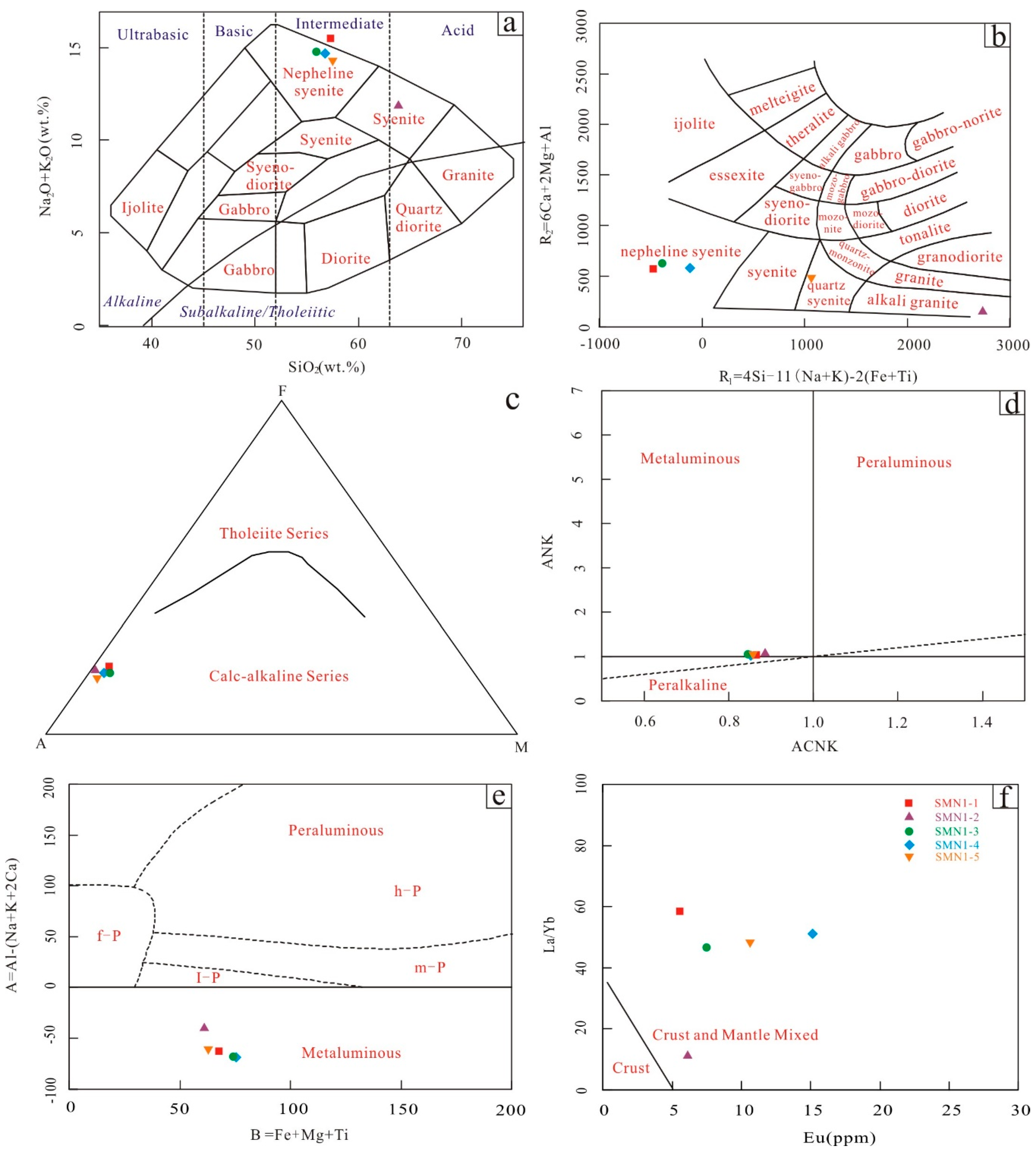
When was CGS system established?
In 1874 the BAAS introduced the CGS system, a three-dimensional coherent unit system based on the three mechanical units centimeter, gram and second, using prefixes ranging from micro to mega to express decimal submultiples and multiples.
