
For public health, the CDC groups stakeholders into three major brackets:
- Programs operations – Management, program staff, partners, funding agencies, and coalition members.
- Those served or affected by the program – Patients or clients, advocacy groups, community members, and elected officials.
- Intended users of the end product – People who could make decisions, including partners, coalition members, the general public, or taxpayers.
Who is the most important stakeholder in the healthcare industry?
- Financial Stakeholders.
- Medical Leaders.
- End-Users: Clinicians.
- Patients.
- Vendors.
- Billing and Audit Functions.
- Continued Engagement and Communication Equals Project Success.
Who are the major stakeholders in the US healthcare industry?
Which are the key players in the US healthcare Industry?
- Member. A member is a person who purchases insurance from (or enrols with) an insurance company. ...
- Provider. A Provider is that entity which offers actual medical services to the members. ...
- Insurer/Carrier. An entity that insures the member in the event of an healthcare service to be provided to the member is called a carrier/insurer.
- Sponsor/Employer. ...
Who are the stakeholders in healthcare policy making?
These stakeholders include patients, providers, payers, and policymakers. The quality of the Healthcare systems depends heavily on how mobilized and concerned these professional groups are in ensuring quality health services. The first stakeholder is the policymakers, ministers, or jurisdictional authorities for deciding the healthcare policies.
What are the duties of a stakeholder?
What are the duties of the Stakeholders in Project Management?
- The Creditors who finance or provide resources.
- Directors, who format the planning and implementation process.
- The Government Agencies for sanctioning of various requirements and providing infrastructure facilitation.
- Shareholders (Owners) who Invest or promise to further invest the Owner's capital.
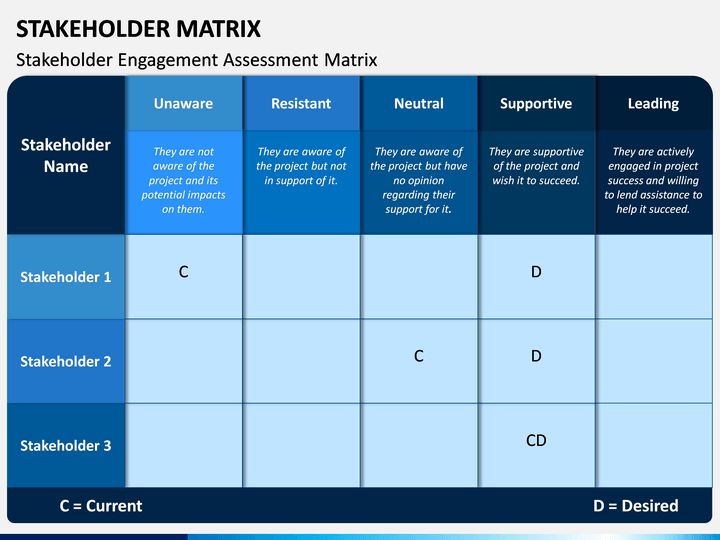
What is the role of healthcare stakeholders?
Stakeholders in healthcare play a major role in the direction of the healthcare industry. Their support is vital as they provide funding, support, strategic direction, solutions and more to the overall healthcare industry.
Who are the main stakeholders?
Typical stakeholders are investors, employees, customers, suppliers, communities, governments, or trade associations. An entity's stakeholders can be both internal or external to the organization.
What type of stakeholder is a hospital?
Patients, physicians, employees, the broader community, and legislative and regulatory bodies are examples of hospital stakeholders — those individuals or groups who are greatly influenced by the hospital and have a vested interest in its success.
What are the 5 main stakeholders?
Types of Stakeholders#1 Customers. Stake: Product/service quality and value. ... #2 Employees. Stake: Employment income and safety. ... #3 Investors. Stake: Financial returns. ... #4 Suppliers and Vendors. Stake: Revenues and safety. ... #5 Communities. Stake: Health, safety, economic development. ... #6 Governments. Stake: Taxes and GDP.
How would you define a stakeholder?
The international standard providing guidance on social responsibility, called ISO 26000, defines a stakeholder as an "individual or group that has an interest in any decision or activity of an organization."
What are the 3 P's in healthcare?
The 3 P's model encompasses an evidence‐based approach to preparation, protection and prevention, for safety of patients and healthcare staff.
