
Who is buried in Durham Cathedral?
Durham Cathedral holds the relics of Saint Cuthbert, transported to Durham by Lindisfarne monks in the ninth century, the head of Saint Oswald of Northumbria, and the remains of the Venerable Bede.
What's in Durham Cathedral?
Durham Cathedral's relics include: Saint Cuthbert 's, transported to Durham by Lindisfarne monks in the 800s; Saint Oswald's head and the Venerable Bede 's remains. The Durham Dean and Chapter Library contains: sets of early printed books, some of the most complete in England; the pre-Dissolution monastic accounts and three copies of Magna Carta.
Where is the Bishop of Durham located?
Location within Durham. The Cathedral Church of Christ, Blessed Mary the Virgin and St Cuthbert of Durham, commonly known as Durham Cathedral and home of the Shrine of St Cuthbert, is a cathedral in the city of Durham, United Kingdom. It is the seat of the Bishop of Durham, the fourth-ranked bishop in the Church of England hierarchy.
Is Durham Cathedral a UNESCO World Heritage Site?
UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Cathedral Church of Christ, Blessed Mary the Virgin and St Cuthbert of Durham, commonly known as Durham Cathedral and home of the Shrine of St Cuthbert, is a cathedral in the city of Durham, England.
Who lived in Durham Castle?
University College The Castle remained the bishop's palace for the Bishop of Durham until Auckland Castle was made the bishops' residence in 1832; the current bishop still maintains offices at that castle, roughly ten miles to the south.
Who's buried in Durham Cathedral?
In 1986 the cathedral and Durham Castle were designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Durham Cathedral's relics include: Saint Cuthbert's, transported to Durham by Lindisfarne monks in the 800s; Saint Oswald's head and the Venerable Bede's remains.
Do monks live in Durham Cathedral?
The Monks' Dormitory has also retained its function as a reading room for the Cathedral Library. The library has an excellent collection, including many priceless manuscripts and early printed books.
Is the Durham Cathedral Catholic or Anglican?
A place of religious worship and learning, Durham Cathedral has stood as a symbol of the power of the Catholic Church for almost 1000 years.
Was Durham Cathedral used in Harry Potter?
The enchanting Durham Cathedral was used as many parts of Hogwarts in the Philosopher's Stone and Chamber of Secrets. In the cloisters of the cathedral, you will see where Harry flies Hedwig in the snow on his first year, and the spot where Ron vomits slugs in the Chamber of Secrets.
What is the oldest cathedral in England?
Canterbury CathedralCanterbury Cathedral, founded in 597, is England's oldest Cathedral, home to the symbolic leader of the Anglican Communion and the Church of England, the Archbishop of Canterbury.
What is Durham Cathedral famous for?
Built in 1093 to house the Shrine of St Cuthbert, Durham Cathedral is renowned for its magnificent Romanesque architecture and spectacular location at the heart of the Durham World Heritage Site. It has been a place of pilgrimage for over a thousand years and is the resting place of the Venerable Bede.
Who was Durham Cathedral built for?
George Gilbert ScottJames WyattAnthony SalvinEdward Robert RobsonRichard FarnhamDurham Cathedral/Architects
What did Durham used to be called?
Dun HolmThe city has been known by a number of names throughout history. The original Nordic Dun Holm was changed to Duresme by the Normans and was known in Latin as Dunelm. The modern form Durham came into use later in the city's history.
Was Durham Cathedral originally Catholic?
Although the church was originally used for Catholic services (just like all early Christian churches in England), it later became a cathedral of the Church of England after Henry VIII established Anglicanism as the official religion of England.
Why is there a moon in Durham Cathedral?
The inflated Moon installation is a fusion of detailed NASA imagery of the lunar surface, moonlight, and surround sound composition. Museum of the Moon is on display until November 11 and marks the second phase of Durham Cathedral's new visual arts programme.
What is difference between church and cathedral?
The cathedral is a much larger place of worship than a church and is run by a bishop. A church is run by a group of clergymen or priests. The bishop usually resides on the cathedral premises.
The Durham Cathedral: Overview
Durham Cathedral is a historic piece of architecture located in Durham, an English city just south of Newcastle. It was one of the first important and long-lasting buildings constructed after the Norman Conquest of 1066.
