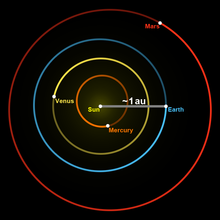
What is the origin of the astronomical unit?
In 1672 the Italian-born French astronomer Gian Domenico Cassini made a reasonably close estimate of the astronomical unit based on a determination of the parallax displacement of the planet Mars—and thus its distance to Earth.
When was the International Astronomical Union system of measurement adopted?
It was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976 via Resolution No. 1, and has been significantly updated in 1994 and 2009 (see astronomical constant ). The system was developed because of the difficulties in measuring and expressing astronomical data in International System of Units ( SI units ).
What is the astronomical system?
The astronomical system of units is a tridimensional system, in that it defines units of length, mass and time. The associated astronomical constants also fix the different frames of reference that are needed to report observations.
What are the other units for astronomical distances?
Other units for astronomical distances Astronomical range Typical units Distances to satellites kilometres Distances to near-Earth objects lunar distance Planetary distances astronomical units, gigametres Distances to nearby stars parsecs, light-years 2 more rows ...
See more

How was the astronomical unit first measured?
The original calculation The first-known person to measure the distance to the sun was the Greek astronomer Aristarchus of Samos (opens in new tab), who lived from about 310 B.C. to 230 B.C. He used the phases of the moon to measure the sizes and distances of the sun and moon.
What is an astronomical unit called?
An Astronomical Unit (AU) is the average distance between Earth and the Sun, which is about 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers. Astronomical units are usually used to measure distances within our Solar System.
What is the astronomical unit used for?
The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars.
What is the value of 1 AU?
1 A.U is equal to the average distance between sun and earth i.e 149,597,870.7 kilometres or 1.4960 * 10^11 meters.
What is bigger than a light-year?
Thus the Light Year is just not a practical unit for our solar system. Astronomers use another distance unit, the parsec, which represents 3.26 light years or about 20 trillion miles.
What is bigger a light-year or an AU?
A light-year, alternatively spelled lightyear, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (9.46×1012 km), or 5.88 trillion miles (5.88×1012 mi)....Light-yearastronomical units63241 au 0.3066 pc10 more rows
How far is an AU in space?
about 93 million milesSo for cosmic distances, we switch to whole other types of units: astronomical units, light years and parsecs. Astronomical units, abbreviated AU, are a useful unit of measure within our solar system. One AU is the distance from the Sun to Earth's orbit, which is about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers).
What is full form AU?
AU Full Form AU stands for Audio Units. AU is a set of API services that helps in the transmission of the audio file in near real-time. AU stands for Audio Units.
What is meant by 1 parsec?
One parsec equals 3.26 light-years, which is equivalent to 3.09 × 1013 km (1.92 × 1013 miles).
Is a Lightyear a unit of speed?
A light-year is a measurement of distance and not time (as the name might imply). A light-year is the distance a beam of light travels in a single Earth year, which equates to approximately 6 trillion miles (9.7 trillion kilometers).
How heavy is the Sun?
1.989 × 10^30 kgSun / Mass
Is a light-year?
Light-year is the distance light travels in one year. Light zips through interstellar space at 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second and 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers) per year.
What is meant by 1 parsec?
One parsec equals 3.26 light-years, which is equivalent to 3.09 × 1013 km (1.92 × 1013 miles).
What is astronomical unit of mass?
The astronomical unit of mass is the solar mass. The symbol M ☉ is often used to refer to this unit. The solar mass ( M ☉), 1.98892×1030 kg, is a standard way to express mass in astronomy, used to describe the masses of other stars and galaxies.
What is an astronomical unit quizlet?
An Astronomical unit is a unit of measurement equal to the average distance between the Sun and Earth, i.e, about 149,600,000 (1.496 times 10 to the power of 8) km. Define light year. A light year is a unit of measurement equal to the distance light travels in one year,i.e, 9.46 time 10 to the power of 12 km.
Is parsec a unit of Time?
A parsec is a unit of distance, not time, so why would Solo use it to explain how quickly his ship could travel? There are two stories going on here.
Why was the astronomical system of units created?
