Full Answer
How many copies of each gene are there?
How many genes are involved in skin color?
What genes affect skin color?
When is a gene expressed?
Is race a trait or gene?
Does genetic imprinting affect gene expression?
Does color blindness depend on gene?
See 2 more
About this website

Which is more dominant gene male or female?
And while it is true that you get half of your genes from each parent, the genes from your father are more dominant, especially when it comes to your health.
Who has stronger genes father or mother?
Genetically, you actually carry more of your mother's genes than your father's. That's because of little organelles that live within your cells, the mitochondria, which you only receive from your mother.
Why is the male gene more dominant?
In natural environments, where both the mother and father are contributing the right stuff, offspring come out at optimal sizes. In the past, other scientists have suggested that dad's genes are more robust because men need their children to look like them in order to believe they're really the baby's father.
Is the male gene dominant?
Genes from your father are more dominant than those inherited from your mother, new research has shown.
Who do first born daughters look like?
There's no set genetic rule that all first born daughters look like their dads, but in many cases – thanks to TikTok – we've seen this theory proved. However, we think this is nothing more than a cute opportunity for Das to be involved with their daughters' TikTok careers.
What genes are inherited from father only?
#2 Y-Linked Traits (for Sons) Sons can only inherit a Y chromosome from dad, which means all traits that are only found on the Y chromosome come from dad, not mom. Background: All men inherit a Y chromosome from their father, and all fathers pass down a Y chromosome to their sons.
Do babies look more like mom or dad?
"Our research, on a much larger sample of babies than Christenfeld and Hill's, shows that some babies resemble their father more, some babies resemble their mother more, and most babies resemble both parents to about the same extent," says Paola Bressan, a psychologist at the University of Padova in Italy who co- ...
Is a child more of the mother or father?
The egg and sperm each have one half of a set of chromosomes. The egg and sperm together give the baby the full set of chromosomes. So, half the baby's DNA comes from the mother and half comes from the father.
Who carries dominant genes?
In order for a person to show the dominant trait, one of the person's parents must have the dominant trait (which is an uppercase letter). Remember that human cells carry 2 copies of each chromosome, one from the biological mother's genes and one from the biological father's genes.
Why do girls look like their dad?
Your dad has more genetic influence It was originally thought that only 95 genes express the parent-of-origin effect. Now it's known that thousands of your genes express themselves according to what your dad added to the genetic pool. Did you know that you don't use an equal amount of genes from both parents?
What genes are inherited from mother only?
Unlike nuclear DNA, which comes from both parents, mitochondrial DNA comes only from the mother.
Are you genetically more like your dad?
Specifically, the research shows that although we inherit equal amounts of genetic materials from our parents – i.e., the mutations that make us who we are instead of some other person – we actually “use” more of the DNA that we inherit from our fathers.
Why are male mutations higher than females?
The standard explanation has been that fathers pass on more genetic mutations, because their sperm-producing cells divide throughout their lifetimes--as many as 400 times in a 30-year-old man. This provides many more chances for mistakes, as the DNA copies itself, than in egg cells, which only divide about 24 times.
Why are male mutation rates higher than female?
It is commonly believed that the rate of mutation is much higher in males than in females because the number of germ-cell divisions per generation is much larger in males than in females.
Why do males inherit less genes than females?
Human X and Y chromosomes determine the biological sex of a person, with XX specifying female and XY specifying male. Although the Y chromosome contains a small region of similarity to the X chromosome so that they can pair during meiosis, the Y chromosome is much shorter and contains many fewer genes.
How many sets of alleles are dominant?
With that being said, there are 2 sets of alleles that can be dominant or recessive. If a person carries a. set of alleles (both uppercase and lower case letter of the gene) then the person will show the dominant trait (being that there is an uppercase letter present). For example, the brown eye allele is dominant, B.
What is the dominant allele?
Dominant alleles are seen as an uppercase of a letter; for example, B. Recessive alleles are seen as a lower case of a letter; b. In order for a person to show the dominant trait, one of the person’s parents must have the dominant trait (which is an uppercase letter). Remember that human cells carry 2 copies of each chromosome, ...
What is a recessive allele?
Recessive alleles are the genes that do not show the trait. If a person has one copy of the brown eye allele (dominant) and one copy of the blue eye allele (recessive) then that person is considered to be a of the blue eye allele, since they would have brown eyes but still have the blue eye trait that is not shown.
What are some examples of different versions of a gene?
The coloring of the blue and brown eyes is an example of different versions of a gene. Different versions of a gene are called . Alleles can be considered dominant or recessive, with dominant being the trait that is observed or shown and recessive being the trait is not seen. Dominant alleles are seen as an uppercase of a letter; for example, ...