What is CGS system also known as?
= The system of units in which length is measured in centimeter, mass in gram and time in second is called CGS system. It is known as the French system of units. The system of units in which length is measured in foot , mass in pound and time in second is called FPS system. It is also known as British system of units.May 20, 2020
Where is CGS system used?
The cgs Gaussian system is nonetheless commonly used in theoretical physics, while the MKS system (based on the meter, kilogram, and second) is commonly used in engineering and physics instruction.
Who introduced the MKS system?
Giovanni GiorgiIn 1901, Giovanni Giorgi proposed to the Associazione elettrotecnica italiana (AEI) that the MKS system, extended with a fourth unit to be taken from the practical units of electromagnetism, such as the volt, ohm or ampere, be used to create a coherent system using practical units.
What is full name CGS?
Table D.1: The centimetre-gram-seconds (CGS) and the metre-kilogram-seconds (SI) unit systems.
What does CGS stand for?
centimeter-gram-secondcentimeter-gram-second.
What is the difference between CGS and MKS?
Answer. CGS system:- It stands for Centimeter, Gram and Second. These are the units that are used for the measurement of length, mass and time. MKS system:- It stands for Metre, Kilogram and Second which are the units used for length, mass and time in this system.Jul 13, 2020
Is MKS and SI same?
Answer. The SI system of units is build upon MKS system of units. The MKS system of units express any measurement of physical quantities using fundamental units of Length,Mass,Time which are metre ,kilogram and second respectively. The SI system of units is Internationally accepted system of units.Jun 8, 2018
What is the other name of MKS system?
International System of Units this situation was called the metre-kilogram-second (MKS) system.
What are the different types of metric units?
On 7 April 1795 the metric system was formally defined in French law. It defined six new decimal units: 1 The mètre, for length – defined as one ten-millionth of the distance between the North Pole and the Equator through Paris 2 The are (100 m 2) for area [of land] 3 The stère (1 m 3) for volume of firewood 4 The litre (1 dm 3) for volumes of liquid 5 The gramme, for mass – defined as the mass of one cubic centimetre of water 6 The franc, for currency.
Why did France use different units of measure?
It has been estimated that on the eve of the Revolution in 1789, the eight hundred or so units of measure in use in France had up to a quarter of a million different definitions because the quantity associated with each unit could differ from town to town, and even from trade to trade. Although certain standards, such as the pied du roi (the King's foot) had a degree of pre-eminence and were used by scientists, many traders chose to use their own measuring devices, giving scope for fraud and hindering commerce and industry. These variations were promoted by local vested interests, but hindered trade and taxation.
What was the Enlightenment?
Age of Enlightenment. Foundational aspects of mathematics and culture, together with advances in the sciences during the Enlightenment, set the stage for the emergence in the late 18th century of a system of measurement with rationally related units and simple rules for combining them.
How long did it take to survey the Paris meridian?
The task of surveying the meridian arc, which was estimated to take two years, fell to Pierre Méchain and Jean-Baptiste Delambre. The task eventually took more than six years (1792–1798) with delays caused not only by unforeseen technical difficulties but also by the convulsed period of the aftermath of the Revolution. Apart from the obvious nationalistic considerations, the Paris meridian was also a sound choice for practical scientific reasons: a portion of the quadrant from Dunkirk to Barcelona (about 1000 km, or one-tenth of the total) could be surveyed with start- and end-points at sea level, and that portion was roughly in the middle of the quadrant, where the effects of the Earth's oblateness were expected to be the largest.
When was the metric system invented?
The first practical realisation of the metric system came in 1799, during the French Revolution, after the existing system of measures had become impractical for trade, and was replaced by a decimal system based on the kilogram and the metre. The basic units were taken from the natural world.
Who were the five scientists who proposed the new weights and measures system?
