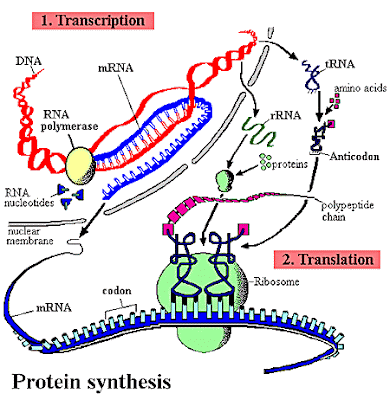
What is the role of RNA in protein synthesis?
The processed RNA molecules take part in protein synthesis with the help of ribosomes. All the three types of RNAs are involved in protein synthesis in the following main steps: (ii) Transfer of amino acid to tRNA, (iii) Initiation of protein synthesis, (iv) Elongation of the polypeptide chain.
Which scientist created an accurate model of the structure of DNA?
Watson and Crick were two scientists that created an accurate model of the structure of double-helix DNA. Levene proposed the poly nucleic model, and stated that DNA and RNA were composed of nucleotides.
How does the ribosome read mRNA and make protein?
The process that ribosomes use to read the mRNA and make protein is called translation. During this process, the ribosome sandwiches its two subunits around the mRNA. The ribosome reads the mRNA in groups of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon is read by an additional molecule, called transfer RNA (tRNA).
What role does RNA play in the formation of peptide bonds?
In addition to proving that RNA is responsible for catalyzing peptide bond formation, these structures have provided important insights into the mechanistic details of how the ribosome functions.

Who discovered RNA role in protein synthesis?
Severo Ochoa won the 1959 Nobel Prize in Medicine after he discovered how RNA is synthesized. The sequence of the 77 nucleotides of yeast tRNA was found by Robert W. Holley in 1965.
Who studied the role of RNA?
The first hypothesis about how RNA fitted into gene function came from the Paris laboratory of André Boivin, who had been one of the earliest and most visionary supporters of Avery's claim that DNA was the hereditary material.
Who discovered RNA structure?
Biophysicist Alexander Rich first mixed two differing strands of RNA in 1956 to discover the RNA double helix. He holds a model of tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid).
Who invented protein synthesis?
Along with other scientists, Palade discovered that ribosomes performed protein synthesis in cells, and he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1974 for his work. Each ribosome has a large component and a small component that together form a single unit composed of several ribosomal RNA molecules and dozens of proteins.
Who is the father of RNA?
Leslie Orgel, 80; chemist was father of the RNA world theory of the origin of life.
Who discovered RNA interference?
Two US geneticists who discovered one of the fundamental mechanisms by which gene expression is controlled have received a Nobel prize for their achievement. Andrew Fire and Craig Mello, who revealed the process of RNA interference (RNAi) in 1998, will share the US$1.4-million award.
What is the discovery of Watson and Crick?
The discovery in 1953 of the double helix, the twisted-ladder structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), by James Watson and Francis Crick marked a milestone in the history of science and gave rise to modern molecular biology, which is largely concerned with understanding how genes control the chemical processes within ...
Who are Watson and Crick and what did they discover?
They were hardly modest, these two brash young scientists who in 1953 declared to patrons of the Eagle Pub in Cambridge, England, that they had "found the secret of life." But James Watson and Francis Crick's claim was a valid one, for they had in fact discovered the structure of DNA, the chemical that encodes ...
Who said DNA makes RNA make proteins?
Francis CrickIs it always DNA to RNA to proteins? The central dogma of molecular biology. Coined by Francis Crick.
How did they discover protein synthesis?
The genetic code was broken by Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich Matthaei, a decade after Watson and Crick's work. Nirenberg discovered that RNA, regardless of its source organism, could initiate protein synthesis when combined with contents of broken E. coli cells.
Who discovered how DNA controls protein synthesis in a cell?
Watson and Crick were the first to realize that the seemingly random sequence of the four bases in DNA formed a code which specified the order of the twenty amino acids that make up most proteins.
Which scientist is related field of genetic RNA?
For related information, see the articles on History of Molecular Biology and History of Genetics. For background information, see the articles on RNA and nucleic acid....Nobel Laureates in RNA biology.NameDatesAwardsCrick, Francis1916–20041962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine32 more rows
What is the role of RNA?
The primary function of RNA is to create proteins via translation. RNA carries genetic information that is translated by ribosomes into various proteins necessary for cellular processes. mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA are the three main types of RNA involved in protein synthesis.
Why is RNA used in protein synthesis instead of DNA?
Although DNA contains the entirety of a cell's genetic code, it needs an intermediate molecule, RNA, to help in protein synthesis. The reason for t...
Where is RNA in protein synthesis?
