
See more
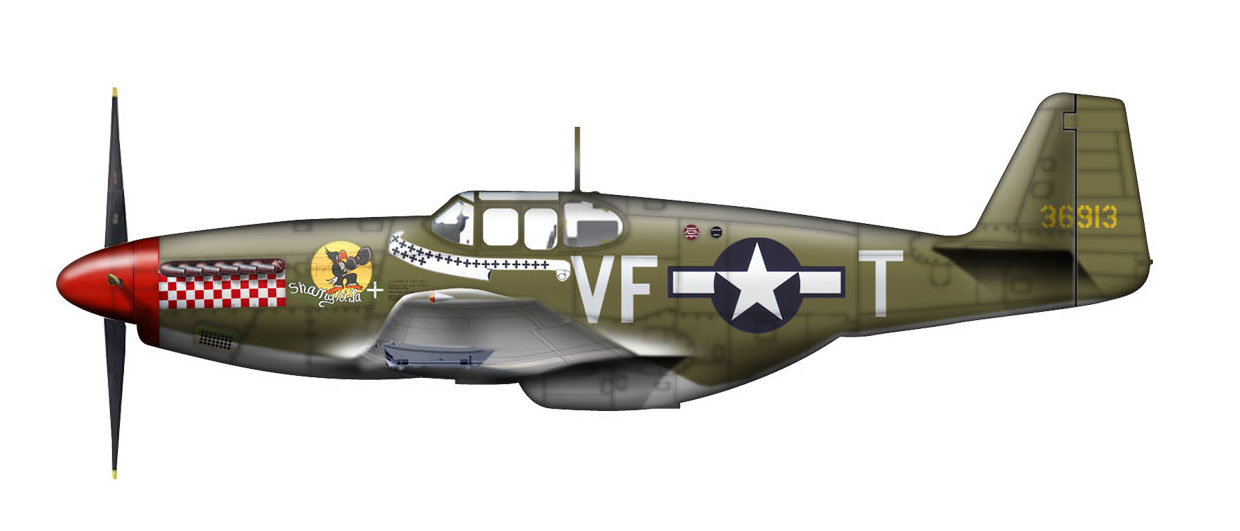
What company built the P-51 Mustang?
P-51, also called Mustang, a single-seat, single-engine fighter aircraft originally designed and produced by North American Aviation for the British Royal Air Force (RAF) and later adopted by the U.S. Army Air Forces (USAAF).
Where was the P-51 Mustang manufactured?
The P-51 Mustang was built by North American Aviation (NAA) and produced in their factories in Inglewood California and Dallas, Texas. The engineering prototype was designed and built in 102 days. The Mustang incorporated the new NACA designed laminar flow wing.
Does Tom Cruise own a P-51 Mustang?
And it doesn't stop with just a license. Cruise's love of aeroplanes has led him to actually collect a couple. According to Bolavip, he owns a vintage P-51 Mustang, which is said to be a World War II aircraft built in 1946.
How many P-51 Mustangs are left in the world?
There are only around 175 Mustangs still flying, with roughly 150 of those in the U.S. About 100 other Mustangs are on display in museums. More than 15,000 rolled off North American Aviation assembly lines in California and Texas during World War II. The "P" stood for pursuit.
How much does a P-51 Mustang cost today?
The original unit cost of the aircraft in 1945 was around $50,985—or equivalent to $590,000 today. That increase outpaces even the rarest of classic cars, but one factor is that while 15,000 or so were built during the Second World War, only about 150 are airworthy and most are in museums.
How much did a P-51 Mustang cost?
A P-51 cost $51,000 in 1945, or about $675,000 today. The Enforcer would probably have cost around a million dollars.
What jet does Elon Musk have?
Elon Musk'S New Gulfstream G700 Jet Is Worth $78 Million: Report.
Who owns the P-51 in Top Gun 2?
See this aircraft Wednesdays thru Sundays from 10:00am until 4:00pm. Planes of Fame is proud to display the P-51 "Mustang" that appears in the hit movie "Top Gun: Maverick." The aircraft is currently on display in our Maloney Hangar and visitors can view it up close and take pictures.
What does Tom Cruise fly in real life?
He has a pilot's license. He owns a P-51 Mustang and flies it himself. He owns a Gulfstream IV and flies it himself. And he's more than capable of taking the stick in a F/A-18 to do a few small maneuvers that look good on film, once the actual pilot lets him.
