What did Li Yuan do for Tang dynasty?
Li Yuan convinced Emperor Gong to relinquish power. Li Yuan established the Tang Dynasty and became Emperor Gaozu on June 18th, 618. He was emperor during the first eight years of the Tang Dynasty. His sons were given royal titles and positions, including Li Shimin, named the Prince of Qin.
What are some interesting facts about the Tang dynasty?
Though separated by 800 years, the empires of the Tang and Western Han were similar in many ways:
- Emergence during a general rebellion against a tyrannical emperor of a large, brutal, and very short-lived empire.
- Confucian bureaucrats ruled in both empires, and the empires prospered under stable rule.
- The populations of both empires were the same at about 50 or 60 million people.
How did the Tang dynasty unify China?
Unification of China. Kublai’s achievement was to reestablish the unity of China, which had been divided since the end of the Tang dynasty (618–907). His accomplishment was that much greater because he was a barbarian (in Chinese eyes) as well as a nomadic conqueror. Even in Chinese official historiography, however, the Mongol Kublai is treated with respect.
Who were the emperors of the Tang dynasty?
Tang dynasty
- Established June 18, 618
- Wu Zhou interregnum 690–705 b
- An Lushan Rebellion 755–763 c
- Abdication in favor of Later Liang

Who was the first ruler of the Tang Dynasty?
GaozuWhile Gaozu (Li Yuan's reign name) was the first of the Tang emperors, it was under his son Taizong (reigned 624-649) that the Tang dynasty consolidated its power and began to achieve a domestic peace that would last for virtually unbroken for three centuries, interrupted only by the nine-year-long An Lushan rebellion ...
What family ruled the Tang Dynasty?
Lǐ familyThe Lǐ family (李) founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule.
How many leaders were in the Tang Dynasty?
EmperorsOrderNameReign Time (years)Tang Dynasty (618 - 907)1Tang Kao Tsu (Li Yuan)618 - 6262Tang Taizong (Li Shimin)627 - 6493Tang Gaozong (Li Zhi)650 - 68321 more rows
Who was the most popular ruler of the Tang Dynasty?
Xuanzong712-756). Xuanzong is widely regarded as the greatest emperor of the Tang Dynasty, who promoted good governance, justice, and civil service.
Who was the last ruler of the Tang Dynasty?
Zhu Wen, Wade-Giles romanization Chu Wen, also called Zhu Quanzhong, later Zhu Huang, temple name (miaohao) (Hou Liang) Taizu, (born 852, Dangshan [now in Anhui province], China—died 912, Kaifeng, Henan province), Chinese general who usurped the throne of the last emperor of the Tang dynasty (618–907) and proclaimed ...
When did the Tang Dynasty rule?
Tang Dynasty (618–907)
Who was the second emperor of the Tang Dynasty?
TaizongLi Shimin reigned as Taizong, second emperor of the Tang dynasty (618-907), from 626 until his death in 649. An energetic ruler, Tang Taizong had played a major part in the military campaigns that brought his father (Li Yuan, Tang Gaozu, r.
What was the Tang Dynasty best known for?
The Tang Dynasty is well remembered for the era's contributions to poetry, partly the result of Xuanzong's creation of an academy for poets, which helped preserve over 48,900 poems written by well over 2,000 poets of the era. One of the best remembered is Li Bai, born in 701 A.D.
Which dynasty in China was the best?
In general, people agree that the 6 greatest and most powerful Chinese dynasties in history are Tang Dynasty, Yuan Dynasty, Ming Dynasty, Han Dynasty, Qin Dynasty and West Zhou Dynasty.
Why did the Tang Dynasty end?
In 907 the Tang dynasty was ended when Zhu Wen, now a military governor, deposed the last emperor of Tang, Emperor Ai of Tang, and took the throne for himself. A year later the deposed Emperor Ai was poisoned by Zhu Wen, and died. Zhu Wen was known posthumously as Emperor Taizu of Later Liang.
What was the Tang Dynasty?