Who are the external stakeholders in healthcare?
Key external stakeholders include patients, insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, and medical equipment companies. Due to patients being more diligent in their medical care, making informed decisions with the information provided by their physicians, their experience is vital as external stakeholders.
Who are the stakeholders in nursing?
Stakeholders may include representatives of nursing homes, trade associations, ombudsmen, State survey agencies, medical directors, directors of nursing, geriatric nursing assistants, other licensed professionals, academicians and consumers.
What are the 4 stakeholder groups?
The easy way to remember these four categories of stakeholders is by the acronym UPIG: users, providers, influencers, governance.
What are examples of stakeholders?
A stakeholder can be a wide variety of people impacted or invested in the project. For example, a stakeholder can be the owner or even the shareholder. But stakeholders can also be employees, bondholders, customers, suppliers and vendors. A shareholder can be a stakeholder.
Who are key stakeholders in a project?
Stakeholders are those with an interest in your project's outcome. They are typically the members of a project team, project managers, executives, project sponsors, customers, and users.
Who are primary and secondary stakeholders?
Primary stakeholders are those who have a direct interest in your organisation, whereas secondary stakeholders have an indirect association or benefit. If you have clear, concise plans of how to address each of your key stakeholder segments, you will ensure your organisation is continuously affirming your relevance.
Why are stakeholders important in healthcare?
Stakeholders are important in healthcare because they promote the continued advancement of health-related products, services, research, and program...
Who are the stakeholders in healthcare projects?
The most important stakeholders are patients. However, providers, policy makers, researchers, schools, pharmaceuticals, local government, health ed...
How do you identify stakeholders in healthcare?
There are many questions that should be asked when identifying a key stakeholder in healthcare, such as: Is the stakeholder involved with any othe...
How Do You Identify Stakeholders in Healthcare?
To identify stakeholders in healthcare you should use a stakeholder identification method . A good starting point would be to download a stakeholder communications template that will help you clearly identify your stakeholders.
Who is the Most Important Stakeholder in The Healthcare Industry?
The most important stakeholders in healthcare are the patients, providers (professionals) and policymakers, the three ‘Ps’.
How can stakeholders influence the public opinion about the healthcare system?
Stakeholders in healthcare can influence the public opinion about the healthcare system and that of its subsidiaries by providing information and opinion on the particular healthcare organisation.
What can stakeholders do to help the healthcare industry?
Stakeholders can provide the healthcare industry with primary research and can respond realistically to proposed changes, helping to shape a modern healthcare industry.
What is Canberra Health Services?
Canberra Health Services deliver a range of health services for patients and consumers across the Australian Capital Territory (ACT) and surrounding Southern New South Wales region. They send out regular communications to their stakeholders keeping them informed of new development across the healthcare sector in Canberra.
How to contact Swift Digital?
To find out how your business can get the best out of Swift Digital’s platform, contact our team today on 02 9929 7001.
What is an iCanquit landing page?
This example from IcanQuit was created for a campaign by the NSW Government. This landing page is used in the campaign to communicate with their stakeholders. The subsidiary being health and social care and health promotion and the stakeholders in healthcare being the patient along with the Government.
What is a healthcare stakeholder?
A stakeholder is ''a person who has something to gain or lose through the outcomes of a planning process, program or project.''. Healthcare policy making is such a process and it affects those involved in the industry.
What are the stakeholders in healthcare?
The stakeholders in healthcare include providers, insurance companies, governments, and patients, and there are others as well. All of these stakeholders affect policy change and reform. Insurance companies are profit-driven and want to keep costs down and claim payments low.
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
What are the government agencies that collect data?
The many government agencies, like the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), have committees and agencies within them that collect data and propose solutions to various healthcare quality problems. They also do research on the cost-effectiveness of various delivery methods of healthcare.
Why do health insurance companies exist?
The health insurance companies exist primarily to make a profit. If it were all up to them, they'd only insure people who are so healthy that they never need any medical care, and certainly no one who had a pre-existing condition, or a chronic health problem that started some time ago and still exists.
What is a provider in healthcare?
The Providers. Providers are the people who actually deliver healthcare. They are trained individuals like physicians, nurses, nurse clinicians, chiropractors, physical therapists, and others who deliver various modalities of care.