Which fighter did the Germans fear the most?
They called it a 'fork-tailed devil. ' Key point: The P-38 was a forerunner of modern multi-role fighters.
What is the most famous P-51 Mustang?
P-51 Gunfighter Colonel Larry Lumpkin (P-51 Gunfighter) Gunfighter is one of the world's most famous P-51 Mustangs, having appeared on the airshow circuit and providing rides for over 35 years. The aircraft is a P-51 "D" model, serial number 44-73264.
Can Tom Cruise fly a fighter jet?
Mission: Impossible's Tom Cruise can be seen flying in Top Gun: Maverick, but as a civilian, he could not fly the primary fighter jet of the film, the F-18 Hornet. He had to start on certain aircrafts like the entry-level airplane, a Cessna 172, to learn the basics.
What engine did the P-51 Mustang use?
Air Force Historical Research Agency. In the meantime, the British had experimented with Mustangs fitted with the powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine , and they discovered that the Merlin’s efficient mechanical supercharger gave the fighter outstanding high-altitude performance.
When was the P-51 made?
The P-51 originated with an April 1940 proposal to the British Aircraft Purchasing Commission by the chief designer of North American Aviation, J.H. (“Dutch”) Kindelberger, to design a fighter from the ground up rather than produce another fighter, the Curtiss P-40, under license. The result was a trim low-wing monoplane powered by ...
What wars did the Mustangs fight?
Mustangs also were used by Nationalist forces in the Chinese Civil War and by Israel in the 1956 Sinai invasion. P-51s continued to serve in less-developed countries into the 1960s and last saw combat in Salvadoran hands during the 1969 Soccer War with Honduras. Women Airforce Service Pilots.
How fast is a Mustang?
It had a maximum speed of about 390 miles (630 km) per hour and a combat range of roughly 750 miles (1,200 km).
How many machine guns did the F-190 have?
All were heavily armed, the Fw 190 with as many as two 7.6-mm machine guns and four 20-mm cannon, the P-47 with eight .50-inch machine guns, and the F6F and P-51 with six .50-inch machine guns. The Fw 190, the P-47, and the…. air warfare: Ground attack.
What was the F-6 used for?
The photo-reconnaissance version of the Mustang, the F-6, was used in all theatres of the war by both the USAAF and the RAF. Unlike photo-reconnaissance versions of the P-38, the F-6 retained its armament, being used primarily in low-altitude operations where it might have to defend itself.
What fighters are in formation at Langley Air Force Base?
Fighters in formation at an air show at Langley Air Force Base, Virginia. From left, A-10 Thunderbolt II, F-86 Sabre, P-38 Lightning, and P-51 Mustang.
When was the Mustang first flown?
The North American prototype, NA-73X, was first flown on Oct. 26, 1940. At least eight versions of the Mustang were produced.
What was the Mustang used for?
Although first designed for the British as a medium-altitude fighter, the Mustang excelled in hedge-hopping strafing runs and long-range escort duty. It made a name for itself by blasting trains, ships and enemy installations in Western Europe and by devastating Axis defenses before the Allied invasion of Italy.
What was the first single engine plane to penetrate Germany?
The Mustang was the first single-engine plane based in Britain to penetrate Germany, first to reach Berlin, first to go with the heavy bombers over the Ploiesti oil fields in Romania, and first to make a major-scale, all-fighter sweep specifically to hunt down the dwindling Luftwaffe.
What was the first fighter plane to push its nose over Europe?
A veteran of World War II and the Korean War, North American Aviation’s P-51 Mustang was the first U.S. built fighter airplane to push its nose over Europe after the fall of France. Mustangs met and conquered every German plane from the early Junkers to the sleek, twin-jet Messerschmitt 262s.
When was the P-51 Mustang made?
Over twenty variants of the North American P-51 Mustang fighter were produced from 1940, when it first flew, to after the Second World War, some of which were employed also in the Korean War and in several other conflicts.
Where was the P-51B made?
American production was started in early 1943 with the P-51B (NA-102) being manufactured at Inglewood, California, and the P-51C (NA-103) at a new plant in Dallas, Texas, which was in operation by summer 1943. The RAF named these models Mustang Mk III.