They were Jean-Charles de Borda, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, Pierre-Simon Laplace, Gaspard Monge and Nicolas de Condorcet. Over the following year, the panel, after studying various alternatives, made a series of recommendations regarding a new system of weights and measures, including that it should have a decimal radix, that the unit of length should be based on a fractional arc of a quadrant of the Earth's meridian, and that the unit of weight should be that of a cube of water whose dimension was a decimal fraction of the unit of length. The proposals were accepted by the French Assembly on 30 March 1791.
What were the units of measure in the Roman Empire?
In the early ninth century, when much of what later became France was part of the Holy Roman Empire, units of measure had been standardised by the Emperor Charlemagne. He had introduced standard units of measure for length and for mass throughout his empire. As the empire disintegrated into separate nations, including France, these standards diverged. In England the Magna Carta (1215) had stipulated that "There shall be standard measures of wine, ale, and corn (the London quarter), throughout the kingdom. There shall also be a standard width of dyed cloth, russet, and haberject, namely two ells within the selvedges. Weights are to be standardised similarly."
Why is the value of G so difficult to measure?
G is quite difficult to measure because gravity is much weaker than other fundamental forces, and an experimental apparatus cannot be separated from the gravitational influence of other bodies.
What is the standard gravitational parameter?
The standard gravitational parameter GM appears as above in Newton's law of universal gravitation, as well as in formulas for the deflection of light caused by gravitational lensing, in Kepler's laws of planetary motion, and in the formula for escape velocity .
Why is the gravitational force so weak?
This is because the gravitational force is an extremely weak force as compared to other fundamental forces.
What is the gravitational constant of proportionality?
The constant of proportionality, G , is the gravitational constant. Colloquially, the gravitational constant is also called "Big G", distinct from "small g" ( g ), which is the local gravitational field of Earth (equivalent to the free-fall acceleration).
What is the gravitational constant?
The gravitational constant is a defining constant in some systems of natural units, particularly geometrized unit systems, such as Planck units and Stoney units. When expressed in terms of such units, the value of the gravitational constant will generally have a numeric value of 1 or a value close to it.
What is Newton's law of gravity?
The existence of the constant is implied in Newton's law of universal gravitation as published in the 1680s (although its notation as G dates to the 1890s), but is not calculated in his Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica where it postulates the inverse-square law of gravitation. In the Principia, Newton considered the possibility of measuring gravity's strength by measuring the deflection of a pendulum in the vicinity of a large hill, but thought that the effect would be too small to be measurable. Nevertheless, he estimated the order of magnitude of the constant when he surmised that "the mean density of the earth might be five or six times as great as the density of water", which is equivalent to a gravitational constant of the order:
What is Newton's constant of gravitation?
Stern (1928) was misquoted as "Newton's constant of gravitation" in Pure Science Reviewed for Profound and Unsophisticated Students (1930), in what is apparently the first use of that term. Use of "Newton's constant" (without specifying "gravitation" or "gravity") is more recent, as "Newton's constant" was also used for the heat transfer coefficient in Newton's law of cooling, but has by now become quite common, e.g. Calmet et al, Quantum Black Holes (2013), p. 93; P. de Aquino, Beyond Standard Model Phenomenology at the LHC (2013), p. 3. The name "Cavendish gravitational constant", sometimes "Newton–Cavendish gravitational constant", appears to have been common in the 1970s to 1980s, especially in (translations from) Soviet-era Russian literature, e.g. Sagitov (1970 [1969]), Soviet Physics: Uspekhi 30 (1987), Issues 1–6, p. 342 [etc.]. "Cavendish constant" and "Cavendish gravitational constant" is also used in Charles W. Misner, Kip S. Thorne, John Archibald Wheeler, "Gravitation", (1973), 1126f. Colloquial use of "Big G", as opposed to " little g " for gravitational acceleration dates to the 1960s (R.W. Fairbridge, The encyclopedia of atmospheric sciences and astrogeology, 1967, p. 436; note use of "Big G's" vs. "little g's" as early as the 1940s of the Einstein tensor Gμν vs. the metric tensor gμν, Scientific, medical, and technical books published in the United States of America: a selected list of titles in print with annotations: supplement of books published 1945–1948, Committee on American Scientific and Technical Bibliography National Research Council, 1950, p. 26).
