
The disorder was described by Richard W. B. Ellis (1902–1966) of Edinburgh
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian, it is located in Lothian on the Firth of Forth's southern shore.
Pediatrics
Pediatrics is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, and adolescents. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends people be under pediatric care up to the age of 21. A medical doctor who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician, or paediatric…
What are the characteristics of Ellis-van Creveld syndrome?
People with this condition have particularly short forearms and lower legs and a narrow chest with short ribs. Ellis-van Creveld syndrome is also characterized by the presence of extra fingers and toes ( polydactyly ), malformed fingernails and toenails, and dental abnormalities.
What is the history of Ellis syndrome?
The disorder was described by Richard W. B. Ellis (1902–1966) of Edinburgh and Simon van Creveld (1895–1971) of Amsterdam. Each had a patient with this syndrome, as they had discovered when they met in the same train compartment on the way to a pediatrics conference in England in the late 1930s.
What kind of Doctor treats Ellis-van Creveld syndrome?
The treatment of Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome is directed toward the specific symptoms that are apparent in each individual. Such treatment may require the coordinated efforts of a team of medical professionals, such as pediatricians, surgeons, cardiologists, dentists, pulmonologists, orthopedists, urologists,...
What is the most common heart defect in Ellis-van Creveld syndrome?
More than fifty percent of the patients with Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome are born with malformations of the heart. The most common heart defect is an abnormal opening in the wall between the two upper heart chambers (atrial septal defect).

How is Ellis Van Creveld syndrome detected?
Diagnosis. Ellis-Van-Creveld syndrome is diagnosed by the observation of short stature, slow growth, skeletal abnormalities determined by imaging techniques and sometimes teeth present at birth (natal teeth). Molecular genetic testing for the EVC and EVC2 genes is available on a research basis only.
What caused Ellis Van Creveld syndrome?
Causes. Ellis-van Creveld syndrome can be caused by mutations in the EVC or EVC2 gene. Little is known about the function of these genes, although they appear to play important roles in cell-to-cell signaling during development.
Is Ellis Van Creveld syndrome fatal?
Approximately 50% of patients with Ellis-van Creveld (EVC) syndrome die in early infancy as a consequence of cardiorespiratory problems.
What is the treatment for Ellis Van Creveld syndrome?
Children should be monitored so they can be treated with surgery to help guide their growth due to misalignment and malrotation of the lower extremities. Surgical procedures are required to remove extra fingers, correct heart defects and to correct knock-knee.
What is Ellis-van Creveld?
Ellis-van Creveld syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects bone growth. Extra digits may be present as an isolated finding, or they may occur as part of a syndrome, in which case other abnormalities are usually present. Humans typically have 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 chromosomes in total.
What is Meckel Gruber syndrome?
Meckel-Gruber syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive lethal malformation characterized by typical manifestations of occipital encephalocele, bilateral polycystic kidneys and post axial polydactyly. The worldwide incidence varies from 1 in 13,250 to 1 in 140,000 live births.
What is Zimmerman laband syndrome?
General Discussion. Laband syndrome, also known as Zimmerman-Laband syndrome, is an extremely rare genetic disorder characterized by abnormalities of the head and facial (craniofacial) area and the hands and feet. Most children with this disorder have abnormally large gums (gingival fibromatosis).
What is Otodental syndrome?
Otodental syndrome is a very rare inherited condition characterized by grossly enlarged canine and molar teeth (globodontia) associated with sensorineural hearing loss.
What does charge syndrome stand for?
CHARGE is an abbreviation for several of the features common in the disorder: coloboma, heart defects, atresia choanae (also known as choanal atresia), growth retardation, genital abnormalities, and ear abnormalities.
What is EVC in cardiology?
Abstract. Ellis-van Creveld (EVC) syndrome is a rare genetic abnormality that has been linked to a mutation in the EVC or EVC2 genes. Common atrium (CA) is an uncommon cardiac malformation, and yet it is commonly found in patients with EVC.
What is Kabuki syndrome?
Kabuki syndrome is a rare, multisystem disorder characterized by multiple abnormalities including distinctive facial features, growth delays, varying degrees of intellectual disability, skeletal abnormalities, and short stature.
What is Amelogenesis imperfecta?
General Discussion. Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) refers to a group of rare, inherited disorders characterized by abnormal enamel formation. The term is typically restricted to those disorders of enamel development not associated with other abnormalities of the body.
Who discovered Ellis van Creveld syndrome?