What was the last production Mustang?
The P-51H (NA-126) was the final production Mustang, embodying the experience gained in the development of the XP-51F and XP-51G aircraft. This aircraft, with minor differences as the NA-129, came too late to participate in World War II, but it brought the development of the Mustang to a peak as one of the fastest production piston-engine fighters to see service.
What engines did the CAC build?
The 21 and 22 used the American-built Packard V-1650-3 or V-1650-7. The Mark 23s, which followed the 21s, were powered by Rolls-Royce Merlin 66 or Merlin 70 engines. The first 26 were built as Mark 21s, followed by 66 Mark 23s; the first 14 Mark 21s were converted to fighter-reconnaissance aircraft, with two F24 cameras in both vertical and oblique positions in the rear fuselage, above and behind the radiator fairing; the designation of these modified Mustangs was changed from Mark 21 to Mark 22. An additional 14 purpose-built Mark 22s, built after the Mark 23s, and powered by either Packard V-1650-7s or Merlin 68s, completed the production run. All of the CA-17s and CA-18s, plus the 84 P-51Ks, used Australian serial numbers prefixed by A68.
What engine did the XP-51B use?
The airframe itself was strengthened, with the fuselage and engine mount area receiving more formers because of the 355 lb (161 kg) greater weight of the Packard V-1650-3 compared with the V-1710. The engine cowling was completely redesigned to house the Packard Merlin, which, because of the intercooler radiator mounted on the supercharger casing, was 5 in (130 mm) taller and used an updraft carburetor, rather than the downdraft variety of the Allison. The new engine drove a four-bladed 11 ft 2 in (3.40 m)-diameter Hamilton Standard propeller that featured cuffs of hard molded rubber. To cater for the increased cooling requirements of the Merlin, a new fuselage duct was designed. This housed a larger radiator, which incorporated a section for the supercharger coolant, and, forward of this and slightly lower, an oil cooler was housed in a secondary duct which drew air through the main opening and exhausted via a separate exit flap.
What was the first aircraft based on the Mustang?
The A-36A was the first aircraft based on the 'Mustang' airframe ordered by the U.S. Government specifically for use by the USAAF. NAA found an unfilled 'Dive Bomber' USAAF contract, which they got mainly by their own initiative. In so doing, NAA was able to keep the production bays open with the hope the USAAF would place orders for it as a fighter. On 16 April 1942, Fighter Project Officer Benjamin S. Kelsey ordered 500 A-36 Apaches, a redesign that included six .50 in (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine guns, dive brakes, and the ability to carry two 500 lb (230 kg) bombs. Kelsey would rather have bought more fighters but was willing instead to initiate a higher level of Mustang production at North American by using USAAF funds earmarked for ground-attack aircraft when pursuit aircraft funding had already been allocated. It was the first airframe of the Mustang "family" (Apache, Invader, or Mustang) to be drop-tank capable. (A 1939 USAAC prohibition prevented manufacturers from making fighters capable of carrying external fuel stores; the Navy had no such restriction.)
What is the serial number of a 1942 Mustang?
A North American Mustang Mk IA on a test flight from NAA's Inglewood facility in October 1942. The painted-over serial number appears to be 41-37416.
What is the real story of the P-51 Mustang?
However, the real P-51 Mustang story is just as much about the difficult gestation of a great new fighter as it is about the quashing of the drop tanks urgently needed to extend the range of existing fighters. Then there’s the guerilla tactics some officials unleashed in the corridors of power to overcome the Army’s “not invented here” hostility ...
What was the P-51 Mustang used for?
The benefits the P-51 Mustang brought to aerial battles in World War II , particularly over Germany, are reasonably well known. The iconic fighter plane could fly higher, faster, farther and generate more kills per sortie than the U.S. Army Air Force’s aviation bureaucracy’s preferred P-47s or P-38s.
How many B-17 bombers were in the German raid?
The crews targeted the naval port at Wilhelmshaven in a raid involving more than 90 B-17 and B-24 bombers. Only 58 bombers — 60 percent — found the target. The bomber force had no escort fighters, but crews claimed they shot down 22 German defenders.
How fast was the first Mustang?
On Oct. 13, 1942, the first converted Mustang took off. With the Merlin engine, the plane’s top speed leapt from 390 to 433 miles per hour, could climb rate of 3,440 feet per minute and had a range of up to 2,000 miles with external drop tanks.
