What was the purpose of the Silk Road?
Silk Road. Written By: Silk Road, also called Silk Route, ancient trade route, linking China with the West, that carried goods and ideas between the two great civilizations of Rome and China. Silk went westward, and wools, gold, and silver went east.
When did the Silk Road open up trade?
The Silk Road may have formally opened up trade between the Far East and Europe during the Han Dynasty, which ruled China from 206 B.C. to 220 A.D., but the transport of goods and services along these routes dates back even further.
How did China make money on the Silk Road?
China Generated Wealth and Developed Economically. Silk and porcelain were the two bestselling products over the centuries of the Silk Road trade. Silk was the most valuable export on the Silk Road since it was light, easy to transport, and was said to be worth its weight in gold during the Roman era.
What goods were transported along the Silk Road?
An abundance of goods traveled along the Silk Road. Merchants carried silk from China to Europe, where it dressed royalty and wealthy patrons. Other favorite commodities from Asia included jade and other precious stones, porcelain, tea, and spices.
See more

How did countries benefit from the Silk Road?
The Silk Roads enriched the countries it passed through, transporting cultures, religions, languages and of course material goods into societies across Europe, Asia and Africa, and uniting them with a common thread of cultural heritage and pluralistic identities.
Who benefited the most from the Silk Road?
Everyone (East and West) benefited from the Silk Road. It opened up trade, communication, different ideas, culture, and religion to the entire world.
What was a major benefit of the Silk Road?
What was a major benefit of the Silk Road? - It created a unified economy across all of Asia. - It shortened travel time between China and Europe for traders. - It connected the countries to the north of China for travel and trade.
Who profited from the Silk Road and why?
Answer and Explanation: The main people who profited from the Silk Road were the wealthy merchants who could afford to finance a trading expedition that would takes years and have an uncertain outcome.
How did the Silk Road Benefit China?
The Silk Road was important because it helped to generate trade and commerce between a number of different kingdoms and empires. This helped for ideas, culture, inventions, and unique products to spread across much of the settled world.
Which city benefited the most from the Silk Road?
Answer: The correct answer is d which is Cairo. 'Silk Road' is in actuality a generally ongoing term, and for most of their long history, these old streets had no specific name.
What were the effects of the Silk Road?
For example the route contributed to the spread of Islam, with many Arab Muslims travelling along the Silk Road to China in order to spread the Islamic faith. Additionally Buddhism, Zoroastrianism, Manichaeism and Nestorianism were all introduced to China and parts of India because of the Silk Roads influence.
How did the Silk Road impact the economy?
The Silk Roads stretched across Eurasia, connecting East and West for centuries. At its height, the network of trade routes enabled merchants to travel from China to the Mediterranean Sea, carrying with them high-value commercial goods, the exchange of which encouraged urban growth and prosperity.
What city benefited the most from the Silk Road?
Answer: The correct answer is d which is Cairo. 'Silk Road' is in actuality a generally ongoing term, and for most of their long history, these old streets had no specific name.
Which group benefited economically from commerce on the Silk Road?
The east-west trade routes between Greece and China began to open during the first and second centuries B.C. The Roman Empire and the Kushan Empire (which ruled territory in what is now northern India) also benefitted from the commerce created by the route along the Silk Road.
What was the biggest impact of the Silk Road?
The Silk Road Legacy The greatest value of the Silk Road was the exchange of culture. Art, religion, philosophy, technology, language, science, architecture, and every other element of civilization was exchanged along these routes, carried with the commercial goods the merchants traded from country to country.
Which was the most important result of Silk Road trade?
One obvious effect of trade along the Silk Road was more goods were available in more places. Silk, owing to its soft texture and appealing shimmer, became so hotly desired that it was used as currency in central Asia.
How did the Silk Road affect the world?
It is hard to overstate the importance of the Silk Road on history. Religion and ideas spread along the Silk Road just as fluidly as goods. Towns along the route grew into multicultural cities. The exchange of information gave rise to new technologies and innovations that would change the world. The horses introduced to China contributed to the might of the Mongol Empire, while gunpowder from China changed the very nature of war in Europe and beyond. Diseases also traveled along the Silk Road. Some research suggests that the Black Death, which devastated Europe in the late 1340s C.E., likely spread from Asia along the Silk Road. The Age of Exploration gave rise to faster routes between the East and West, but parts of the Silk Road continued to be critical pathways among varied cultures. Today, parts of the Silk Road are listed on UNESCO ’s World Heritage List.