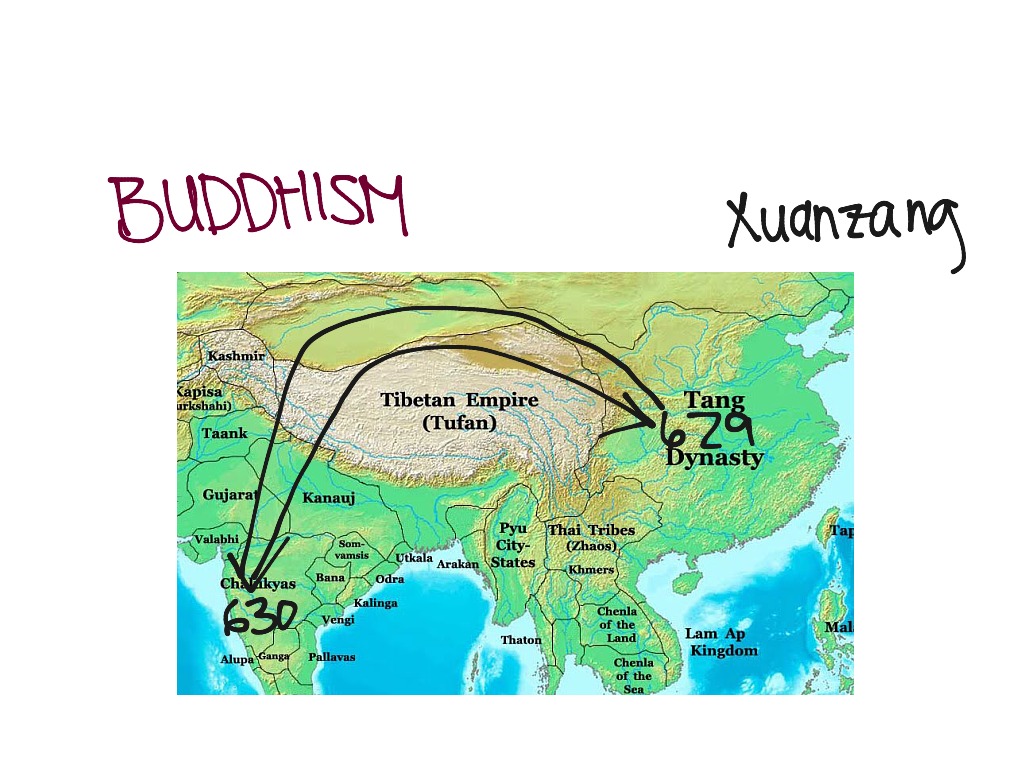
The Tang Dynasty is considered a golden age of Chinese arts and culture. In power from 618 to 906 A.D., Tang China attracted an international reputation that spilled out of its cities and, through the practice of Buddhism, spread its culture across much of Asia.
How many poems did the Tang Dynasty write?
The Tang Dynasty is well remembered for the era’s contributions to poetry, partly the result of Xuanzong’s creation of an academy for poets, which helped preserve over 48,900 poems written by well over 2,000 poets of the era.
What did Xuanzong do?
Xuanzong had a passion for music and horses. To this end he owned a troupe of dancing horses and invited renowned horse painter Han Gan into his court. He also created the Imperial Music Academy, taking advantage of the new international influence on Chinese music. The fall of Xuanzong became an enduring love story in China.
What was Bai Juyi's style of poetry?
Bai Juyi, born in 772 A.D., ushered in a new style of poetry that was written to be understood by peasants and addressed political issues and social justice. Bai Juyi was a lifelong government worker and died in 846 A.D.
What did Taizong do to help the Confucian scholars?
Taizong also set up more aggressive systems to identify Confucian scholars and put them in civil service placements. He created Confucian state schools along with a sanctioned state version of The Five Classics, which also allowed talented scholars with no family connections to work their way up in the government.
Which dynasty ruled China from 581 to 617 A.D.?
At the beginning of the sixth century A.D., north and south China were divided, but would be united through conquest by the Sui Dynasty, which ruled from 581 to 617 A.D. The Sui were led by General Yang Jian of the unified north. The Sui, however, lasted for only two emperors before falling to Li Yuan, ...
Who was the Great Khan of Mongolia?
His son Taizong ascended the throne after killing his two brothers and several nephews. In 630 A.D., Taizong seized a portion of Mongolia from the Turks and earned the title “Great Khan.”. The Tangs made use of Turkish soldiers in an invasion of Khitan (far eastern Asia) and joint expeditions along the Silk Road.
What was the Tang Dynasty?
edit. The Tang dynasty ( / tɑːŋ /, [tʰǎŋ]; Chinese: 唐朝 ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period.
Which kingdoms paid tribute to the Tang Dynasty?
Some of the kingdoms paying tribute to the Tang dynasty included Kashmir, Nepal, Khotan, Kucha, Kashgar, Silla, Champa, and kingdoms located in Amu Darya and Syr Darya valley. Turkic nomads addressed the Emperor of Tang China as Tian Kehan.
What was the role of religion in Tang's political life?
From the outset, religion played a role in Tang politics. In his bid for power, Li Yuan had attracted a following by claiming descent from the Taoism sage Lao Tzu ( fl. 6th century BC). People bidding for office would request the prayers of Buddhist monks, with successful aspirants making donations in return. Before the persecution of Buddhism in the 9th century, Buddhism and Taoism were both accepted.
How did the Lushan Rebellion affect the Tang Dynasty?