Why did Arnold forbid the development of a 52 gallon drop tank for the P-36 fighter?
Since drop tanks cut into the bomb load he considered so all-important, “ [i]n February 1939, Arnold forbid the development of a 52-gallon drop tank for the P-36 fighter because of ‘safety reasons’ ,” Trent Telenko wrote in a detailed post for the blog Chicago Boyz.
When did the Air Force ask for jettisonable fuel tanks?
Eight months later, in October 1942 “… Eighth Air Force … inquired whether jettisonable fuel tanks could be made available for the P-47,” scholar William Emerson said in a lecture, titled Operation POINTBLANK: A Tale of Bombers and Fighters. “ Nothing came of the request.”
Who ordered the development of auxiliary fuel tanks?
At a meeting on Feb. 20, 1942, “Arnold ordered the all-out development of auxiliary fuel tanks,” U.S. Air Force Maj. Robert Eslinger wrote in a research paper at the Air Command and Staff College.
Where is the SW-51 Mustang made?
Build your dream SW-51 Mustang. We provide expert assistance at our ScaleWings manufacturing facility in Krosno, Aviation Valley, Poland. The “Build Your Legend” supports Amateur Builders with guaranteed success.
What is the finish on a Mustang?
All-carbon design with more than 100,000 texture details of the Original Mustang. Polished aluminum finish.
Is the SW-51 Mustang a replica?
The SW-51 Mustang is an accurate replica of the legendary P-51 Mustang. A 70% true-to-scale aircraft in classic aluminum appearance, perfected from all-carbon design. More than 100,000 textures of the original aircraft embedded in all airframe surfaces create the ultimate reincarnation of the legendary icon. A perfect blend of classic style and cutting-edge technology.

Overview
Merlin-engined Mustangs
In April 1942, the RAF's Air Fighting Development Unit (AFDU) tested the Mustang and found its performance inadequate at higher altitudes. As such, it was to be used to replace the P-40 in Army Cooperation Command squadrons, but the commanding officer was so impressed with its maneuverability and low-altitude speeds, he invited Ronnie Harker (from Rolls-Royce's Flight Test establishment…
Allison-engined Mustangs
The prototype of the Mustang, designated NA-73X, was rolled out by North American Aviation on 9 September 1940, albeit without an engine, and was first flown the following 26 October. The Mustang was originally designed to use a low-altitude rated Allison V-1710 engine. Unlike later models, Allison-powered Mustangs were characterized by the carburetor air intake placed on the dorsal …
The "lightweight" Mustangs
The lightweight Mustangs had a new wing design. The airfoil was switched to the NACA 66,2-(1.8)15.5 a=.6 at the root and the NACA 66,2-(1.8)12 a=.6 at the tip. These airfoils were designed to give less drag than the previous NAA/NACA 45-100. In addition, the planform was a simple trapezoid, with no leading edge extension at the root.
Experimental Mustangs
In early 1944, the first P-51A-1-NA, 43-6003. was fitted and tested with a lightweight retractable ski kit replacing the wheels. This conversion was made in response to a perceived requirement for aircraft that would operate away from prepared airstrips. The main oleo leg fairings were retained, but the main wheel doors and tail wheel doors were removed for the tests. When the undercarriag…
Summary of P-51 variants
NA-73X The initial prototype Mustang Mk I (NA-73/83) The first production contract was awarded by the British for 320 NA-73 fighters. A second British contract for 300 more Mustang Mk Is was assigned a model number of NA-83 by North American. The RAF mostly used its Allison-engined Mustangs as tactical-photo reconnaissance fighters, fitting many of its Mustang Is, IAs, and …
Dimensions and performance
The basic dimensions of the P-51/A-36 variants remained consistent from the XP-51 through to the experimental "lightweight" P-51s, although there were relatively minor variations in height and wing area. The P-51H was the first production version of the Mustang to feature a lengthened fuselage and taller tailfin.
The power rating for the engines could vary according to the type of supercharger fitted, the size …
External links
• "A Fighter From the Ground Up." Popular Science, July 1943, one of earliest detailed articles on P-51A
• "Wild Horses of the Sky," Popular Mechanics, November 1943
• Joe Baugher, North American P-51 Mustang