What is the CGS approach?
We believe that God and the child have a unique relationship with one another, particularly before the age of six; that growth of this relationship should be assisted by the adult, but is directed by the Spirit of God; that children need their own place to foster the growth of that relationship;
What is the catechesis of the good shepherd?
The Catechesis of the Good Shepherd was born from the joy of the children in their encounter with God and lives in being nourished by this joy. It has also been observed that children of the same developmental stage even though belonging to different cultural backgrounds, respond to certain elements of the Christian message in the same way. Over time through being with children in a specially prepared environment called an atrium, observing and listening to their responses, scriptural and liturgical themes developed that most resonated with children’s religious needs according to their age levels. Thus the Catechesis of the Good Shepherd divests itself of any strictly scholastic character, so as to become an experience of life, an education in faith, and a celebration of the encounter with the Father, in listening to Jesus, the one Teacher, and in obedience to the Holy Spirit.
How old is the child when they enter the Eucharist?
The 3-6 year old child enters the mystery of the Eucharist by first learning the names of the articles used on the altar and then through the most important gestures including the preparation of the chalice, the epiclesis and offering, and the sign of peace.
What is interpersonal relationship?
An interpersonal relationship is always a mystery, all the more so when that relationship is between God and the child. We believe that there is a deep bond between God and the child which produces in the child the desire to draw nearer to God.
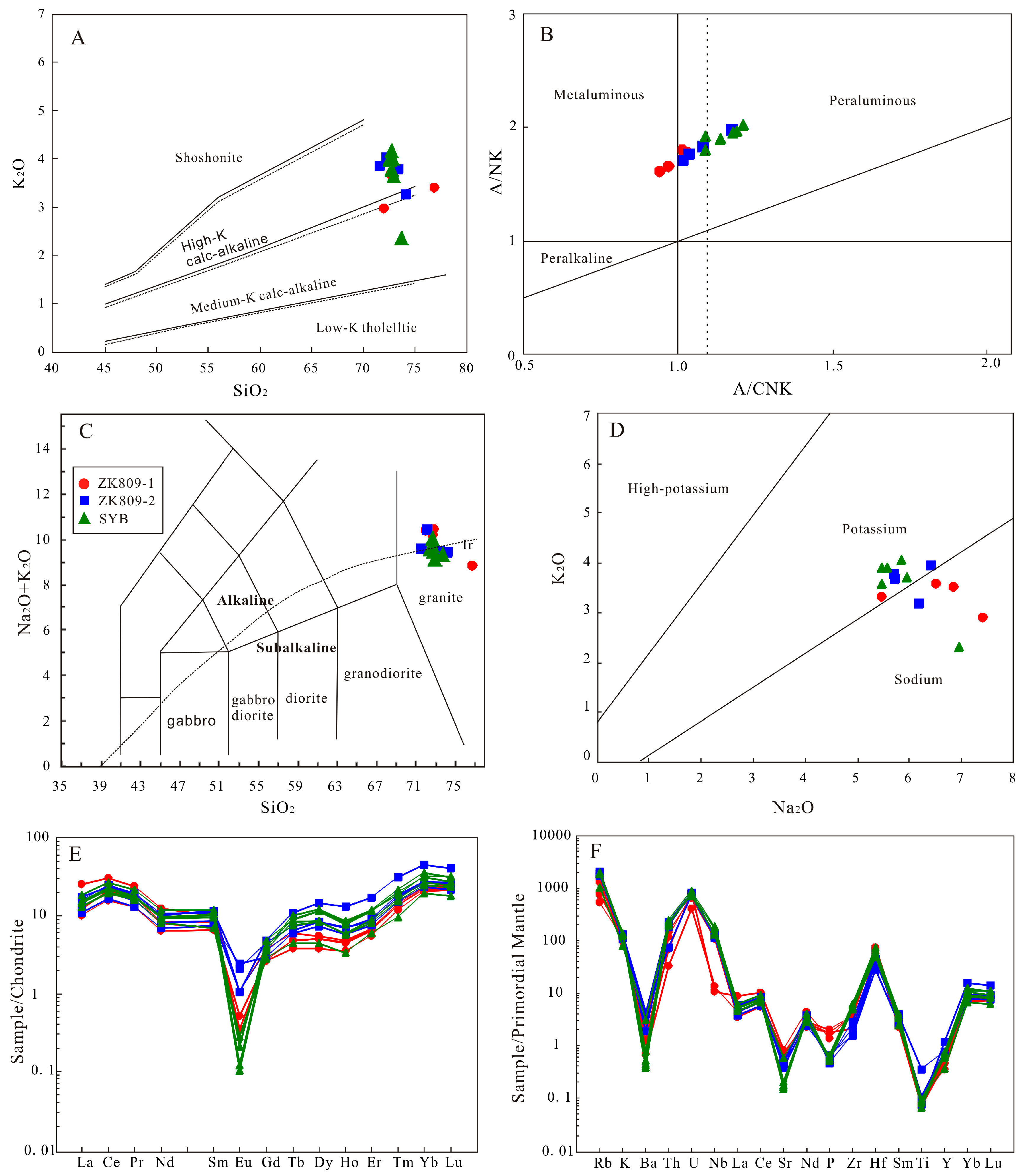
Age of Enlightenment
Implementation in Revolutionary France
- Weights and measures of the Ancien Régime
It has been estimated that, on the eve of the Revolution in 1789, the eight hundred or so units of measure in use in France had up to a quarter of a million different definitions because the quantity associated with each unit could differ from town to town, and even from trade to trade.: 2–3 Alt… - The units of weight and length
In 1790, a panel of five leading French scientists was appointed by the Académie des sciences to investigate weights and measures. They were Jean-Charles de Borda, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, Pierre-Simon Laplace, Gaspard Monge, and Nicolas de Condorcet.: 2–3 : 46 Over the following y…
Development of Non-Coherent Metric Systems