What goods did the Silk Road bring?
Other favorite commodities from Asia included jade and other precious stones, porcelain, tea, and spices. In exchange, horses, glassware, textile s, and manufactured goods traveled eastward.
Why is the Silk Road called the Silk Road?
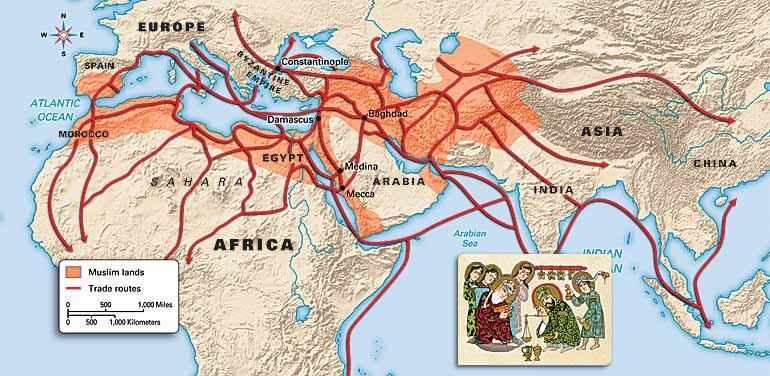
Although the trade network is commonly referred to as the Silk Road, some historians favor the term Silk Routes because it better reflects the many paths taken by traders. The Silk Road extended approximately 6,437 kilometers (4,000 miles) across some of the world’s most formidable landscapes, including the Gobi Desert and the Pamir Mountains.
What is the Silk Road?
Today, parts of the Silk Road are listed on UNESCO ’s World Heritage List. A tourist looks around the ancient city of Kharanaq, Iran. Towns such as these played a crucial role in the operation and success of the Silk Road. (1400s-1800s) period during which Europeans traveled the world by ocean in search of trade.
What did horses contribute to the Mongol Empire?
The horses introduced to China contributed to the might of the Mongol Empire, while gunpowder from China changed the very nature of war in Europe and beyond. Diseases also traveled along the Silk Road.
When was the Silk Road invented?
German geographer and traveler Ferdinand von Richthofen first used the term “silk road” in 1877 C.E. to describe the well-traveled pathway of goods between Europe and East Asia. The term also serves as a metaphor for the exchange of goods and ideas between diverse cultures. Although the trade network is commonly referred to as the Silk Road, ...
Who was the most famous traveler on the Silk Road?
One of the most famous travelers of the Silk Road was Marco Polo (1254 C.E. –1324 C.E.). Born into a family of wealthy merchants in Venice, Italy, Marco traveled with his father to China (then Cathay) when he was just 17 years of age. They traveled for over three years before arriving at Kublai Khan’s palace at Xanadu in 1275 C.E. Marco stayed on at Khan’s court and was sent on missions to parts of Asia never before visited by Europeans. Upon his return, Marco Polo wrote about his adventures, making him—and the routes he traveled—famous.
Why was the Silk Road untraveled?
With the gradual loss of Roman territory in Asia and the rise of Arabian power in the Levant, the Silk Road became increasingly unsafe and untraveled. In the 13th and 14th centuries the route was revived under the Mongols, and at that time the Venetian Marco Polo used it to travel to Cathay (China). It is now widely thought that the route was one of the main ways that plague bacteria responsible for the Black Death pandemic in Europe in the mid-14th century moved westward from Asia.
What was the Silk Road?
Silk Road, also called Silk Route, ancient trade route, linking China with the West, that carried goods and ideas between the two great civilizations of Rome and China. Silk went westward, and wools, gold, and silver went east. China also received Nestorian Christianity and Buddhism (from India) via the Silk Road.
How long did the Silk Road last?
The trade route from China to Asia Minor and India, known as the Silk Road, had been in existence for 1,400 years at the time of Marco Polo’s travels ( c. ad 1270–90). It came into partial existence about 300 bc, when it was…
How did the Silk Road become unsafe?