The History of the Durham Cathedral in England
Why is Durham Cathedral important? Whose shrine does the Durham Cathedral house? Durham Cathedral in England has existed for centuries but remains a source of fascination for many. Understanding how this cathedral came to be can provide helpful insight into England's history.
The Design and Style of the Durham Cathedral
As mentioned above, Durham Cathedral was essentially the first construction of its kind in England. It was built using techniques that were innovative at the time, making it stand out in the 12th century landscape of Durham and allowing it to remain an important architectural marvel for centuries.
Who was the cantor of Durham Cathedral?
Symeon of Durham was a monk and, for some time, the Cantor at Durham Cathedral. He is one of fewer than a dozen people known to have been in attendance at the building’s ground-breaking in 1093 as well as the formal interment of St. Cuthbert’s body, just over a decade later.
When was Durham Cathedral built?
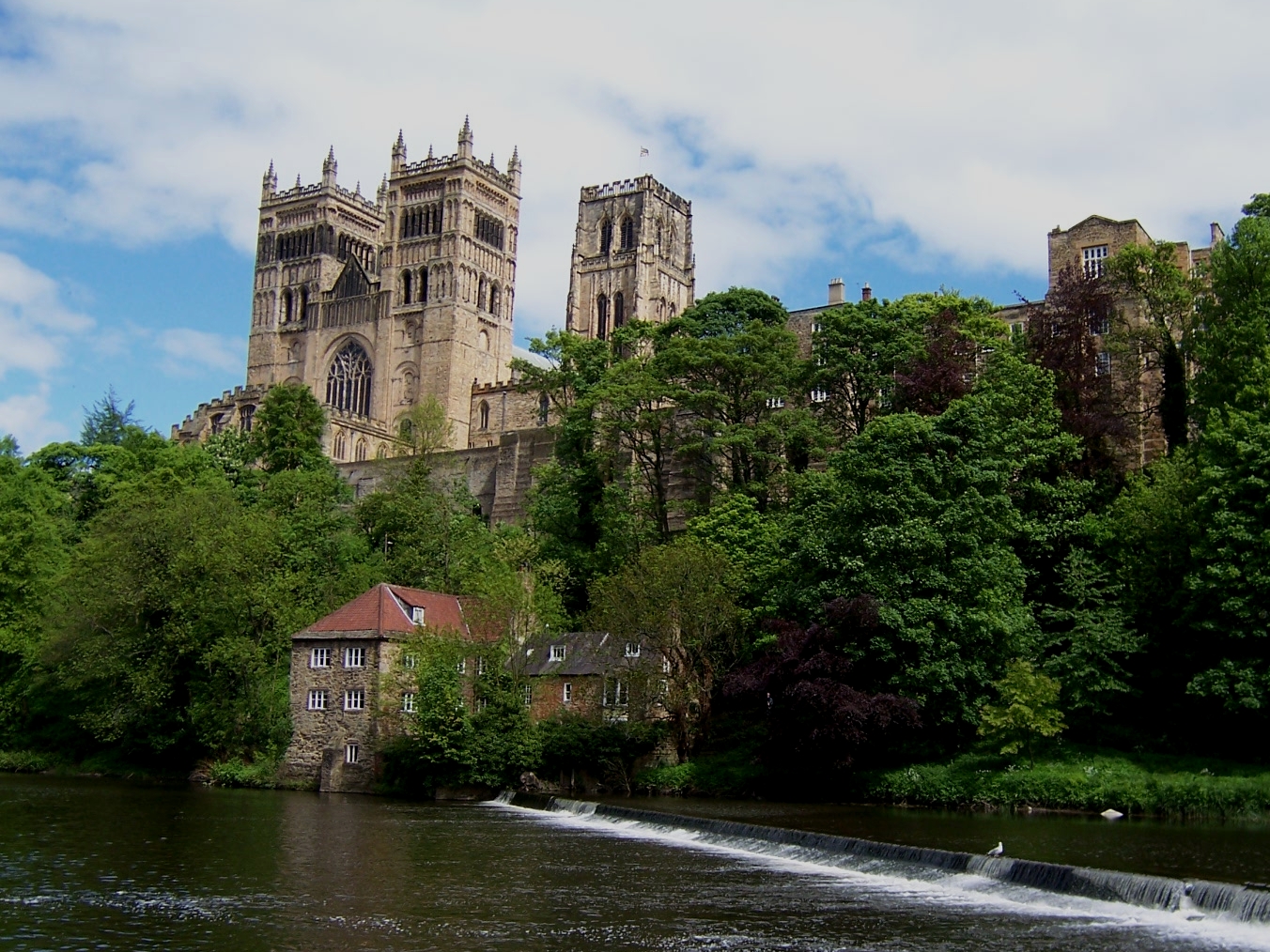
Durham Cathedral from the northwest, begun 1093 (photo: mattbuck, CC BY-SA 2.0)
What kind of sculptures did Durham have?
