How did the Gupta Empire end?
The Huna People, also known as Huns, invaded Gupta territory and caused significant damage to the empire. The Gupta Empire ended in 550 CE, when it disintegrated into regional kingdoms after a series of weak rulers and invasions from the east, west, and north.
How did the Guptas defeat the Hunas?
The Hunas were ultimately defeated by a coalition of Indian princes that possibly included the Indian king Yasodharman. He and possibly the Gupta emperor, Narasimhagupta, defeated a Huna army and their ruler Mihirakula in 528 CE and drove them out of India. The Guptas are thought to have played only a minor role in this campaign.
Who was the last king of the Gupta dynasty?
The last great king of the Gupta dynasty, Skandagupta was the son of Kumaragupta I. He was able to repulse an attack by the Hunas but this strained his empire’s coffers. The Gupta Empire declined after the death of Skandagupta in 467 AD. He was followed by many successors.
Who became the overlord of North India after the Gupta Empire?
He followed by hisson, Mihirakula, who became the overlord of north India. Indeed he was defeated by Yashodharman of Malwa but the repercussions of these invasions were disastrous for the Gupta Empire.
See more

How did the Gupta Empire end?
The Gupta empire ended with the invasion of the White Huns, a nomadic tribe of people from central Asia, at the end of the fifth century CE. Until the sixteenth century, there was no unifying empire; regional political kingdoms ruled India.
Who had destroyed the Gupta Empire?
In the 480's the Alchon Huns under Toramana and Mihirakula broke through the Gupta defences in the northwest, and much of the empire in the northwest was overrun by the Huns by 500. According to some scholars the empire disintegrated under the attacks of Toramana and his successor Mihirakula.
Who defeated the last Gupta ruler?
Jivitagupta II, the last known ruler of the dynasty, appears to have been defeated by Yashovarman of the Varman dynasty of Kannauj circa 750 CE.
Why did Gupta Empire fall?
The Huna People, also known as Huns, invaded Gupta territory and caused significant damage to the empire. The Gupta Empire ended in 550 CE, when it disintegrated into regional kingdoms after a series of weak rulers and invasions from the east, west, and north.
Who was the real founder of Gupta dynasty?
Chandra Gupta I, king of India (reigned 320 to c. 330 ce) and founder of the Gupta empire.
Who defeated Huns in India?
Gupta ruler SkandaguptaThe Alchon Huns invaded parts of northwestern India from the second half of the 5th century. According to the Bhitari pillar inscription, the Gupta ruler Skandagupta already confronted and defeated an unnamed Huna ruler circa 456-457 CE.
Who is the last king of Gupta dynasty?
Kumaragupta's son Skandagupta was the last ruler of the Gupta empire. After defeating Pushyamitra, he assumed the title of Vikramaditya. He faced the Hunas and defeated them in 455CE.
Who was the greatest ruler of Gupta dynasty?
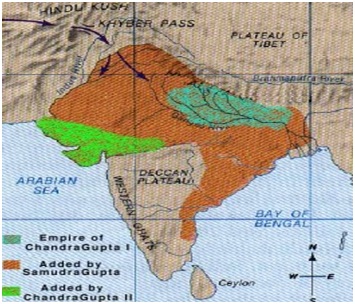
SamudraguptaThe greatest king of the Gupta dynasty is believed to be Samudragupta because the Gupta Empire reached its greatest extent under his rule.
Who ruled before Gupta Empire?
The Kushan reign in north India came to an end around c. 230 CE and then a good part of central India came under the domain of the Murundas (possible kinsmen of the Kushanas). The Murundas ruled for only 25 – 30 years. Around the last decade of the 3rd century CE (about 275 CE), the dynasty of the Guptas came to power.
Why Gupta age is called golden period?
The Gupta age in ancient India has been called the 'Golden Age of India' because of the many achievements in the field of arts, science, and literature that Indians made under the Guptas. The prosperity under the Guptas initiated a period of splendid accomplishments in arts and sciences.
Who defeated Huns?
Ardaric defeated the Huns at the Battle of Nedao in 454 CE in which Ellac was killed. After this engagement, other nations broke away from Hunnic control. Jordanes notes that, by Ardaric's revolt, "he freed not only his own tribe, but all the others who were equally oppressed" (125).