Why do insurance companies want to keep the costs of care low?
Insurance companies want to keep the costs of care low, so they don't want the doctor to order every test available. But patients and families want to be sure nothing's wrong, or that whatever is wrong is found and treated.
What are the stakeholders in nursing homes?
The patient is the individual who needs to receive the care provided by nursing homes. Another key stakeholder is the patient’s family. In many cases a family member is the power of attorney for the patient that is being admitted into the nursing home. These people need to be kept apprised of the different levels of care that are needed for the patient as well as any changes in the overall health of the patient .
Why is it important to have a strategy for handling stakeholders?
Strategies for handling Stakeholders. It is important when working with stakeholders to have communication skills. If you are unable to communicate in a professional manner it will cause problems when handling the different stakeholders who work with your company. It is also necessary to be able to manage the expectations of your stakeholders. Stakeholder mapping will help you to determine who your stakeholders are and be able to develop plans to meet the different expectations that they have.
What is a nursing home?
A nursing home or long-term care facility is a place that is used to assist elderly and disabled patients with their daily care. These individuals do not need to be in a hospital so they find a facility that can help them provide the assistance they need to complete their activities of daily living. In a nursing home there is a person or people on site to provide care for the residents twenty-four hours a day seven days a week. The set up of a nursing home is dependent on the type of care they wish to offer. Some will offer not only assistance with daily activities but also different types of therapy to their residents.
How does a primary care physician play a role in reducing healthcare costs?
Physicians play a key role in ensuring that their patients receive adequate healthcare, but also in controlling the rising costs of healthcare. They have to find a balance between having a gatekeeper role for the insurance companies and being an advocate for the patient. Assigning a gatekeeper role to primary care physicians had the intention of lowering healthcare costs because fewer tests and referrals would be made. However, this is not working and it may be best to re-evaluate the role a primary care physician has in regards to referring patients. A coordinator role may be more beneficial than gatekeeper status. Also, since primary care physicians have increased the number of patients seen in a day to compensate for their decrease in revenue, this causes an increase in defensive diagnostic testing. The doctors do not have adequate time to review the chart or spend time with the patient, so they order more tests to reduce their liability risks. These actions cause healthcare spending to increase as well. By placing the physician between these two roles, a conflict of interest is created. Ethically, the doctor has a fiduciary duty to protect the interests of his patient, but in the current managed care environment, insurance companies give incentives to physicians to order fewer referrals and to cram more patients into each workday. Edmund Pellegrino stated, “What our health policies do to the individual patient serves as a reality check to what values we hold most dear and the ethical foundation of the policies we develop and impose”. It appears that money is at the center of our values.
What are the stakeholders of pharmaceutical companies?
Two of the stakeholders, pharmaceutical firms and insurance companies, are publically owned corporations listed on the stock exchange. Their primary responsibility is to maximize stockholder wealth. Likewise, the primary goal of employers is to make money; however, their provision of health insurance for employees is a benefit, ...
What are the rights of the Declaration of Independence?
The Declaration of Independence seems to juxtapose two rights: the right to equality and the right to liberty. Equalitarians emphasize the former; libertarians, the latter. Equalitarians hold that healthcare is a human right; libertarians hold that healthcare is a commodity. Equalitarianism emphasizes the role of government and is more appealing to democrats; libertarianism emphasizes the role of free market and is more appealing to republicans. The fundamental chiasm between these two contrasting ideologies which are operative in American culture remains an impediment to healthcare reform in the United States.
Why do pharmaceutical companies play a key role in healthcare?
Pharmaceutical companies also play a key role in the healthcare system because many patients rely on their products. The prices for drugs are rising, and there are no caps to prevent them from reaching extravagant prices. The argument that the pharmaceutical companies need to charge ever higher prices to cover research costs is simply not true. Although PHARMA spent $43 billion on R&D in 2006, it spent nearly twice as much on promotion, and it consistently has profit margins far above those of most Fortune 500 companies.
What is the obligation of a physician?
Physicians also have obligations to patients independent of insurance companies. A physician has an obligation of beneficence to do whatever is necessary to benefit his patient. However if he acts independently (“doctor knows best”) without taking into account the desires of his patient, he is practicing paternalism. Thus, the obligation of beneficence must be balanced by the principle of patient autonomy. Each patient is unique and has the right to participate completely in decisions about his health.