Bold linear carvings abounded: chevrons (or zigzags), lozenges, and even spirals.
What is Durham's apogee?
On account of its sheer precision, its scale, its vaulting and—in particular—its precocious pointed ribs, Durham has come to represent a sparkling new apogee, not only to the first generation of post-Conquest building, but to a continent-wide narrative of “progressive” structural experimentation.
What architectural elements were used in Norman architecture?
Another was the sudden influx of architectural elements such as rounded arches, supremely thick walls, alternating piers and columns, barrel vaults, and decorative arcading, among other motifs, that defined Norman and early Christian architecture on the Continent.
Who was the last king of England?
In September 1066, thousands of invaders led by William, the Duke of Normandy (also known as William the Conqueror) crossed the English Channel from Normandy (Northern France). The last pre-Norman King of England (Edward the Confessor) had died without a direct heir. By Christmas, 1066, William had been crowned King of England.
What is Durham Cathedral?
Durham Cathedral is a Norman building constructed between 1093 and 1133 in the Romanesque style. It was founded as a monastic cathedral built to house the shrine of St Cuthbert, replacing an earlier church constructed in his honour.
Why is Durham Cathedral important?
Durham Cathedral is also valuable because its Norman architecture has survived largely intact – the addition of two chapels and a later central tower notwithstanding. Most other important Norman buildings in Britain were substantially modified, often beyond recognition. As such, it is recognised both as an exemplar of the Romanesque architecture, and as one of the world’s greatest cathedrals. Find out more.
Is Durham Cathedral a living church?
Durham Cathedral: A Living Church. The Cathedral has been in continuous use since its original construction 900 years ago. It remains a place of worship and pilgrimage , and is also an important visitor attraction. Over 600,000 people passed through its doors in 2009.
What is Durham Cathedral?
Durham Cathedral is one of the world’s great cathedrals, and full of historical treasures – many of which are exhibited. Not only does the Cathedral hold the remaining bits of St Cuthbert, St Oswald and the Venerable Bede; it has an impressive collection of other unique artefacts (including the original sanctuary knocker), early printed books and three copies of the Magna Carta. Wandering around, you get a distinct sense of power – both spiritual and temporal – and the long history of the place. For me, though, Durham belongs to Cuthbert and Bede and is a tangible link with the early medieval, pre-conquest, Anglo-Saxon, land of our ancestors.
What was the first church in Durham?
The first church at Durham was probably timber framed with wattle and daub walls. Whitewashed, it was known as Alba Ecclesia, the White Church. Just three years later, the monks moved Cuthbert to a new and larger church, probably built in stone. Unsurprisingly, the cult of Cuthbert ensured that Durham became a place of pilgrimage, and the town grew up around the monastic community. It also had strategic importance, which William the Conqueror recognised as he took stock of his new kingdom following the Norman victory at Hastings in 1066. In 1072, he ordered the construction of a castle at Durham, as a base both to help control restless English rebels and to defend his territory against marauding Scots. And in 1075, William appointed the Bishop of Durham ‘Prince-Bishop’, a title which bestowed an enormous amount of power, including the right to raise an army, levy taxes and mint coins – provided always that the bishops maintained their loyalty to the King of England and protected the northern border with Scotland. The first Prince Bishop was Walcher of Lotharingia (a province corresponding with parts of modern Holland, Belgium, France and Germany), but he was murdered in 1081 and William replaced him with a Norman, William de St Calais, or William Carileph. It was Bishop Carileph who begun the construction of the new, Norman, cathedral in 1093, which was substantially completed by 1133. The Galilee Chapel was added in 1175, the two western towers between 1217 and 1226 and the Gothic Chapel of the Nine Altars was completed between 1242 and 1280.
Where did Bede die?