What caused the fall of the Gupta Empire quizlet?
What group of invaders caused the decline of the Gupta Empire? The Hunas, a group closely related to the Huns, attacked and defeated the Gupta Empire.
What happened during the Gupta Empire?
Gupta developed the religion hinduism through the different belief systems that citizens believed in. When these beliefs combined Hinduism was formed. Gupta had developed advancements in Science, Engineering, art, dialectics, laterature, logic, mathematics, astronomy, religion, and philosophy.
How did the Maurya empire fall?
In 180 BCE, Brihadratha Maurya, was killed by his general Pushyamitra Shunga in a military parade without any heir. Hence, the great Maurya empire finally ended, giving rise to the Shunga Empire.
Who is known as Napoleon of India?
Answer: (b) Samudragupta. Samudragupta, the ruler of the Gupta Empire is known as the Napoleon of India.
What tribes were the Huna?
The Huna were a Central Asian Xionite tribe that consisted of four hordes: Northern Huna, also known as the Black Huns; Southern Huna, the Red Huns; Eastern Huna, the Celestial Huns; and the White Huns, the Western Huna. The White Huns, those who invaded the Gupta Empire during the reign of Kumaragupta, were also known as the Hephthalites, and caused great damage to the failing Gupta Empire. Skandagupta died in 467 CE, and was followed onto the throne by his half-brother, Purugupta, who ruled from 467-473 CE.
What is the coin of Kumaragupta?
Coin of Kumaragupta I. A silver coin from the reign of Gupta Emperor Kumaragupta I, c. 415-455 CE. As his grandfather and father did before him, Kumaragupta also issued news coins to mark his reign. They were stamped with images of his namesake god, Lord Kumara, regarded by Hindus as Regent of Earth.
Which tribe was responsible for the fall of the Gupta Empire?
A Central Asian Xionite tribe that consisted of four hordes that repeatedly invaded Gupta territory, and helped cause the downfall of the Gupta Empire.
Who succeeded Chandragupta II?
In 415 CE, Chandragupta II was succeeded by his second son, Kumaragupta I , who ruled successfully until 455 CE. The late years of his reign, however, faced difficulties. The Pushyamitras, a tribe of central India, rose up in rebellion against Kumaragupta, while Gupta territories were invaded by the Western Huna people, also known as White Huns.
Which Indian empire fell by 550 CE?
A minor line of the Gupta Clan continued to rule Magadha, one of the 16 Indian Mahajanapadas, or “Great Countries,” but the Gupta Empire fell by 550 CE.
When was the Gupta Dynasty?
The emperor of the Gupta Dynasty of ancient India from c. 380-415 CE.
Who was the Gupta Empire under?
The Gupta Empire flourished under Chandragupta II, but began to falter under his son, Kumaragupta, and grandson, Skandagupta.
What were the factors that led to the decline of the Gutpas?
Foreign invasions was the second major factor in the decline and disappearance of the Gutpas. The invasion of barbaric tribe Pushyamitra was not the decisive. A far more important invasion was that of the White Huns, who, after settling in the Oxus vally, invaded India. First appeared during the reign of Budhagupta. Again they reappeared under the command of Toramana who annexed a large portion of the north-western region including parts of Moder U.P. He followed by hisson, Mihirakula, who became the overlord of north India. Indeed he was defeated by Yashodharman of Malwa but the repercussions of these invasions were disastrous for the Gupta Empire.
What was Yasodharman's rule?
Indeed Yasodharman's rule was short lived, but he dealt a severe blow to the Gupta empire. The Gupta empire was further undermined by the rise of the feudatories. The governors appointed by the Gupta kings in north Bengal and their feudatories in Samatata or south-east Bengal broke away from the Gupta control.
What were the causes of the fall of the Guptas?
Over and above the usual causes of administrative inefficiency, weak successors and stagnant the fall of the Guptas: dynastic dissensions, foreign invasions and some internal rebellions.
Where is the Gupta coin found?
After the reign of Skanda Gupta (467 AD) any Gupta coin or inscription has been found in western Malwa and Saurashtra. The migration of guild of Silk weavers from Gujarata to Malwa in AD 473 and their adoption of non-productive professions show that there was not much demand for cloth produced by them.