The story of Ellis–van Creveld syndrome is one of serendipity. By chance, Simon van Creveld and Richard Ellis purportedly met on a train and combined their independently encountered patients with short stature, dental anomalies and polydactyly into one landmark publication in 1940. They included a patient used in work published previously by Rustin McIntosh without naming McIntosh as a coauthor. This patient was followed radiologically by Caffey for nearly two decades. In 1964, Victor McKusick felt compelled to investigate a brief report in an obscure pharmaceutical journal on an unusual geographic cluster of short-statured Amish patients in Pennsylvania. This review highlights the lives of the individuals involved in the discovery of Ellis–van Creveld syndrome in their historic context.
How is Ellis van Creveld syndrome inherited?
Ellis–van Creveld syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion with variable expression. It is often associated with the founder effect, which is a loss of genetic variation when new populations are established by a small number of individuals. If, by chance, the group of founding individuals has a relatively high proportion of a certain gene mutation, their offspring develop a higher incidence of the resulting phenotype. This effect may be particularly striking for recessive genes, in which the founders themselves may be asymptomatic.
What is EVC syndrome?
Ellis–van Creveld syndrome (EVC, OMIM 225500) is clinically characterized by short stature, polydactyly, congenital cardiac disease and genu valgum, as well as dysplastic fingernails and teeth [ 1 ]. The psychomotor development of the patients is normal. The inheritance is autosomal recessive and has variable expression; the responsible genetic defects in the EVC1 and EVC2 genes are located on chromosome 4p16. Affected patients have short ribs and small chests, which can lead to respiratory compromise. The condition was coined in 1940 by Simon van Creveld and Richard Ellis [ 2 ], reporting on two of their own patients and a third patient contributed by Rustin McIntosh, which he had included in a publication 7 years earlier [ 3 ].
Who is the father of pediatric radiology?
John Caffey (Fig. 3) is regarded as the father of pediatric radiology [ 7 ]. He was born in Utah in 1895, the same year Conrad Röntgen discovered X-rays. He graduated medical school at the University of Michigan in 1919 and then spent 3 years in Eastern Europe with the American Red Cross. He returned to the United States for training in medicine at the University of Michigan and later in pediatrics at Columbia University in New York. As a private practice pediatrician in New York City, he became interested in radiology and eventually established a pediatric radiology department at Columbia’s Babies Hospital in 1929. He remained chairman of that department and worked there with McIntosh until his retirement in 1960. He died in 1978.
Who is Richard Ellis?
Richard W.B. Ellis (Fig. 2) was a British pediatrician who lived from 1902 to 1966. He studied at King’s College in Cambridge and at the St. Thomas’ Hospital in London. He trained in Pediatrics at the Boston Children’s Hospital for 2 years under Kenneth Blackfan, after which he returned to London’s Guy’s Hospital. In 1937, he helped evacuate 4,000 Basque refugee children during the Spanish civil war. Although he was a Quaker, a religious group that generally subscribes to pacifism, he served in the Royal Air Force during World War II in North Africa, Italy and Belgium. In 1946, he became professor and chairman of the Department for Child Life and Health at the University of Edinburgh, during which time he authored a popular textbook of pediatrics. Anecdotally, but not historically proven, van Creveld and Ellis met on a train on their way to a medical congress. During conversation, they noticed they both had a patient with similar symptoms about whom they were planning to publish. They wrote up a paper including their own patients and another one contributed by McIntosh. Apparently, Ellis was named as the first author because he and van Creveld found that the sequence Ellis–van Creveld sounded better.
Who is Simon van Creveld?
Simon van Creveld (Fig. 1) was a Dutch pediatrician who lived from 1894 to 1971 [ 4 ]. He graduated medical school in 1918 at the University of Amsterdam. Subsequently, he worked at the Institute for Physiology of the University of Groningen and in Berlin. In 1923, he returned to Amsterdam, where he specialized in Pediatrics and eventually became chairman and professor of pediatrics at the Wilhelmina Gasthuis in 1933. In 1941, during the occupation of The Netherlands by Nazi Germany, he lost this position because of his Jewish faith. In this tragic episode of history, he rendered pediatric care to children in the concentration camps set up by the Nazis in the occupied Netherlands at great risk to himself. He eventually was forced to go underground from 1943 to 1945. After the war, he resumed his professional activities and later became an expert in the field of hemophilia [ 5 ]. After his landmark paper, he never published on EVC again.
How is the prognosis of EVC determined?
The overall prognosis of EVC is usually determined by the severity of the structural heart disease and respiratory changes due to the thoracic deformity. Since EVC affects multiple organ systems, management is based on an interdisciplinary approach.
How is Ellis Van Creveld syndrome diagnosed?
Ellis-Van-Creveld syndrome is diagnosed by the observation of short stature, slow growth, skeletal abnormalities determined by imaging techniques and sometimes teeth present at birth (natal teeth). Molecular genetic testing for the EVC and EVC2 genes is available on a research basis only. Prenatal diagnosis is possible by ultrasound.
