What is the lac operon model?
Jacques Monod, together with François Jacob has formulated lac operon model for the regulation of gene expression in the late 1950s. The two of them, together with their colleague André Lwoff were awarded with “The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine” in 1965.
What is the function of the lac operon in E coli?
Lac Operon: Mechanism and Regulation. The lac operon is a well-known example of an inducible gene network that regulates the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli. It encodes the genes for the internalization of extracellular lactose and then its conversion to glucose.
What is the function of the lactose operon?
The lactose operon ( lac operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in E.coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available through the activity of beta-galactosidase.
What is the Shine-Dalgarno sequence of the lac operon genes?
Each of the three genes on the mRNA strand has its own Shine-Dalgarno sequence, so the genes are independently translated. The DNA sequence of the E. coli lac operon, the lacZYA mRNA, and the lacI genes are available from GenBank (view) .

How did Jacob and Monod discover lac operon?
Well, Monod started to make mutants, he made mutants which were unable to use lactose, that is to eat lactose and to metabolize lactose, and he showed that in these, some of these mutant there was no galactosidase made.
What was the first operon discovered?
The lac operonThe lac operon of the model bacterium Escherichia coli was the first operon to be discovered and provides a typical example of operon function. It consists of three adjacent structural genes, a promoter, a terminator, and an operator.
What did Jacob and Monod discover?
Jacob and Monod discovered that a protein, which they called lac repressor, binds to the gene that produces the required metabolic enzyme and suppresses the gene's transcription and translation when lactose is not present in the environment.
Who discovered operon system?
The operon theory was first proposed by the French microbiologists François Jacob and Jacques Monod in the early 1960s.
Who discovered the lac repressor?
Jacques Monod ForMemRSJacques MonodJacques Monod ForMemRSDiedMay 31, 1976 (aged 66) Cannes, FranceNationalityFrenchKnown forLac operon Allosteric regulationAwardsNobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1965) Legion of Honour ForMemRS (1968)5 more rows
Who elucidated lac operon?
Lac operon was elucidated by the Francois Jacob and Jacque Monod.
What is lac operon concept?
The lac operon is an operon, or group of genes with a single promoter (transcribed as a single mRNA). The genes in the operon encode proteins that allow the bacteria to use lactose as an energy source.
Why is the lac operon important?
The lac operon is one of the best known gene regulatory circuits and constitutes a landmark example of how bacteria tune their metabolism to nutritional conditions. It is nearly ubiquitous in Escherichia coli strains justifying the use of its phenotype, the ability to consume lactose, for species identification.
What are the two types of operons?
Operons can be of two types:Inducible – This type of operon is switched on in the presence of an inducer, e.g. Lac operon.Repressible – It is usually present in anabolic pathways. The operon is active and the functional product or enzyme is present normally in the cell.
Who explained lac operon model first time?
The mechanisms of regulation of expression of genes responsible for coding the involved enzymes was first explained by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod while working on inducible system for synthesis of β-galactosidase enzyme in E. coli.
How was operon discovered?
In the early 1960s, just as scientists were discovering how cells transcribed information from DNA to create the necessary proteins for life, French scientists Jacques Monod and François Jacob found that the bacterium Escherichia coli used three specialized genes to create the proteins it needed to break down and ...
Why was the lac operon an interesting scientific discovery?
The discovery of the operon marked a pivotal point in science - the discovery not only provided a model for gene regulation, but also established a new era in science with the emergence of molecular biology. By the 1940's, it had been established that bacteria metabolize sugars for energy production.
How many operons are there?
Based on the frequency distance distributions, we estimated a total of 630 to 700 operons in E. coli. This step opens the possibility of predicting operon organization in other bacteria whose genome sequences have been finished.
How many types of operons are there?
Operons are of two types: Inducible operon - This type of operon is activated where there is an inducer, e.g., Lac operon. Depression operon - It is usually seen in anabolic pathways. The operon is active whereas the functional product or enzyme is normally present in the cell.
What is an operon in biology?
An operon is a sequence of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter. Hence, genes within an operon will always be expressed together or not at all (their expression patterns are linked)
How did operon evolve?
Operons, which are found in the chromosomes of bacteria but not in more advanced organisms, have puzzled biologists since their discovery in the 1960s. The new study suggests operons evolved as a means of reducing "noise" in biochemical signal processing.
Who discovered the lac operon?
Francois Jacob and Jaçques Monod figured out how bacteria controlled the production of an enzyme called beta-galactosidase. This system of feedback and negative regulation became the lac operon and was the first model for the control of protein productio
Who talks about identifying the lac operon repressor?
Walter Gilbert talks about identifying the lac operon repressor.
Who worked with bacteria to break large sugars into smaller pieces?