What happened after the death of Kumaragupta?
There is evidence to show that following the death of Kumaragupta and Skandagupta, there were civil wars and struggles for the throne. For instance, wehave the successors of Buddhagupta, highlighting the rule of more than just one king. Those were Vinayagupta in Bengal and Bhanugupta in Iran.
What was the saboteur of political consciousness?
Along with this development one more saboteur of political consciousness was the religious perception of ancient Indians. Beginning before the Christian are it came to be gradually established that the kingship has its own dharma known as rajya-dhrma while the people had a handul of dharmas like varnashrama dharma and the grihadharma. All these dharmas led the individual loyalty or perception towards a non-political entity. This thinking is given religious sanction by the priestly order. This thinking is given religious sanction by the priestly order of the day. Thus the State never was the architectonic factor in the life of ancient Indian except during the Mauryan era. It is this perception of ancient India that made the emergence and disappearance of hundreds of States mere non-events.
What was the first factor that contributed to the outlook of Indians?
The first factor that contributed for this outlook of Indians was the emergence of feudalism about which evidence is there from the days of the Satavahanas. This tendency grew in the Christian ara and was firmly established by the seventh century AD.
What was the impact of Yashodharman's rule on the Gupta Empire?
Although Yashodharman’s rule was short-lived, it certainly gave a huge blow to the Gupta empire. The other feudatories too rose in rebellion against the Guptas and ultimately became independent in Bihar, Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Valabhi, Gujarat, Malwa and so on.
What were the factors that led to the fall of the Gupta Empire?
The rise of feudatories was another factor that led to the fall of the Gupta empire. Yashodharman of Malwa (belonged to the Aulikara feudatory family) after defeating Mihirkula successfully challenged the authority of the Guptas and set up, in 532 CE, pillars of victory commemorating his conquest of almost the whole of northern India. Although Yashodharman’s rule was short-lived, it certainly gave a huge blow to the Gupta empire. The other feudatories too rose in rebellion against the Guptas and ultimately became independent in Bihar, Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Valabhi, Gujarat, Malwa and so on. It is important to mention that after the reign of Skandagupta (467 CE) hardly any coin or inscription has been found in western Malwa and Saurashtra.
What was the effect of the Guptas on India?
By the end of the 5th century, the Guptas had lost western India and this must have deprived the Guptas of the rich revenues from trade and commerce and hence crippled them economically. The economic decline of the Guptas is indicated by the gold coins of later Gupta rulers, which have less percentage of gold metal. The practice of land grants for religious and other purposes also reduced the revenues which resulted in economic instability.
How long did the Murundas rule?
The Murundas ruled for only 25 – 30 years. Around the last decade of the 3rd century CE (about 275 CE), the dynasty of the Guptas came to power. The Gupta empire established its control over a good part of the former dominions of both the Kushanas and the Satavahanas. The Guptas (possibly Vaishyas) kept northern India politically united ...
How did the Gupta Dynasty reach its peak?
During Chandragupta Ⅱ’s reign, the Gupta dynasty reached its peak by expanding territories through conquests as well as by marriage alliances. He married Kuberananga, a Naga princess and had a daughter, Prabhavati with her. He married Prabhavati to a Vakataka prince, Rudrasena Ⅱ (Deccan). After the death of her husband, Prabhavati ruled the territory as regent to her minor sons with the help of her father. Thus Chandragupta Ⅱ indirectly controlled the Vakataka kingdom.
What were the two major political powers in the Mauryan Empire?
The decline of the Mauryan empire resulted in the rise of two major political powers – the Kushanas and the Satavahanas in the north and south respectively. Both these empires brought political unity and economic growth in their respective areas.
What dynasty ruled India?
In Ancient India, the Gupta Dynasty ruled the mid-to-late 3rd century (approximately) to 543 AD. Founded by Sri Gupta, the dynasty rose to fame with rulers like Chandragupta-I, Samudragupta, etc. An important topic in the History syllabus, it is also important for the IAS Exam. This article will provide you with useful notes on the Gupta Empire. These notes will also be useful for other competitive exams like banking PO, SSC, state civil services exams, and so on.