Few persons traveled the entire route, and goods were handled in a staggered progression by middlemen. With the gradual loss of Roman territory in Asia and the rise of Arabian power in the Levant, the Silk Road became increasingly unsafe and untraveled.
What did the Chinese export to the Western world?
Chinese merchants exported silk to Western buyers. From Rome and later from Christian kingdoms, wools, gold, and silver traveled eastward.
Is the Silk Road still in use?
Part of the Silk Road still exists, in the form of a paved highway connecting Pakistan and the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang, China. The old road has been the impetus behind a United Nations plan for a trans-Asian highway, and a railway counterpart of the road has been proposed by the UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP). The road inspired cellist Yo-Yo Ma to found the Silk Road Project in 1999, which explored cultural traditions along its route and beyond as a means for connecting arts worldwide across cultures.
Why is the Silk Road important?
The Silk Road Is an Important Tourist Attraction. Partly due to the recent news of the Chinese government's interest in reviving Silk Road trade , there is increased interest in touring the ancient trade routes' main sites in China, Central Asia and Europe. Backpackers are traveling the old trade routes between Europe and China by bus and rail.
How significant is the Silk Road?
1. The Longest Land Trade Route Connected the Most Powerful Civilizations.
What empires made porcelain?
Porcelain was heavier and fragile. Though the Han and later empires were the world leaders in its manufacture, it wasn't until the Song Empire and especially the Ming Empire (1368–1644) that the porcelain industry reached its height in China. Those two empires engaged in Maritime Silk Road trade, built big factories that increased productivity, and exported porcelain on a grand scale. See more about How Porcelain Changed China's Development.
Why did the Han Emperor initiate the Silk Road trade?
The main reason that the Han Emperor initiated Silk Road trade about the year 139 BC was to obtain the larger horse breeds. Camels were also prized for desert transportation, and sheep were another useful animal.
How did Buddhism affect China?
Buddhism affected China deeply from the Han era onwards through the adoption of Central Asian style Buddhism, and Christianity and Islam had less of an effect during the Silk Road times. The Mongols played a big role in spreading Islam by bringing in Muslims to live in their empire via the Silk Road routes.
What were the two major empires that were involved in the Han Dynasty?
During the Han Dynasty era, there were two other large contemporaneous empires in the West. These were the Parthian Empire in Central/West Asia and the Roman Empire in Europe and around the Mediterranean.
How many people died on the Silk Road?
It killed an estimated 75 to 200 million people in Eurasia, and in Europe it may have killed about 30 to 60% of the population. 4. China Generated Wealth and Developed Economically. Silk and porcelain were the two bestselling products over the centuries of the Silk Road trade.
What was the purpose of the Silk Road?
The Silk Road routes included a large network of strategically located trading posts, markets and thoroughfares designed to streamline the transport, exchange, distribution and storage of goods.
How long has the Silk Road been used?
Although it’s been nearly 600 years since the Silk Road has been used for international trade, the routes had a lasting impact on commerce, culture and history that resonates even today.
What was the Silk Road?
Eastward Exploration. Sources. The Silk Road was a network of trade routes connecting China and the Far East with the Middle East and Europe. Established when the Han Dynasty in China officially opened trade with the West in 130 B.C., the Silk Road routes remained in use until 1453 A.D., when the Ottoman Empire boycotted trade with China ...
Why did Marco Polo use the Silk Road?
The Silk Road routes also opened up means of passage for explorers seeking to better understand the culture and geography of the Far East. Venetian explorer Marco Polo famously used the Silk Road to travel from Italy to China, which was then under the control of the Mongolian Empire, where they arrived in 1275.
Why is the Silk Road called the Silk Road?
Even though the name “Silk Road” derives from the popularity of Chinese silk among tradesmen in the Roman Empire and elsewhere in Europe, the material was not the only important export from the East to the West.
Where did the Silk Road lead?
Silk Road routes also led to ports on the Persian Gulf, where goods were then transported up the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Routes from these cities also connected to ports along the Mediterranean Sea, from which goods were shipped to cities throughout the Roman Empire and into Europe.
Which empires were involved in the Silk Road?
The east-west trade routes between Greece and China began to open during the first and second centuries B.C. The Roman Empire and the Kushan Empire (which ruled territory in what is now northern India) also benefitted from the commerce created by the route along the Silk Road.