What is a sex-linked gene?
Sex-linked genes are genes that are inhererited through the X chromosome. Remember that a biological female carries 2 sets of X chromosomes (XX) and a biological male carries one set of the X and one set of Y chromosomes (XY). If the offspring is a boy, the X chromosome comes from the mother and the Y comes from the father.
What is it called when you have two copies of the alleles that are both dominant?
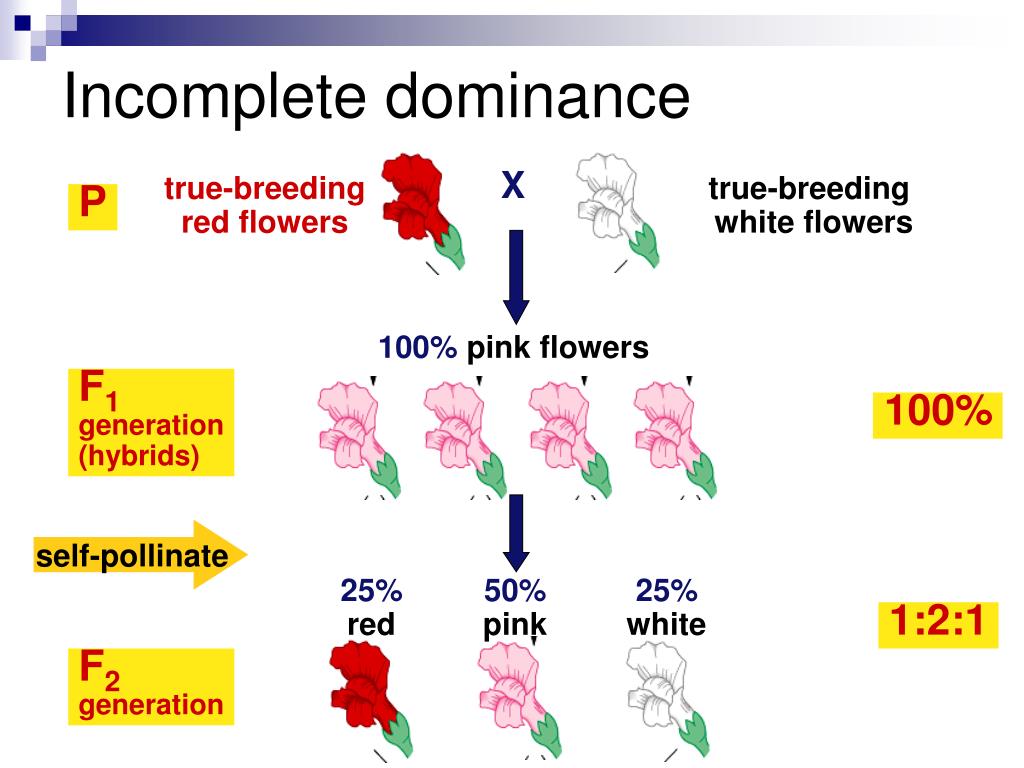
When you have two copies of the alleles that are both dominant, this is called. codominance. . For example, if the dominant trait is red for flowers and another dominant trait is white, then the flower will have both red and white as the dominant traits are expressed equally. If a person carries two copies of the brown eye allele, ...
Where does the X chromosome come from?
If the offspring is a boy, the X chromosome comes from the mother and the Y comes from the father. If the offspring is a girl, one of the X chromosomes comes from the mother and the other X chromosome comes from the father. In some genetic diseases that are caused by sex-linked genes, for example. haemophila.
How many boys are born for every 100 females?
In most countries, for as long as records have been kept, more boys than girls have been born. In the UK and US, for example, there are currently about 105 males born for every 100 females.
Why are men with more sons more likely to father boys?
As the odds were in favour of men with more sons seeing a son return from the war, those sons were more likely to father boys themselves because they inherited that tendency from their fathers. In contrast, men with more daughters may have lost their only sons in the war and those sons would have been more likely to father girls.
What chromosomes combine to make a boy?
An X chromosome combines with the mother's X chromosome to make a baby girl (XX) and a Y chromosome will combine with the mother's to make a boy (XY). The Newcastle University study suggests that an as-yet undiscovered gene controls whether a man's sperm contains more X or more Y chromosomes, which affects the sex of his children.
How many parts are in a gene?
A gene consists of two parts, known as alleles, one inherited from each parent. In his paper, Mr Gellatly demonstrates that it is likely men carry two different types of allele, which results in three possible combinations in a gene that controls the ratio of X and Y sperm;
Why do grandchildren have Mf?
The grandsons have the mf combination of alleles, because they inherited an m from their father and f from their mother.
Do men have more sons or daughters?