Which is more appealing to democrats, egalitarianism or libertarianism?
Equalitarians hold that healthcare is a human right; libertarians hold that healthcare is a commodity. Equalitarianism emphasizes the role of government and is more appealing to democrats; libertarianism emphasizes the role of free market and is more appealing to republicans.
Who are the stakeholders in healthcare?
The major stakeholders in the healthcare system are patients, physicians, employers, insurance companies, pharmaceutical firms and government. Insurance companies sell health coverage plans directly to patients or indirectly through employer or governmental intermediaries. Pharmaceutical firms develop and then market medications which are prescribed by doctors to treat patients. Typically they receive remuneration through insurance or governmental drug-benefit plans. Many employers offer health insurance coverage with varying deductibles and co-pays for their employees. Physicians are the providers of medical care; patients are the recipients. And government subsidizes healthcare for the elderly, the disabled and the poor. All stakeholders have duties and responsibilities.
Why are clinical registry data important?
Clinical registries are an essential part of the learning healthcare system.3They collect pre-specified structured data longitudinally and derive information, evidence and actionable knowledge to improve the patient’s healthcare. They also monitor whether a change in care results in improvement, no change, or deterioration over time. Improvement in health and care can result from reduction of mortality, morbidity or complications, maintenance or improvement of quality of life, more equal distribution of healthcare (e.g. can prevent over- and under-treatment) and better distribution and sustainability of available resources. Another use of registry data relates to the prevention of adverse events and threats to patients and to public health. Tissue responses from cobalt ions produced from excessive wear in metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty or implant-related infections are examples of serious adverse events which impact on patient outcome. Moreover, the evidence derived from clinical registries has an important role in guiding the innovation process towards relevant, usable and sustainable innovations.4
What is a registry?
The registry is perceived as an instrument for quality control of care providers and institutions and also as a cost-control tool. In particular, registries provide information and evidence for reimbursement decisions (e.g. coverage of a new device or technique conditional on evidence development).20.
What is the most important stakeholder group in healthcare?
Patients are the single most important stakeholder group with regard to the learning healthcare system. They are both the donors of personal clinical data and the ultimate beneficiaries from the knowledge gained.’11
What are the stakeholders in healthcare?
Stakeholders are ‘A person, group or organization that has interest or concern in an organization. Stakeholders can affect or be affected by the organization’s actions, objectives and policies’.7In healthcare the main stakeholders are Patients, Providers (professionals and institutions), Payors, and Policymakers (‘The four Ps’ in healthcare).8Moreover, industry (e.g. medical device, pharmaceutical, biotechnology), regulators, research community, and media are also important. Stakeholders largely differ in interest and need, in support and attitude, and in influence; the latter in the positive as well as the negative sense. This makes their identification and the analysis of their points of view and interests crucial for the success of a mission-driven long-term collaborative effort, such as a clinical registry. It is of utmost importance that the governing board/committee and the registry data team are independent from any single stakeholder interest.
What is registry stakeholders?
Registry stakeholders: relevant and interested parties and their relationships with the registry. The governing board(s) guides and guarantees the purpose/mission of the registry, is responsible for the appropriate use of the data,6and communicates with the data team and the stakeholders. Registry stakeholders.
What is clinical registries?
Clinical registries are health information systems, which have the mission to collect multidimensional real-world data over the long term, and to generate relevant information and actionable knowledge to address current serious healthcare problems.
Why are public health agencies important?
They therefore need data on the overall clinical activity for public health purposes, needs assessments and for planning the macro-economic policies related to healthcare. Moreover, they rely on registry information among others for health technology assessment and subsequent reimbursement policies.13,21Public health agencies are also keen to ensure that the institutions under their supervision provide high-quality and complication-free healthcare to the overall population. The agencies will also have an interest in benchmarking hospitals and in keeping insurance and third-party payor costs down to a minimum. National and international regulatory bodies play an important role in supervising implant systems, as they seek to guarantee that the industrial specifications of nationally manufactured and imported implants are safe, efficient and reliable for public usage. In this endeavour they strongly rely on the evidence generated from international, national and regional registries.22–24