Jacques Monod and François Jacob work with how bacteria breaks large sugars into smaller pieces.
Who worked on the role of mRNA?
François Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matt Meselson worked on the role of mRNA. An on/off switch involving mRNA seemed a logical control point for protein production.
Why can't mutated repressor proteins bind to the lac operator?
The mutated repressor protein can't bind at the lac operator because it doesn't recognize the DNA sequence of the lac operator and RNA polymerase transcribes the proteins.
Which gene won't allow E. coli to switch over from eating glucose to lactose?
They identified the lac repressor gene which won't allow the e. coli to switch over from eating glucose to lactose thus making the e. coli die.
Does lactose bind to the operator?
Lactose binds to the repressor protein, causing it to change shape and be unable to bind to the operator.
Who invented the lac operon model?
Jacques Monod, together with François Jacob has formulated lac operon model for the regulation of gene expression in the late 1950s. The two of them, together with their colleague André Lwoff were awarded with “The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine” in 1965.
What is the mechanism of the lac operon?
The lac operon is a well-known example of an inducible gene network that regulates the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli. It encodes the genes for the internalization of extracellular lactose and then its conversion to glucose.
What are the two proteins that communicate with genes?
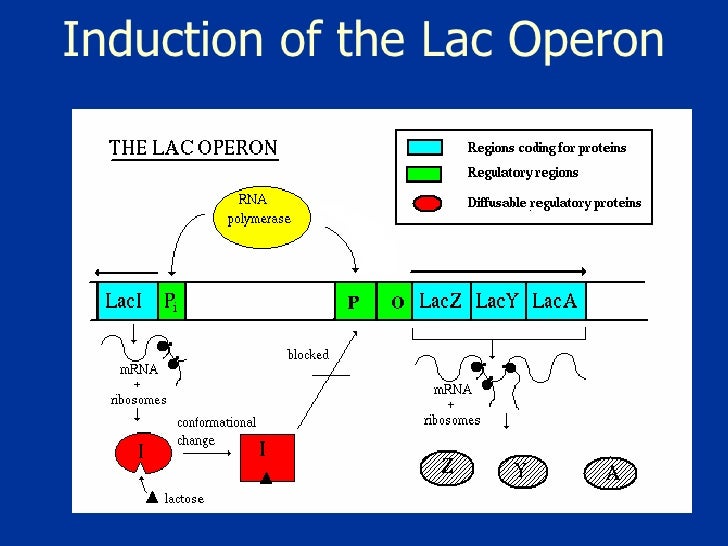
Two regulatory proteins communicate these signals with the genes: Positive regulators (activators): Activator increases transcription of the regulated genes. In lac operon, activator ( called CAP) acts as a glucose sensor. It activates the transcription of the operon when glucose is absent/low.
When does CAP bind to DNA?
When the level of glucose in the environment is low or nil, abundant cAMP binds CAP to form the CAP-cAMP complex, which binds DNA. When CAP–cAMP binds DNA, the efficiency of RNA polymerase binding is increased at the lac operon promoter resulting in a higher level of transcription of the structural genes.
When is the lactose operon turned on?
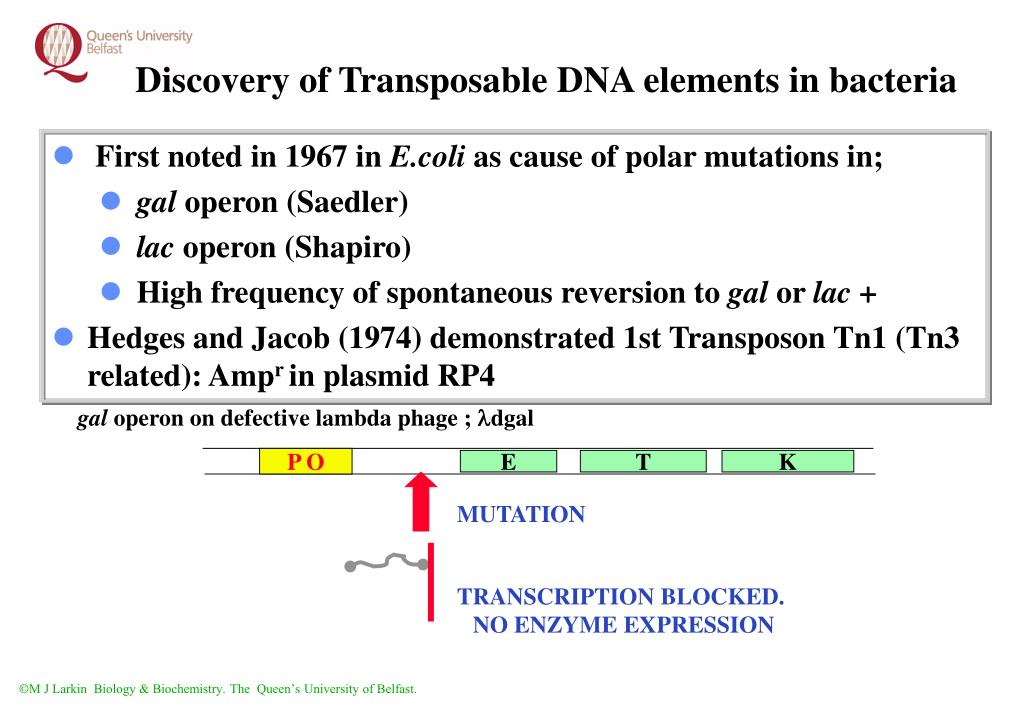
The lactose operon of E. coli is turned ON only when lactose is available (and glucose, the preferred energy source, is absent). When there is an absence of lactose the transcription of the lac operon genes is blocked by a repressor protein (as there will be no use of operon’s gene products). 2.0.1 1.