The work by Corry Gellatly, a research scientist at the university, has shown that men inherit a tendency to have more sons or more daughters from their parents. This means that a man with many brothers is more likely to have sons, while a man with many sisters is more likely to have daughters. The research, published online today by ...
Do men have only sons?
It is a simplified example, in which men either have only sons, only daughters, or equal numbers of each, though in reality it is less clear cut. It shows that although the gene has no effect in females, they also carry the gene and pass it to their children. In the first family tree (A) the grandfather is mm, so all his children are male.
Why do dads have more genes?
In the past, other scientists have suggested that dad’s genes are more robust because men need their children to look like them in order to believe they’re really the baby’s father. That makes intuitive evolutionary sense, given that men can’t be certain about their children’s parentage the way women are. But the evidence is actually all over the place, with just as many studies suggesting babies look more like their moms.
Why are father's genes more expressive?
While epigenetic mechanisms are clearly at play, why a father’s genes are more expressive remains unclear. Still, researchers are making headway, and many think it may start with a war all the way back in the womb.
Why is dad genetics so aggressive?
This parasitism is only exacerbated by the fact that dad genes tend to be really aggressive. Evolutionarily, a dad wants his babies to survive and thrive. That way, they’ll continue to pass on his genes, making him evolutionarily fit. But that means that his gene s want to pull resources away from the mother, who is — at least in an evolutionary context — only important to a guy insofar as she helps his baby live.
What happens if you knock out your father's genes?
Conversely, Chuong says, if you knock out a father’s genes, the babies become small — too small, actually. Turns out, the mother’s growth-suppressing genes weren’t always there.
How much of the father's genes are expressive?
While each parent technically contributed half of an offspring’s genome, approximately 60 percent of the dad’s genes were more expressive than the mom’s. These epigenetic factors can play a role in numerous parts of your life, but they aren’t just about quirks like eye color or whether or not you can roll your tongue.
How does epigenetics affect DNA?
Basically, epigenetics influence the way your DNA is actually expressed. This can alter your dad’s sperm, which in turn may affect you. It can also affect the way the genes you have are read — and the proteins they produce — across your lifetime.
Which gene suppresses the father's IGF?
This protein, which promotes growth, is strongly expressed by paternal genes. Maternal genes, meanwhile, express something called IGF2R, which actively suppresses the father’s IGF protein production and, therefore, the baby’s growth. “In mice, if you knock out the maternal genes, the babies become giant,” Chuong says.
How many copies of each gene are there?
However, we have two copies of each gene, and some genes are recessive. A famous example of a recessive gene that determines a visible trait is the gene for blondness. You have to have two copies of this gene to be blonde. So for example according to 23 and Me, I have one copy of the gene (there are a lot of blondes in my family), but as you can see from my picture, my hair is brown.
How many genes are involved in skin color?
Skin color isn’t like, oh, say, flower color in garden peas. There are at least eight genes that have a major influence on human skin color, all of them involved in regulating the production of melanin, the dark skin pigment. There are others that regulate, not skin color as such, but the tanning response—which is why some people develop truly savage tans in summer and others sunburn so easily; that has a
What genes affect skin color?
Table 1 and the abstract list eight genes that have a sizable effect on skin color (some also affect eye color or hair color): TYR, TYRP1, OCA2, SLC45A2, SLC24A5, MC1R, ASIP, and KITLG —along with three new candidate genes. Most of them have more than two alleles. (Interestingly, they’re all homologous with mouse genes for different coat colors—some are even homologous with color genes in zebrafish and stickleback fish.) Actually, if you read farther down, there are 279 genes in mice that can have some effect on skin pigmentation. (This has been updated; there are 378 mouse genes that can potentially affect pigmentation; see Color Genes - ESPCR & IFPCS for the current list.) All of those genes have homologues in the human genome. Not all of them routinely affect coat color, and some in fact are linked with diseases. Still, the total number of human genes that affect skin color is likely to end up being higher than eight.
When is a gene expressed?
It doesn’t work like that. A gene is expressed when it’s dominant, or suppressed when it’s recessive, unless there is a recessive gene from both parents, in which case it’s expressed. Some genes are codominant, meaning they’re both expressed or they code for a completely different trait when present.
Is race a trait or gene?
To begin with, there is no gene or trait that determines race. Rather, some alleles (variants of genes) are more common in some regions than others.
Does genetic imprinting affect gene expression?
There are a few fascinating cases in which genetic imprinting marks the parent-of-origin and has strong effects on gene expression. In Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes, the same genetic variant (allele) causes each syndrome, but the syndrome depends on which parent the allele is inherited from.
Does color blindness depend on gene?
It doesn’t depend on which gene came from whom , except in a very few cases (red-green color blindness, for example).