As if the bones of Cuthbert and the skull of Oswald weren’t sufficient, Durham Cathedral is also the final resting place for Bede, aka the Venerable or the Venomous, depending on your inclination and sense of humour. Bede was born around 673 AD, died in 735 AD and spent almost his entire life from the age of 7 at the twin monasteries of St Peter and St Paul at Monkwearmouth-Jarrow, Tyne and Wear. However, Bede’s reputation is not as a monk but as a scholar and, most famously, for his Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum, The Ecclesiastical History of the English People. I can still picture my history professor, a man seemingly far removed from life’s realities, and not easy to like, eyes partly closed, hands together as if in prayer, discussing Bede in his very precise, mid-European accented English. I think he truly venerated this long-dead cleric, one academic to another as it were. Indeed, I have a grudging affection for old Bede myself – for where would our knowledge of pre-conquest Britain be without him? His History covers the period from Julius Caesar’s invasion of 55 BC to 731 AD and it is a fascinating, often amusing, if hardly fast-paced, read. Leave aside any scepticism you may have about miracles and the supernatural, appreciate Bede’s bias and role as a propagandist for the Church of Rome (the clue’s in the work’s title) and realise that, for all its potential pitfalls, this is one of the few primary sources we have for the period. Only a small minority would begrudge Bede being referred to as ‘the father of English history’ – though, in truth, his work offers an insight on the whole island.
Why was St. Cuthbert's grave disturbed?
In 1899, Cuthbert’s resting place was disturbed once again – possibly to refute theories that he had been re-interred somewhere else, possibly to recover more fragments of his 7 th century coffin. The exhumation was led by cathedral librarian Canon William Greenwell, described in the Northern Echo as “a hugely respected archaeologist and angler”. According to the Northern Echo, as well as Cuthbert’s skeleton (and it was somehow proven to be that of the saint), there were other bones, possibly relics of other saints, as well as the bones of a child and “the frontal bone of a large skull, of which one half of the forehead had been cut away, apparently by the stroke of a sharp sword. This, there can be little doubt, is a portion of the skull of King Oswald, whose head, after he had been killed in battle, was ultimately deposited in the shrine of St Cuthbert.”
When did Durham's story start?
Durham’s story is a fascinating piece of the story of England. It is partly a tale of saints and kings and moving bones, and it begins back in the 7 th century.
Who was Ealdhun's daughter?
An alternative, far less enjoyable, explanation for founding a community at Durham was that Ealdhun’s daughter, Ecgfrida, was betrothed to Uchtred (or Uhtred) the Bold, son of Waltheof of Bamburgh. Durham’s lofty and defensible position offered the prospect of greater safety for the holy community, as well as the protection of the Bishop’s son-in-law – whose men apparently helped the monks clear the ground for building. From Uchtred’s perspective, the presence of St Cuthbert would add a celebrity cachet to the place and do something for local tourism.
What does HIC SUNT mean in the tombstone of the Venerable Bede?
Neat, eh? It means something like “In this grave are the bones of the Venerable Bede.”
What are some interesting facts about Durham Cathedral?
Built in 1093 to house the Shrine of St Cuthbert, Durham Cathedral is renowned for its magnificent Romanesque architecture and spectacular location at the heart of the Durham World Heritage Site. It has been a place of pilgrimage for over a thousand years and is ...
Why was Durham Cathedral burned?
They burned anything wooden to keep warm, but left the medieval Prior’s Clock untouched. According to legend, this was because there is a thistle engraved on the clock – the emblem ...
How many alabaster figures are on the Neville screen?
However, the screen is missing 107 alabaster figures.
What is the setting of the chapter house?
The Chapter House is the setting for Professor McGonagall’s classroom when she teaches the young wizards to turn animals into water goblets. 2. The medieval tomb of Ralph Neville, who was a great benefactor of the Cathedral, is surrounded by figures said to represent Ralph’s 19 children.
Which cathedral is the highest in Christendom?
4. Standing at one inch higher than the Pope’s, Durham Cathedral’s Cathedra (Bishop’s throne) is the highest throne in Christendom. Bishop Hatfield allegedly ordered his representatives to go to the Vatican to measure the height of the Pope’s throne, as he wanted his to be the tallest.
Where was the Harry Potter movie filmed?
Durham Cathedral famously appeared as a filming location for the blockbuster Harry Potter film series. The cloister became the snow-covered quadrangle, where Harry sets his owl flying in the Philosopher’s Stone.
