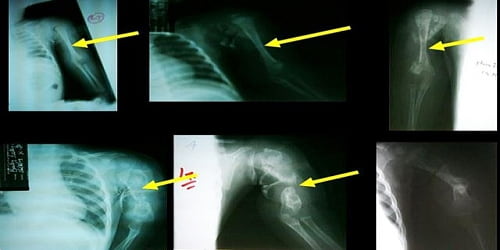
Symptoms
- Fever (may be high when osteomyelitis occurs as the result of a blood infection)
- Pain and tenderness in the affected area
- Irritability in infants who can’t express pain
- Feeling ill
- Swelling of the affected area
- Redness in the affected area
- Warmth in the affected area
- Difficulty moving joints near the affected area
- Difficulty bearing weight or walking
Causes
What Happens If Osteomyelitis Is Left Untreated?
- Osteomyelitis A patient will notice osteomyelitis first at the site of their wound or trauma site. ...
- Necrosis Necrosis is cell death triggered by infection, trauma, lack of blood supply, or a combination of several conditions. ...
- Sepsis
Prevention
- A combined medical and surgical approach is usually needed
- Dead tissue must be removed
- Poorly-vascularized tissue is unlikely to heal
- Empiric therapy not guided by culture results is more likely to fail
- With few exceptions, infection is very difficult to eradicate from prosthetic material
Complications
Surgery can incorporate:
- Draining any pus or fluid that has developed in response to the infection.
- Removing an infected bone or any surrounding tissue with signs of infection.
- Restoring blood flow to the damaged bone by placing a piece of bone tissue or skin from another part of the body.
What is the life expectancy of someone with osteomyelitis?
What happens if osteomyelitis is left untreated?
How to rule out osteomyelitis?
How to cure bone infection?

Who is most likely to osteomyelitis?
Infections can also begin in the bone itself if an injury exposes the bone to germs. Smokers and people with chronic health conditions, such as diabetes or kidney failure, are more at risk of developing osteomyelitis. People who have diabetes may develop osteomyelitis in their feet if they have foot ulcers.
What are the risk factors that increase chance for osteomyelitis?
You're more at risk for getting osteomyelitis if you have:Artificial joint, such as a hip replacement.Blood infection or conditions like sickle cell anemia.Diabetes, especially a diabetes-related foot ulcer.Metal implants in bone, such as a screw.Pressure injuries (bedsores).Recent broken bone or bone surgery.More items...•
What is the most common cause of bone infection?
Bone infection is most often caused by bacteria. But it can also be caused by fungi or other germs. When a person has osteomyelitis: Bacteria or other germs may spread to a bone from infected skin, muscles, or tendons next to the bone.
Where does osteomyelitis occur in adults?
In adults, the vertebrae are the most common site of hematogenous osteomyelitis, but infection may also occur in the long bones, pelvis, and clavicle. Primary hematogenous osteomyelitis is more common in infants and children, usually occurring in the long-bone metaphysis.
What can cause osteomyelitis?
What Causes Osteomyelitis? In most cases, a bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus, a type of staph bacteria, causes osteomyelitis. Certain chronic conditions like diabetes may increase your risk for osteomyelitis.
Can osteomyelitis be prevented?
Can Osteomyelitis Be Prevented? One way to prevent osteomyelitis is to keep skin clean. All cuts and wounds — especially deep wounds — should be cleaned well. Wash a wound with soap and water, holding it under running water for at least 5 minutes to flush it out.
What is the most common bone site of osteomyelitis?
Among children and teens, the long bones of the legs and arms are most frequently affected. In adults, osteomyelitis most often affects the vertebrae of the spine and/or the hips. However, extremities are frequently involved due to skin wounds, trauma and surgeries.
When should you suspect osteomyelitis?
Suspect acute osteomyelitis most commonly in an unwell child with a limp, or in an immunocompromised patient. Suspect chronic osteomyelitis most commonly in adults with a history of open fracture, previous orthopaedic surgery, or a discharging sinus.
What is the gold standard for diagnosing osteomyelitis?
The gold standard for the diagnosis of osteomyelitis is bone biopsy with histopathologic examination and tissue culture. When the patient is clinically stable, one should consider delaying empiric antimicrobial treatment until bone biopsy is performed.
Which is the most common organism causing osteomyelitis in all age group?
Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of acute and chronic hematogenous osteomyelitis in adults and children.
How is osteomyelitis diagnosed?
The preferred diagnostic criterion for osteomyelitis is a positive bacterial culture from bone biopsy in the setting of bone necrosis. Magnetic resonance imaging is as sensitive as and more specific than bone scintigraphy in the diagnosis of osteomyelitis.
What does bone pain feel like?
Bone pain usually feels deeper, sharper, and more intense than muscle pain. Muscle pain also feels more generalized throughout the body and tends to ease within a day or two, while bone pain is more focused and lasts longer. Bone pain is also less common than joint or muscle pain, and should always be taken seriously.
Who Is Affected by Osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis can affect both adults and children. The bacteria or fungus that can cause osteomyelitis, however, differs among age groups. In adult...
What Causes Osteomyelitis?