- At the start of the nineteenth century, the French Academy of Sciences' artefacts for length and mass were the only nascent units of the metric system that were defined in terms of formal standards. Other units based on them, except the litre, proved to be short-lived. Pendulum clocks that could keep time in seconds had been in use for about 150 years, but their geometries were l…
Convention of The Metre
- With increasing international adoption of the metre, the shortcomings of the mètre des Archives as a standard became ever more apparent. Countries which adopted the metre as a legal measure purchased standard metre bars that were intended to be equal in length to the mètre des Archives, but there was no systematic way of ensuring that the countries were actually working to the sa…
Measurement Systems Before World War II
- The 20th century history of measurement is marked by five periods: the 1901 definition of the coherent MKS system; the intervening 50 years of coexistence of the MKS, cgs and common systems of measures; the 1948 Practical system of unitsprototype of the SI; the introduction of the SI in 1960; and the evolution of the SI in the latter half century.
Working Draft of Si: Practical System of Units
- The 9th CGPM met in 1948, fifteen years after the 8th CGPM. In response to formal requests made by the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics and by the French government to establish a practical system of units of measure, the CGPM requested the CIPM to prepare recommendations for a single practical system of units of measurement, suitable for adoption b…
International System of Units
- In 1952, the CIPM proposed the use of wavelength of a specific light source as the standard for defining length, and, in 1960, the CGPM accepted this proposal using radiation corresponding to a transition between specified energy levels of the krypton 86 atom as the new standard for the metre. The standard metre artefact was retired. In 1960, Giorgi's proposals were adopted as the …
Evolution of The Modern Si
- The evolution of the SI after its publication in 1960 has seen the addition of a seventh base unit, the mole, and six more derived units, the pascal for pressure, the gray, sievert, and becquerel for radiation, the siemens for electrical conductance, and katalfor catalytic (enzymatic) activity. Several units have also been redefined in terms of physical constants.
Redefinition in Terms of Fundamental Constants
- At its 23rd meeting (2007), the CGPM mandated the CIPM to investigate the use of natural constants as the basis for all units of measure rather than the artefacts that were then in use. The following year, this was endorsed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP). At a meeting of the CCU held in Reading, United Kingdom, in September 2010, a resolution and d…