods implemented based on the hazard?
At a hazardous waste site, decontamination facilities should be located in the Contamination Reduction Zone (CRZ), which is the area between the Exclusion Zone (the contaminated area) and the Support Zone (the clean area).
What are the methods of decontamination?
Methods of decontaminationPhysical cleaning. ... Ultrasonication. ... Disinfection. ... Antisepsis. ... Sterilisation. ... Disinfection and sterilisation using heat. ... Autoclaving. ... Thermal washer disinfection.More items...•
Know your hazmat zones | ISHN
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 1992 Standard on Liquid Splash-Protective Ensembles and Clothing for Hazardous Materials Emergencies, 2005 Edition, is designed to set the minimum protection requirements for PPE for persons involved in the warm zone — or second tier — decontamination areas where Level B, C and D protection is needed.
AWR 160 pretest Flashcards | Quizlet
According to Title 18 United States Code (USC) § 2332a, "...any weapon that is designed or intended to cause death or serious bodily injury through the release, dissemination, or impact of toxic or poisonous chemical or their precursors" is called a:
Hot, Warm, and Cold Zones
is an emergency medicine physician who currently serves as professor and vice chairman of Opera - tional Medicine at Georgia Regents University, Augusta, Geor -
HazMat Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which acronym is used to remember potential WMD material? A) TRACEM B) NIMS C) RAIN D) CBRNE, Which of the three components of the NIMS systematically manages personnel, supplies, teams, and facilities? A) ongoing management and maintenance B) planning C) resource management D) communications and information management, Which of ...
Where can contaminants be found?
Contaminants can be located either on the surface of personal protective equipment or permeated into the PPE material. Surface contaminants may be easy to detect and remove; however, contaminants that have permeated a material are difficult or impossible to detect and remove. If contaminants that have permeated a material are not removed by decontamination, they may continue to permeate to either surface of the material where they can cause an unexpected exposure.
Where should decontamination facilities be located?
At a hazardous waste site, decontamination facilities should be located in the Contamination Reduction Zone (CRZ), i.e., the area between the Exclusion Zone (the contaminated area) and the Support Zone (the clean area) as shown in 3.
What is the purpose of the decontamination chapter?
In addition, this chapter provides general guidelines for designing and selecting decontamination procedures at a site, and it presents a decision aid for evaluating the health and safety aspects of decontamination methods. The chapter does not cover decontamination of radioactively contaminated personnel or equipment. A health physicist should be consulted if this situation arises.
What is decontamination in hazardous waste?
Decontamination - the process of removing or neutralizing contaminants that have accumulated on personnel and equipment - is critical to health and safety at hazardous waste sites. Decontamination protects workers from hazardous substances that may contaminate and eventually permeate the protective clothing, respiratory equipment, tools, vehicles, and other equipment used on site; it protects all site personnel by minimizing the transfer of harmful materials into clean areas; it helps prevent mixing of incompatible chemicals; and it protects the community by preventing uncontrolled transportation of contaminants from the site.
Why is decontamination important?
While decontamination is performed to protect health and safety, it can pose hazards under certain circumstances. Decontamination methods may: Be incompatible with the hazardous substances being removed (Le., a decontamination method may react with contaminants to produce an explosion, heat, or toxic products).
How many stations are there in a decontamination line?
1.3 The maximum decontamination procedures for all levels of protection consist of specific activities at nineteen stations. Each station emphasizes-an important aspect of decontamination. When establishing a decontamination line, each aspect should be incorporated separately or combined with other aspects into a procedure with fewer steps (such as the Minimum Decontamination Procedures).
Why is contact time important in decontamination?
Contact time. The longer a contaminant is in contact with an object, the greater the probability and extent of permeation. For this reason, minimizing contact time is one of the most important objectives of a decontamination program.
What is the transition zone between the contaminated area and the clean area?
The Contamination Reduction Zone lies outside the Hotline and serves as the transition area between the contaminated area (the Exclusion Zone) and the clean area (the Support Zone).
What is the boundary of the exclusion zone?
The Exclusion Zone is where the actual contamination occurs or could occur. The boundary of the Exclusion Zone is called the “Hotline, ” and should be clearly marked with lines, placards, hazard tape, or signs. Sometimes even physical barriers like fences or ropes are used around the Hotline to block off the Exclusion Zone.
What is the Contamination Reduction Corridor?
While the area of the Contamination Reduction Zone that is nearest the Hotline remains contaminated, the level of contamination decreases the further away you move from the Hotline in the direction of the Support Zone. Within the Contamination Reduction Zone is an area called the “Contamination Reduction Corridor.”.
What is the support zone?
The Support Zone is the outermost zone that borders the Contamination Reduction Zone. This is where administrative and other support personnel remain in order to regulate the activities happening in the other work zones and to oversee the operation at large.
What are the activities that are required to be performed in an exclusion zone?
The primary activities performed inside the Exclusion Zone include: Mapping, photographing, and sampling. Installation of wells. Cleanup work.
What is an access control point?
Access Control Points are usually established to regulate the personnel and equipment entering and exiting the Exclusion Zone.
How many work zones are there in OSHA?
There are three distinct work zones as defined by OSHA.
Group, private, package and specialist trips to Chernobyl, Pripyat and Ukraine
Contamination Zone is a group of people who are united by our love for the Chernobyl Zone – we spend large parts of our life talking and teaching about the zone because it is so much more than “just a place” or “just a job” to us.
Reviews
I went with my two friends on a 1 day private tour with Contamination Zone.
What is contaminated zone?
A Contaminated Zone is an area of the map that contain toxic gas, which will rapidly injure and then kill any players going into the zone unprepared.
What will contaminated zones do to wildlife?
Contaminated Zones will also kill all other types of Infected and Wildlife in an area and replace it with a Military NBC variant Infected .
How many stages are there in a dynamic contaminated zone?
A dynamic Contaminated Zone can be broken down into 3 stages.
How often do dynamic contaminated zones spawn?
Dynamic Contaminated Zones are a type of Dynamic Event that will spawn across the map around once every 15 minutes. There can be between 2-4 on the map at any one time spread across 78 possible positions on Chernarus .
What is the exclusion zone?
The three most frequently identified zones are below: The exclusion zone (or hot zone) is the area with actual or potential contamination and the highest potential for exposure to hazardous substances.
What is the warm zone?
The contamination reduction zone (or warm zone) is the transition area between the exclusion and support zones. This area is where responders enter and exit the exclusion zone and where decontamination activities take place.
Why are safety zones established?
These zones are established primarily to reduce the accidental spread of hazardous substances by workers or equipment from contaminated areas to clean areas. Safety zones specify: The type of operations that will occur in each zone;
What is a support zone?
The support zone (or cold zone) is the area of the site that is free from contamination and that may be safely used as a planning and staging area.