It can be caused by a variety of microbial agents (most common in staphylococcus aureus) and situations, including: 1. An open injury to the bone,...
What Are The Symptoms of Osteomyelitis?
The symptoms of osteomyelitis can include: 1. Pain and/or tenderness in the infected area. 2. Swelling, redness and warmth in the infected area. 3....
Which approach is useful in classifying the risk factors for the development of acute osteomyelitis?
An approach that is useful in classifying the risk factors for the development of acute osteomyelitis is the same as one commonly employed to discuss the mechanisms responsible for pathogenesis: hematogenous dissemination, direct inoculation, and contiguous spread from an adjacent area of soft tissue infection.
How does osteomyelitis develop?
The second major mechanism for the development of acute osteomyelitis is by direct inoculation. Injuries due to penetrating bites and puncture wounds of the food may serve to infect bone directly.
What are the factors that favor the development of acute bone infection?
These include indwelling intravascular catheters, distant foci of infection, and intravenous drug abuse. The distant sites of focal infection that are most commonly associated with acute osteomyelitis include the skin as well as urinary ...
What is the most common cause of infection of the mandible, maxilla, and frontal or masto
Infection of the mandible, maxilla, and frontal or mastoid bones may result from persistent or neglected infection of the teeth, paranasal sinuses , or middle ear cavity, respectively. The major risk factor for chronic infection of bone is inadequate or delayed management of acute osteomyelitis or completely unrecognized bone infection.
What are the long term complications of osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis requires long-term care to prevent further complications, including care to prevent the following: Fractures of the affected bone. Stunted growth in children (if the infection has involved the growth plate) Gangrene infection in the affected area.
How do you know if you have osteomyelitis?
The following are the most common symptoms of osteomyelitis; however, each individual may experience symptoms differently: Fever (may be high when osteomyelitis occurs as the result of a blood infection) Pain and tenderness in the affected area. Irritability in infants who can’t express pain. Feeling ill.
What tests are done to check for osteomyelitis in children?
The provider treating your child will first do a thorough history and physical exam that may indicate signs of osteomyelitis like those listed above. An additional workup generally includes blood tests that look at white blood cells as well as markers for inflammation that are usually elevated during an infection.
What is the term for inflammation of the bone?
Osteomyelitis is inflammation or swelling that occurs in the bone. It can result from an infection somewhere else in the body that has spread to the bone, or it can start in the bone — often as a result of an injury. Osteomyelitis is more common in younger children (five and under) but can happen at any age. Boys are usually more affected ...
How long does osteomyelitis last?
Intravenous or oral antibiotic treatment for osteomyelitis may be very extensive, lasting for many weeks.
Can Osteomyelitis be a chronic disease?
This includes people with sickle cell disease or HIV or those receiving immunosuppressive medications like chemotherapy or steroids. Osteomyelitis can have a sudden onset, a slow and mild onset or may be a chronic problem, depending on the source of the infection. ViewMedica 8. Start Picture-in-Picture. Get Embed Code.
Can osteomyelitis be treated with antibiotics?
Boys are usually more affected than girls. Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat osteomyelitis. Surgery may also be recommended in certain cases.
What is osteomyelitis infection?
What is osteomyelitis? Osteomyelitis is a bacterial, or fungal, infection of the bone. Osteomyelitis affects about 2 out of every 10,000 people. If left untreated, the infection can become chronic and cause a loss of blood supply to the affected bone.
Why is it important to treat osteomyelitis?
The objective of treating osteomyelitis is to eliminate the infection and prevent the development of chronic infection. Chronic osteomyelitis can lead to permanent deformity, possible fracture, and chronic problems, so it is important to treat the disease as soon as possible.
What is the disease that can cause bone tissue death?
Osteomyelitis. Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone that can affect both adults and children. If left untreated, it can lead to bone tissue death over time. Appointments 216.444.2606. Appointments & Locations. Contact Us. Overview. Symptoms and Causes. Diagnosis and Tests.
How do you know if you have osteomyelitis?
The symptoms of osteomyelitis can include: Pain and/or tenderness in the infected area. Swelling, redness and warmth in the infected area. Fever. Nausea, secondarily from being ill with infection. General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling. Drainage of pus (thick yellow fluid) through the skin.
What causes a bone to break out?
It can be caused by a variety of microbial agents (most common in staphylococcus aureus) and situations, including: An open injury to the bone, such as an open fracture with the bone ends coming out through the skin.
What causes a blood clot in the bone?
A minor trauma, which can lead to a blood clot around the bone and then a secondary infection from seeding of bacteria. Bacteria in the bloodstream (bacteremia), which is deposited in a focal (localized) area of the bone. This bacterial site in the bone then grows, resulting in destruction of the bone.
Is osteomyelitis more common in the tibia or humerus?
They include the femur and tibia in the legs and the humerus and radius in the arms. Osteomyelitis is not more common in a particular race or gender. However, some people are more at risk for developing the disease, including: People with diabetes. Patients receiving hemodialysis.
Why is osteomyelitis long term?