Where does Ellis Van Creveld syndrome occur?
Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome occurs in many ethnic groups throughout the world and effects males and females in equal numbers. This condition has been reported in approximately 150 individuals. It is more common in the Old Order Amish population of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania and in the native population of Western Australia.
What are the symptoms of Ellis Van Creveld syndrome?
Extra fingers (polydactyly) are present in all patients with this condition and both hands are usually affected. Ectodermal abnormalities include abnormal development of hair, nails and teeth.
What is the genetic disorder of the fingers and toes?
General Discussion. Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by short limb dwarfism, additional fingers and/or toes (polydactyly), abnormal development of fingernails and, in over half of the cases, congenital heart defects. Motor development and intelligence are normal.
Is Ellis Van Creveld a recessive gene?
Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome is inherited as an autosomal recessive genetic condition. Recessive genetic disorders occur when an individual inherits two copies of an abnormal gene for the same trait, one from each parent. If an individual receives one normal gene and one gene for the disease, the person will be a carrier for the disease.
Is the National Organization for Rare Disorders copyrighted?
The content of the website and databases of the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) is copyrighted and may not be reproduced, copied, downloaded or disseminated, in any way, for any commercial or public purpose, without prior written authorization and approval from NORD.
Is Ellis Van Creveld syndrome autosomal recessive?
Some affected individuals do not have mutations in these genes, so it is likely that other unknown genes are also responsible for EVC. Ellis- Van Creveld syndrome is inherited as an autosomal recessive genetic condition.
What is the cause of Ellis van Creveld syndrome?
Ellis-van Creveld syndrome can be caused by mutations in the EVC or EVC2 gene. Little is known about the function of these genes, although they appear to play important roles in cell-to-cell signaling during development. In particular, the proteins produced from the EVC and EVC2 genes are thought to help regulate the Sonic Hedgehog signaling ...
How many babies are affected by Ellis van Creveld syndrome?
In most parts of the world, Ellis-van Creveld syndrome occurs in 1 in 60,000 to 200,000 newborns. It is difficult to estimate the exact prevalence because the disorder is very rare in the general population. This condition is much more common in the Old Order Amish population of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, and in the Indigenous (native) ...
What mutations cause EVC2?
The mutations that cause Ellis-van Creveld syndrome result in the production of an abnormally small, nonfunctional version of the EVC or EVC2 protein. It is unclear how the defective proteins lead to the specific signs and symptoms of this condition. Studies suggest that they prevent normal Sonic Hedgehog signaling in the developing embryo, ...
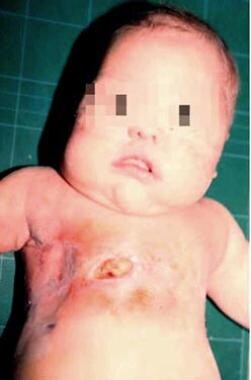
Overview
History
The disorder was described by Richard W. B. Ellis (1902–1966) of Edinburgh and Simon van Creveld (1895–1971) of Amsterdam. Each had a patient with this syndrome, as they had discovered when they met in the same train compartment on the way to a pediatrics conference in England in the late 1930s. A third patient had been referred to by L. Emmett Holt, Jr. and Rustin McIntosh in a textbook of pediatrics (Holt and McIntosh, 1933) and was included in full in the paper by Ellis an…
Signs and symptoms
It involves numerous anomalies including:
• Post-axial polydactyly
• Congenital heart defects (most commonly an atrial septal defect producing a common atrium, occurring in 60% of affected individuals)
• Teeth present at birth (natal teeth)
Genetics
Ellis–Van Creveld syndrome often is the result of founder effects in isolated human populations, such as the Amish and some small island inhabitants. Although relatively rare, this disorder does occur with higher incidence within founder-effect populations due to lack of genetic variability. Observation of the inheritance pattern has illustrated that the disease is autosomal recessive, meaning that both parents have to carry the gene in order for an individual to be affected by the d…
Treatment
There is no causative / curative therapy. Symptomatic medical treatments are focussing on symptoms caused by orthopaedic, dental or cardiac problems. Regarding perioperative / anesthesiological management, recommendations for medical professionals are published at OrphanAnesthesia.
Nomenclature
'Six-fingered dwarfism' ('digital integer deficiency') was an alternative designation used for this condition when it was being studied in the Amish and may have served a useful function in defining this then little known condition for the medical profession, as well as the lay public. The term, however, has been found offensive by some because of the reference to the polydactyly, which is seen as a 'freakish' label. For this reason, six-fingered dwarfism has been removed as a…