How many mills were there in Durham in the 15th century?
In the 15th century there were two fulling mills in Durham. The money they earned was used for the upkeep of the Jesus Altar in the Cathedral.
What river runs through the Cathedral?
The Cathedral lies in a loop of the River Wear. On one side is the medieval city and on the other wonderful woodlands filled with footpaths. Inheriting an 18th century landscape. Today’s woodlands and the buildings within them are what is left of a ‘romantic’ planned landscape created in the 18th century.
What were the occupants of the Mill?
Instead various occupants lived there including a mason, riverbanks constables, a plumber and a water bailiff.
When was the Banks Cottage built?
This building was built around the 1820s. It is named after Polish 'Count' Joseph Boruwlaski who lived in nearby Callamanco Hall, or Banks Cottage as it later became known.
Why was Durham Castle important?
In defensive terms, Durham Castle was of strategic importance both to defend the troublesome border with Scotland and to control local English rebellions, which were common in the years immediately following the Norman Conquest, and led to the so-called Harrying of the North by William the Conqueror in 1069.
What was the pre Norman castle?
Pre-Norman History of the Castle. Archaeological evidence suggests that an Anglo-Saxon defensive structure pred ated the Norman Castle. This was not unusual, and in fact was the case in Dover, London, Exeter, Hastings, Winchester, and Pevensey, where castles were constructed after the Norman Conquest.
Why was the Castle built?
The Historia Regum, a literary work about the history of the English kings written in 1136, mentions that the Castle was constructed “to keep the bishop and his household safe from the attacks of assailants”.
Was Durham Castle built of stone?
There is also debate about whether or not Durham Castle was original ly a stone or a wooden structure. Historic sources mention that its keep (fortified tower) was built of wood, but there is enough archaeological evidence to indicate that even in the late 11 th century when it was first built, it had numerous stone buildings.

Overview
History
The See of Durham takes its origins from the Diocese of Lindisfarne, founded by Saint Aidan at the behest of Oswald of Northumbria in about 635, which was translated to York in 664. The see was reinstated at Lindisfarne in 678 by the Archbishop of Canterbury. Among the many saints who originated at Lindisfarne Priory, the greatest was Saint Cuthbert, Bishop of Lindisfarne from 685 until his …
Architecture
There is some evidence that the aisle of the choir had the earliest rib vaults in England, as was argued by John Bilson, English architect, at the end of the nineteenth century. Since then it has been argued that other buildings like Lessay Abbey in northwest France provided the early experimental ribs that created the high technical level shown in Durham. There is evidence in the clerestory wall…
Other burials
• Stephen Kemble, actor of the Kemble family
• William de St-Calais, in the chapter house
• Ranulf Flambard, also in the chapter house (where his tomb was opened in 1874)
• Geoffrey Rufus, also in the chapter house (where his grave was also excavated in the 19th century)
Other memorials
• Bishop Joseph Butler
• Bishop Edward Maltby
• John Robert Davison QC MP
• Brigadier General Herbert Conyers Surtees
Dean and chapter
The cathedral is governed by the chapter which is chaired by the dean. Durham is a "New Foundation" cathedral in which there are not specific roles to which members of the chapter are appointed, with the exception of the Dean and the Van Mildert Professor of Divinity. The other roles, sub-dean, precentor, sacrist, librarian and treasurer, are elected by the members of the chapter annually.
Music
In the 17th century Durham had an organ by Smith that was replaced in 1876 by 'Father' Willis (Henry Willis & Sons), with some pipes being reused in Durham Castle chapel. Harrison & Harrison worked on the organ from 1880, restored between 1905 and 1935, rebuilt again in 1970 with a new console, and adding a Classically-voiced Positive division, and further refurbishments and minor changes in 1981 and 1996. The cases, designed by C. Hodgson Fowler and decorated by Cl…
Meridian line
In 1829 the Dean and Chapter authorised the engraving of a meridian line upon the floor and wall of the north cloister. A circular aperture about 1 inch (2.5 cm) in the tracery of the adjoining window about 10 feet (3 m) above the level of the floor directs a beam of sunlight to fall upon the line at the precise time when the sun passes the meridian. It was constructed by William Lloyd Wharton, of Dryburn in the city, and Mr Carr, then Head Master of Durham School.