Osteomyelitis needs long-term care to prevent complications such as: Fractures of the affected bone. Stunted growth in children, if the infection has involved the growth plate. Tissue death (gangrene) in the affected area.
Why does osteomyelitis start suddenly?
Diabetes. A weak immune system (such as HIV or getting cancer treatment) A prosthetic device. Osteomyelitis can have a sudden start, a slow and mild start, or may be a chronic problem. This depends on the source and cause of the infection.
What is the inflammation of bone tissue?
Osteomyelitis is an inflammation or swelling of bone tissue. It’s most often caused by an infection. Bone infection may occur for many reasons. It can affect children or adults.
Can osteomyelitis affect anyone?
Osteomyelitis can affect anyone. But, it is more common in babies, children, and older adults. People at greater risk include those with a weak immune systems, recent injury or surgery, or diabetes.
Can Staphylococcus aureus spread to bones?
This infection can spread to the bone. It’s most common in babies and children. It usually affects their long bones such as the thighbone or upper arm bone. In adults, it often affects the bones in the spine. The source of the blood infection is usually Staphylococcus aureus. But it may be caused by other germs.
What is the most common cause of osteomyelitis?
Many different types of germs (bacteria) can cause osteomyelitis. However, infection with a bacterium called Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause. Infection with a fungus is a rare cause.
How long does it take to cure osteomyelitis?
If the infection is treated promptly, there is a good chance of a complete cure. The best outcome occurs if you have treatment within 3-5 days of the start of infection. (In the days before antibiotic medicines, osteomyelitis was a very serious illness which sometimes caused death and often caused severe disability.)
What happens if you have an infection in your bone?
As a rule, there is more risk of developing complications if the infection develops after a serious bone injury, or after surgery to a bone: If the infection is left untreated, a ball of pus (abscess) may develop in the bone and surrounding tissue.
Can you have plastic surgery on a bone infection?
Dead and infected bone may need to be removed to allow the infection to clear. Sometimes plastic surgery is needed at the same time to cover any wound to give the best chance of cure.
Can you get osteomyelitis at any age?
Anyone at any age can develop osteomyelitis. However, you have an increased risk if you: Have recently broken (fractured) a bone. Have a bone prosthesis (an artificial hip, a screw in a bone following surgery, etc). Have recently had surgery to a bone. Have diabetes, especially if also have a foot ulcer.
Can antibiotics cause osteomyelitis?
An antibiotic is usually started as soon as possible. The initial antibiotic chosen is one that is likely to kill the germs (bacteria) which commonly cause osteomyelitis. However, the antibiotic is sometimes changed to a different one when the results of the tests confirm which bacterium is causing the infection.
Why are older people more prone to osteomyelitis?
Older adults are more prone to osteomyelitis because they experience more disorders that can lead to infection, namely orthopedic surgeries and diabetes mellitus. The overall observed trend in osteomyelitis is that it has been increasing over the last few decades.
How to prevent osteomyelitis in adults?
In order to prevent osteomyelitis in adults following open trauma, prophylactic antibiotics should be given intravenously (via IV) to reduce the risk of soft tissue infection. If possible, antibiotic therapy should be tailored to the findings of the tissue culture.
How long does osteomyelitis treatment last?
The antibiotic treatment may last from several days to a few weeks, but the therapy duration is not certain and is usually individualized based on a given patient’s progress. Antibiotic therapy of osteomyelitis usually requires prolonged regimen of medication, typically in the form of outpatient IV antibiotics.
What is the oldest disease in the world?
Osteomyelitis is one of the oldest diseases ever recorded. Evidence of the disease has been found in the fractured spine of a Permian reptile, close to 250 million years ago. This evidence consisted of bone inflammation based on the roughened swollen area above the fracture, hinting that the injury was in fact infected. Hippocrates (460-370 BC) also recognized infection after bone fracture, but it was only in 1773 that an Englishman named William Bromfield published on the observed “abcessus in medulla”, referring to the infected fatty tissues within the inner cavity of the bone. In 1844, French physician and renowned surgeon Auguste Nélaton coined the term “osteomyelitis”, which described an infectious condition of the entire bone, but included “itis” in the word so as to make reference to the inflammatory damage. Bone is usually good at fighting infection, but trauma, bacteremia, surgery, or foreign body insertion may disrupt blood flow and lead to the development of osteomyelitis. Early diagnosis is very important because fast antibiotic delivery may prevent permanent bone loss.
What is the difference between osteomyelitis and myelitis?
Osteomyeli tis can be broken down into “ osteo ” meaning bone, and “ myelitis ” , meaning inflammation of the fatty tissues within the bone. Osteomyelitis is caused by an infection of the bone or joint, and can be both acute and chronic. It can occur at any age and involve any bone.
What joints are affected by osteomyelitis?
These joints include the knees, wrists hip, ankles, symphysis pubis, and shoulders. Chronic osteomyelitis usually occurs after an acute episode of osteomyelitis when the infection has not been totally cured, and is sometimes associated with a draining sinus tract.
What is the most common site of osteomyelitis?
In prepubescent children, it usually affects the long bones: the tibia and the femur. The most common site of infection is the metaphysis, which is the narrow portion of the long bone).