Where is the promoter located in the mRNA?
The promoter is the binding site for RNA polymerase, the enzyme that performs transcription. The lac promoter is located at 5′ end of lacZ and directs transcription of all the three genes as a single mRNA. This mRNA is translated to give three protein products (shown in the table below) Structural gene. Enzyme.
Does lactose repressor block transcription?
Lactose must be present: There must be an inducer (such as lactose) so that lactose repressor does not block transcription by binding to the operator. Each of the regulatory proteins (CAP and lac repressor) responds to one environmental signal and communicates it to the lac genes.
Which codon in mRNA undergoes translation?from quizlet.com
the first codon in the transcribed mRNA that undergoes translation. During protein synthesis, the tRNA recognizes this specific codon with the help of some initiation factors and starts translation of mRNA
What is the term for the molecules that transfer the DNA triplet code from the nucleus of a cell to?from quizlet.com
mRNA. molecules that transfer the DNA triplet code from the nucleus of a cell to the cytoplasm during the process of protein synthesis. Reading frame. refers to one of three possible ways of reading a nucleotide sequence on the positive strand.
What is the sequence of nucleotides that are complementary to codons?from quizlet.com
sequences of nucleotides that are complementary to codons. Each codon in the mRNA is matched with an anti-codon containing the complementary bases. The tRNAs that string proteins together each have one anticodon that corresponds to one mRNA codon, and one amino acid attached.
What are the codons that signal the end of the polypeptide chain?from quizlet.com
UAG, UAA, UGA. These codons signal the end of the polypeptide chain during translation. These codons are also known as termination codons as they do not code for an amino acid. During protein synthesis, these codons cause the release of the new polypeptide chain from the ribosome.
Which pol synthesizes DNA on lagging strand from primer 2?from quizlet.com
a) pol III synthesizes DNA on lagging strand from primer 2
What is the role of oric in bacteria?from sciencedirect.com
Each genome contains at least one fixed site, termed oriC, from which DNA replication initiates. In every cell cycle, two newly initiated DNA replication forks proceed from oriC, moving bidirectionally until the entire chromosome is duplicated. The majority of gene transcription proceeds away from the replication origin, in the same direction as replication forks. In most species of bacteria, the fixed position of oriC is closely associated with genes whose products play a direct role in regulation of DNA replication (e.g., see dnaA below). E. coli ’s oriC remains exceptional, positioned between the genes encoding ATP synthetase and asparagine synthetase, which are not directly involved in DNA synthesis.
How many proteins are in a microbe's genome?from sciencedirect.com
Bacterial genome size ranges from 0.6 to 8.0 megabases (Mb) and generally encodes 600–6000 proteins. In spite of abundant gene sequence data, still 30% of genes in a microbial genome are left orphaned. The key component required for such drug discovery is the presence of table of microbial functions that can be acquired by the identification of homologs in different organisms providing additional information on motif and superfamilies.
Where is the 16S ribosomal gene located?from sciencedirect.com
These are genes coding for an approximately 1500-nucleotide RNA molecule found in the small subunit of the bacterial ribosome.
Which polymerase is used to check for accuracy?from quizlet.com
A) They are checked for accuracy by DNA polymerase III.
Is Salmonella a low GC gene?from sciencedirect.com
The strong majority of these genes has significantly lower %GC than the ancestral housekeeping genes. Notably, the genes that are common and unique to all isolates of Salmonella were likely acquired by over 100 million year ago by HGT—but during that time most of these sequences have kept a low %GC.
Can a cell proofread DNA?from quizlet.com
C) the cell can proofread its newly synthesized DNA only part of the time.