The devastating An Lushan Rebellion (755–763) shook the nation and led to the decline of central authority in the dynasty's latter half. Like the previous Sui dynasty, the Tang maintained a civil-service system by recruiting scholar-officials through standardized examinations and recommendations to office.
What dynasty was Wu Zhou?
Imperial dynasty of China from 618 to 907. For other uses, see Tang dynasty (disambiguation). Tang. 唐. 618–690, 705–907. (690–705: Wu Zhou) The empire during the reign of Gaozong, c. 669. The empire during the reign of Wu Zetian, c. 700. Capital.
Why did the Tang government depend on the governors?
The Tang government relied on these governors and their armies for protection and to suppress locals that would take up arms against the government. In return, the central government would acknowledge the rights of these governors to maintain their army, collect taxes and even to pass on their title to heirs.
Where is the Tang slave found?
Found in the Astana Cemetery in Turfan.
What is the Tang Dynasty?
Tang dynasty, Wade-Giles romanization T’ang, (618–907 ce ), Chinese dynasty that succeeded the short-lived Sui dynasty (581–618), ...
Who was the first Tang emperor?
The first Tang emperor, Li Yuan, known by his temple name, Gaozu, began as a contender for the rule of the Sui, of which he had been an official. He overcame various rivals and rebels, and by 621 he controlled China’s eastern plain; in 624 he added most of the rest of North and South China, although some rebels remained in the North throughout the dynasty. He directed many complex military operations in his tenure and established the basic institutions of the Tang state. He emulated the first Sui emperor in establishing a highly competent bureaucracy, and he adopted the same pattern of local administration.
What type of glaze did Tang potters use?
Finishes in white porcelain, three-colour pottery and figurines, stoneware with a rich black glaze, and a type of celadon all were developed by Tang potters; and, in keeping with the general interest in things foreign, their wares were often in foreign shapes and followed foreign motifs.
What was the Tang culture?
Tang culture. The years of the Tang were brilliant times for the arts and culture. Major imperial ceremonies saw a revival and elaboration of the ancient orchestras and companies of courtly dancers. The musicians played on bells, stone chimes, flutes, zithers, and drums.
Which dynasty succeeded the Sui dynasty?
Alternative Title: T’ang Dynasty. Tang dynasty, Wade-Giles romanization T’ang, (618–907 ce ), Chinese dynasty that succeeded the short-lived Sui dynasty (581–618), developed a successful form of government and administration on the Sui model, and stimulated a cultural and artistic flowering that amounted to a golden age.
What happened to the aristocracy in the 8th century?
In the second half of the 8th century, however, rebellion broke out in the northeast and spread rapidly, forcing the emperor Xuanzong to flee west to Sichuan.
When did the dynasty reach its peak?
The dynasty reached the peak of its wealth and power during the early 8th century, which was a golden age for its arts.
Why was the Tang Dynasty so successful?
The Tang Dynasty is largely seen as a success because of a series of very effective rulers early on. We'll start with the founder of the dynasty, Gaozu (r. 618-626). Gaozu had been a minister in the Sui Dynasty and rose to power in the rebellions. As emperor, Gaozu set himself to reforming China. Perhaps most notably, he wrote a new set of laws which could be revised every two decades to keep them relevant. This legal code was so effective that it was maintained all the way into the 14th century.
What was the first time China was united?
The Han Dynasty was one of the first times that nearly all of China was unified under leaders who were seen as wise and benevolent. Then, the Han Dynasty fell and people worried that China would never be so united again. After a few generations of warring states, however, most of China was unified by the Sui Dynasty (581-618 CE). Unfortunately, while the Sui emperors made major infrastructural improvements, they did so by heavily taxing the peasantry and conscripting them into labor. After major losses in wars with Korea, the people revolted and the Sui fell.
Who was the first emperor of the Tang Dynasty?
Like all ancient Chinese dynasties, the Tang Dynasty was a monarchy, ruled by an all-powerful emperor since it was founded by the ancient Li family in 618. Li Yuan was the first emperor of the Tang Dynasty.
What was the Tang Dynasty's system of government?
The Tang system of government was the model upon which all subsequent dynasties based their own systems, and it was also used by other countries and kingdoms, such as those in Vietnam and Korea. Another factor for the success of the Tang Dynasty system of government was the emphasis on education. The Tang rulers felt that a well-educated public was ...
How many departments did the Tang Dynasty have?
The Tang Dynasty government had three basic departments that created policies and laws. These frameworks of laws were administered by six ministries, which were personnel administration, military, finance, rites, justice, and public works. This super-efficient system of government worked so well, it outlived the Tang Dynasty itself, ...
What were the factors of success of the Tang Dynasty?
One of the factors of success of the Tang Dynasty governing system was the reforms it instituted by modifying and building upon the Sui legal code.
Why did the Tang Dynasty collapse?