The system was developed because of the difficulties in measuring and expressing astronomical data in International System of Units ( SI units ). In particular, there is a huge quantity of very precise data relating to the positions of objects within the Solar System which cannot conveniently be expressed or processed in SI units. Through a number of modifications, the astronomical system of units now explicitly recognizes the consequences of general relativity, which is a necessary addition to the International System of Units in order to accurately treat astronomical data.
What is the astronomical system?
The astronomical system of units, formerly called the IAU (1976) System of Astronomical Constants, is a system of measurement developed for use in astronomy. It was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976 via Resolution No. 1, and has been significantly updated in 1994 and 2009 (see astronomical constant ).
What is the unit of mass?
The astronomical unit of mass is the solar mass. The symbol M☉ is often used to refer to this unit. The solar mass ( M☉ ), 1.988 92 × 1030 kg, is a standard way to express mass in astronomy, used to describe the masses of other stars and galaxies. It is equal to the mass of the Sun, about 333 000 times the mass of the Earth or 1 048 times the mass of Jupiter .
Is the unit of length a physical constant?
The system is a conventional system, in that neither the unit of length nor the unit of mass are true physical constants, and there are at least three different measures of time.
Who was the first person to estimate the astronomical unit of Mars?
In 1672 the Italian-born French astronomer Gian Domenico Cassini made a reasonably close estimate of the astronomical unit based on a determination of the parallax displacement of the planet Mars —and thus its distance to Earth.
How to find the astronomical unit of the Sun?
In principle, the easiest way to determine the value of the astronomical unit would have been to measure the Earth-Sun distance directly by means of the parallax method. In this approach, two observers stationed at the ends of a long, accurately known baseline—ideally, a baseline as long as Earth’s diameter—would simultaneously record the position of the Sun against the essentially motionless background of the distant stars. Comparison of the observations would reveal an apparent shift, or angular (parallax) displacement, of the Sun against the remote stars. A simple trigonometric relationship incorporating this angular value and the baseline length then could be used to find the Earth-Sun distance. In practice, however, the method cannot be applied, because the Sun’s intense glare blots out the background stars needed for the parallax measurement.
What is the distance from the Sun that a massless particle in a circular orbit would have a period of?
In 1976 the International Astronomical Union (IAU) defined the astronomical unit as the distance from the Sun at which a massless particle in a circular orbit would have a period of one year. This definition relied on a solely Newtonian model of the solar system.
How far is Uranus from the solar goal line?
Neptune is where things start to get way out. It is 60 yards from our solar goal line on the imaginary football field.
How far is one AU?
One AU, about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers), represents the average distance from the Sun to the Earth. It would take an airliner more than 20 years to fly that distance — and that's just a one-way ticket. (That's traveling at about 400 mph or 644 kilometers per hour.)
Why is the Earth's location in the solar system important?
We are at the perfect distance from the Sun for life to flourish. Venus is too hot. Mars is too cold. Scientists sometimes call our region of space the "Goldilocks Zone" because it appears to be just right for life.
What are the inner planets?
The inner planets — Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars — are about the size of grains of sand on a football field scale. They would be dwarfed by a typical flea, which is about 3 millimeters long. Closest to the goal line is Mercury, just under a yard from the end zone (.8 yards to be specific).
How far is Voyager 1 from the Sun?
As of Feb. 1, 2020, Voyager 1 is about 13.8 billion miles (22.2 billion kilometers) from the Sun — nearly four times the average distance from ...
How big is the Sun?
On this scale, the Sun, by far the largest thing in our solar system, is only a ball about two-thirds of an inch (17 millimeters) in diameter sitting on the goal line — that's about the width of a U.S. dime coin. Considering a typical honeybee is about half an inch long, the fans are going to need telescopes to see the action.
How far is Mercury from the Sun?
In reality, the average distance from the Sun to Mercury is roughly 35 million miles (58 million kilometers) or 0.4 AU. At this scale, Mercury's diameter would be scarcely as large as the point of a needle. Venus is next. It is 1.4 yards from the end zone.
How many light years have been created?