What period did Hunas invade?
In this article we will discuss about the invasions of Hunas during the Gupta period.
How did the Hunas affect India?
The Hunas were finally absorbed in the Indian society, yet, they affected Indian polity and society in several ways. Of course, their role in the fall of the Gupta empire was only secondary’ but they, certainly, encouraged the attitude of disintegration and regional autonomy which grew in India when the Gupta empire broke into pieces.
Which empire did the Hunas destroy?
the Hunas became a powerful force in Central Asia and, proceeding towards India, they occupied Gandhara Pradesh on the north-west. Skanda Gupta, however, gave them a crushing defeat about 460 A.D. which checked their advance into India for nearly next fifty’ years. However, they destroyed the Persian empire and by the end of the fifth century A.D. established a vast empire with its capital at Balkh.
Did Toramana succeed in Balkh?
The attacks of Toramana and Mihirakula were not so fierce and it is also doubtful that they had any connections with the central power of the Hunas in Balkh. Therefore, they did not succeed much in India and, at times, were defeated also.
Did the Hunas succeed in India?
The later invasions of the Hunas on India, of course, succeeded and it is also accepted that they also contributed to the fall of the Gupta empire. Yet, the success of the Hunas in India was neither wide-spread nor permanent. The primary credit for safeguarding India from their barbaric invasions goes to Skanda Gupta who checked their advance when they were at the height of their power.
Was Toramana a Huna?
Though there is no conclusive evidence that Toramana was a Huna yet, mostly he had been accepted so . This time the Hunas succeeded and occupied Kashmir, then Punjab, Rajasthan and parts of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. Bhanu Gupta had to fight against Toramana.
When did the Gupta Empire disintegrate?
established a vast empire with its capital at Balkh. In the beginning of the sixth century A.D. when the Gupta empire was disintegrating, they repeated their invasion under their ruler Toramana.
What are the Hunas?
The Hunas are thought to have included the Xionite and/or Hephthalite, the Kidarites, the Alchon Huns (also known as the Alxon, Alakhana, Walxon etc.) and the Nezak Huns. Such names, along with that of the Harahunas (also known as the Halahunas or Harahuras) mentioned in Hindu texts, have sometimes been used for the Hunas in general; while these groups (and the Iranian Huns) appear to have been a component of the Hunas, such names were not necessarily synonymous. Some authors suggest that the Hunas were Ephthalite Huns from Central Asia. The relationship, if any, of the Hunas to the Huns, a Central Asian people who invaded Europe during the same period, is also unclear.
What was the name of the tribe that ruled the Indian subcontinent?
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: Hūṇā) was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian Subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century. The Huna Kingdom occupied areas as far south as Eran and Kausambi, greatly weakening the Gupta Empire.
What are the Huna kings?
In Buddhist sources, Huna kings are described as 'rude and cruel'. They were responsible for the destruction of Buddhist monasteries and centers of learning in the Northwest regions of the country.
What religions did the Hunas practice?
The religious beliefs of the Hunas is unknown, and believed to be a combination of ancestor worship, totemism and animism.
What are the white huts called?
The Ephthalitae Huns, who are called White Huns [...] The Ephthalitae are of the stock of the Huns in fact as well as in name, however they do not mingle with any of the Huns known to us, for they occupy a land neither adjoining nor even very near to them; but their territory lies immediately to the north of Persia [...] They are not nomads like the other Hunnic peoples, but for a long period have been established in a goodly land... They are the only ones among the Huns who have white bodies and countenances which are not ugly. It is also true that their manner of living is unlike that of their kinsmen, nor do they live a savage life as they do; but they are ruled by one king, and since they possess a lawful constitution, they observe right and justice in their dealings both with one another and with their neighbours, in no degree less than the Romans and the Persians
What was the largest domain in 500 CE?
Asia in 500 CE, showing the Huna domain at its greatest extent.
Where did the Hunas live?
The Mongolian-Tibetan historian Sumpa Yeshe Peljor (writing in the 18th century) lists the Hunas alongside other peoples found in Central Asia since antiquity, including the Yavanas (Greeks), Kambojas, Tukharas, Khasas and Daradas.