But even the best designed systems of government have their flaws, and the Tang Dynasty eventually collapsed for a variety of complex reasons, some of which had to do with plain old bad luck, such as the occurrences of natural disasters .
What was the political system of the Tang Dynasty?
The prosperity during the Tang Dynasty profited from its enlightened political system: comprehensive administration and official system, strict legal system, and equitable imperial examination system.
What was the Tang Dynasty's organizational structure?
The Tang Dynasty (618 - 907) initiated the organizational structure 'Dao' and 'Fu' to divide the political districts. During Zhen Guan's Reign, the national territory was divided into ten political districts called 'Dao', which increased to 15 in the Heyday of Kaiyuan. The subordinate political districts were called 'Zhou' or 'Fu'.
What was the Tang Lushu Yi?
The Tang Lushu Yi, compiled in the reign of Emperor Gaozong was a representative code of feudal laws, which contained criminal law, law of safeguard and defense, law for imperial officers, law of marriage and census registers. The regulations were fairly complete and the legal provisions were rather concise.
What was Taizong's role in the early period of Zhen Guan's reign?
Especially, in the early period of Zhen Guan's Reign, Emperor Taizong focused much attention on listening to wise advice while enforcing the law. In this way, a peaceful social order was established, setting up a good example for later dynasties and even for some other imperial states in Asia.
What were the three departments of the Emperor?
The second level was the three departments: Chancellery, Department of State Affairs, and Central Secretariat. They control six ministries which dealt with the whole state’s affairs of Personnel, Revenue, Rites, Defense, Justice, and Works.
How many ministries were there in the Sui Dynasty?
The central official system followed the Sui Dynasty's (581 - 618) Three Departments and Six Ministries system. In addition, nine 'Si's and five 'Jian's were set up to work with the six ministries. The local official system was in line with the political administrative structures, of which the chief official title were called 'Guancha Shi' ...
Which dynasty had the most comprehensive legal system?
Legal System. Compared with any other dynasties in Chinese history, the Tang Dynasty had the most comprehensive and the most detailed legal system. Generally, the legal system included four basic forms, namely, 'Lu' (criminal law), 'Ling' (institutional regulations), 'Ge' (administrative rules) and 'Shi' (formulas of official documents).
Overview
The Tang dynasty , or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the militar…
History
The Li family had ethnic Han origins, and it belonged to the northwest military aristocracy prevalent during the Sui dynasty . According to official Tang records, they were paternally descended from the founder of Taoism, Lao Tzu (whose personal name was Li Dan or Li Er), the Han dynasty general Li Guang, and Li Gao, the founder of the Han-ruled Western Liang kingdom. This family was known a…
Administration and politics
Taizong set out to solve internal problems within the government which had constantly plagued past dynasties. Building upon the Sui legal code, he issued a new legal code that subsequent Chinese dynasties would model theirs upon, as well as neighboring polities in Vietnam, Korea, and Japan. The earliest law code to survive was the one established in the year 653, which was divided into 500 …
Military and foreign policy
The 7th and first half of the 8th century are generally considered to be the era in which the Tang reached the zenith of its power. In this period, Tang control extended further west than any previous dynasty, stretching from north Vietnam in the south, to a point north of Kashmir bordering Persia in the west, to northern Korea in the north-east.
Economy
Through use of the land trade along the Silk Road and maritime trade by sail at sea, the Tang were able to acquire and gain many new technologies, cultural practices, rare luxury, and contemporary items. From Europe, the Middle East, Central and South Asia, the Tang dynasty were able to acquire new ideas in fashion, new types of ceramics, and improved silver-smithing techniques. The …
Culture and society
Both the Sui and Tang Dynasties had turned away from the more feudal culture of the preceding Northern Dynasties, in favor of staunch civil Confucianism. The governmental system was supported by a large class of Confucian intellectuals selected through either civil service examinations or recommendations. In the Tang period, Taoism and Buddhism were commonly practiced ideologies that pl…
Science and technology
Technology during the Tang period was built also upon the precedents of the past. Previous advancements in clockworks and timekeeping included the mechanical gear systems of Zhang Heng (78–139) and Ma Jun (fl. 3rd century), which gave the Tang mathematician, mechanical engineer, astronomer, and monk Yi Xing (683–727) inspiration when he invented the world's first clockwork
Historiography
The first classic work about the Tang is the Old Book of Tang by Liu Xu (887–946) et al. of the Later Jin, who redacted it during the last years of his life. This was edited into another history (labeled the New Book of Tang) in order to distinguish it, which was a work by the Song historians Ouyang Xiu (1007–1072), Song Qi (998–1061), et al. of the Song dynasty (between the years 1044 and 1060). Both of them were based upon earlier annals, yet those are now lost. Both of them also ra…