No one “created” light years. A light-year is the distance light travels in a year, around 5.7 trillion miles, and is therefore a naturally occurring relation in the universe. According to Wikipedia a British scientist was the first to suggest that one way of looking at a star’s distance from the Earth is to consider how long it would take light from that star to reach us. While he spoke of a “light year”, the term really began to be used by a German writer with a master’s degree in science, Otto Eduard Vincenz Ule. Scientists generally prefer the unit “parsecs”. A light year may also be expressed as 9,460,730,472,580,800 meters or 0.0306607 parsecs.
Who invented the light bulb?
The story of the light bulb starts many years before Edison 's name is associated with the invention of the incandescent lamp. Various sources credit English electrochemist Humphry Davy with demonstrating the incandescent lamp and the arc light in the early 1800s. Frederick de Moleyns of England was granted the first patent for an incandescent lamp in 1841. Joseph Swan first demonstrated the first carbon-filament incandescent light bulb in 1878.
What is the light year?
Lightyear is not some physical object that can be "invented" or "discovered". It is just another shorthand way of representing astronomically large distances. Friedrich Bessel in 1838 was the first recorded user of the term; but since the speed of light was not accurately known at that time, the term was less popular; and sometimes considered "irrelevant". Astronomical Unit (1 AU=Average distance between the Sun & Earth=149,597,871 kilometres) was more preferred. The "light-year" unit appeared, however, in 1851 in a German popular astronomical article by Otto Ule. The term is still confusing for several people since "a distance unit name ending on year " is an obvious awkwardness. Even though the term is still very much in use; another larger unit " parsec " is much more popular in the scientific community.
Why were the Babylonians interested in 360?
Lomb says it's likely that the Babylonians were interested in 360 because that was their estimate for the number of days in a year. Their adoption of a base 60 system was probably allowed them to make complex calculations using fractions. They derived their number system from the Sumerians who were using it as early as 3500 BC.
What is the unit of measurement of distance?
Distance is the measure of length or space between two objects or two points in free space. Distances are measured in meters (SI Unit). There are many units to measure distances, namely meters , miles, inches etc.
Where did the hour into minute come from?
DIVISION of the hour into 60 minutes and of the minute into 60 seconds comes from the Babylonians who used a sexagesimal (counting in 60s) system for mathematics and astronomy.
Is the light year an object?
Lightyear is not some physical object that can be "invented" or "discovered". It is just another shorthand way of representing astronomically large distances. Friedrich Bessel in 1838 was the first recorded user of the term; but since the speed of light was not accurately known at that time, the term was less popular; and sometimes considered "irrelevant". Astronomical Unit (1 AU=Average distance between the Sun & Earth=149,597,871 kilometres) was more preferred. The "light-year" unit appeared, however, in 1851 in a German popular astronomical article by Otto Ule. The term is still confusing

Overview
The astronomical system of units, formerly called the IAU (1976) System of Astronomical Constants, is a system of measurement developed for use in astronomy. It was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976 via Resolution No. 1, and has been significantly updated in 1994 and 2009 (see astronomical constant).
The system was developed because of the difficulties in measuring and expressing astronomica…
Astronomical unit of time
The astronomical unit of time is the day, defined as 86400 seconds. 365.25 days make up one Julian year. The symbol D is used in astronomy to refer to this unit.
Astronomical unit of mass
The astronomical unit of mass is the solar mass. The symbol M☉ is often used to refer to this unit. The solar mass (M☉), 1.98892×10 kg, is a standard way to express mass in astronomy, used to describe the masses of other stars and galaxies. It is equal to the mass of the Sun, about 333000 times the mass of the Earth or 1 048 times the mass of Jupiter.
In practice, the masses of celestial bodies appear in the dynamics of the Solar System only thro…
Astronomical unit of length
The astronomical unit of length is now defined as exactly 149 597 870 700 meters. It is approximately equal to the mean Earth–Sun distance. It was formerly defined as that length for which the Gaussian gravitational constant (k) takes the value 0.01720209895 when the units of measurement are the astronomical units of length, mass and time. The dimensions of k are those of the constant of gravitation (G), i.e., L M T . The term “unit distance” is also used for the length …
See also
• Astronomical constant
• Standard gravitational parameter
• Planetary mass
• Natural units
External links
• The IAU and astronomical units
• "2014 Selected Astronomical Constants" in The Astronomical Almanac Online, USNO–UKHO.