During protein synthesis, RNA travels from the nucleus (after being generated from DNA) to a ribosome in the cell's cytoplasm. The ribosome is the...
Is RNA needed for protein synthesis?
RNA is necessary for protein synthesis. mRNA copies the cell's genetic code from DNA. rRNA generates ribosomes. tRNA assembles and links together a...
What are the 3 types of RNA and their function in protein synthesis?
mRNA copies the cell's genetic code from DNA. rRNA generates ribosomes. tRNA assembles and links together amino acids to form a protein.
What are the codons in the mRNA of a new frame?
These codons specify the amino acid sequence: methionine (Met), tyrosine (Tyr), and glycine (Gly).
What is the difference between insertion and deletion?
An insertion occurs when one or more bases are added to a DNA sequence. A deletion occurs when one or more bases are removed from a DNA sequence. Because the genetic code is read in codons (three bases at a time), inserting or deleting bases may change the "reading frame" of the sequence.
What is the stop codon in mRNA?
Each three-letter sequence of mRNA nucleotides corresponds to a specific amino acid, or to a stop codon. UGA, UAA, and UAG are stop codons. AUG is the codon for methionine, and is also the start codon. Codon chart.
What is the process of transcribed DNA into a similar RNA?
In transcription, a DNA sequence is rewritten, or transcribed, into a similar RNA "alphabet.". In eukaryotes, the RNA molecule must undergo processing to become a mature messenger RNA ( mRNA ). In translation, the sequence of the mRNA is decoded to specify the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide.
What is the meaning of mRNA sequence?
The mRNA sequence is: Translation involves reading the mRNA nucleotides in groups of three, each of which specifies and amino acid (or provides a stop signal indicating that translation is finished). In transcription, a DNA sequence is rewritten, or transcribed, into a similar RNA "alphabet.".
What is the schematic of central dogma?
Simplified schematic of central dogma, showing the sequences of the molecules involved. Transcription of one of the strands of DNA produces an mRNA that nearly matches the other strand of DNA in sequence. However, due to a biochemical difference between DNA and RNA, the Ts of DNA are replaced with Us in the mRNA.
How many bases are in RNA?
The four bases of RNA form a language with just four nucleotide bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U). The genetic code is read in three-base words called codons. Each codon corresponds to a single amino acid (or signals the starting and stopping points of a sequence). Genetic code table.
What is the starting amino acid of methionine?
Therefore, formyl group containing methionine is called N- formyl methionine. In prokaryotes as well as in eukaryotes initiation of protein synthesis occurs through a specific methionyl tRNA which is commonly known as initiation tRNA (i.e. tRNA met ).
What is the process of transferring activated amino acids to tRNA?
The process of transfer of activated amino acids to tRNA is called charging of tRNA. The tRNAs are specific to their specific amino acid. Therefore, tRNAs are named according to specific amino acid such as tRNA ala (for alanine), tRNA val (for valine), etc. Therefore, the activated amino acid is transferred to its specific tRNA.
Which enzyme synthesizes specific amino acids?
This shows that the enzyme tRNA synthetase has two specific sites. One site recognises the specific amino acids and the other site recognises the specific tRNA molecule. Thus, the tRNA synthetase brings the specific amino acid and tRNA molecule together.
Where does the peptide chain bind to?
When the peptide bond is formed, the growing peptide chain binds to the tRNA that carries the incoming amino acid and occupies the A site of ribosome. The discharged tRNA after dissociating itself from the peptide chain is released from the P site (Fig. 10.16D-E). It is known so far that ribosome consists of two sites (A and P) but the recent evidences suggest that it consists of three sites: A, P and E. The E site is specific for de-acylated tRNA (E).
Which amino acids are not used in protein synthesis?
In addition, the other amino acids which are not used in protein synthesis are citrulline, alanine, β-alanine, etc. Each amino acid has a specific aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (charging enzyme) and a specific tRNA. At least 32 tRNAs are required to recognise all the amino acid codons, but some cells used more than 32.
What are the components of initiation?
The essential components required for initiation are: initiation factors, ribosome, mRNA, guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and aminoacyl-tRNase.
What are the initiation factors of protein synthesis?
There are certain initiation factors (IF) which are required for the initiation of protein synthesis. In prokaryotes three IF (i.e.IF-1, 9,000 MW; IF-2, 1,15,000 MW and IF-3,22,000 MW) are involved in the initiation process, whereas in eukaryotes no IF equivalent to IF-1 and IF-2 are found.
What is the role of transcription factors in initiation?
During initiation, transcription factors locate around the start of a gene, called a promoter sequence, and recruit RNA polymerase. Helicase opens up the DNA, which serves as a template. During elongation, the RNA polymerase reads the message in the DNA strand and adds new nucleotides according to Chargaff's rule. Chargaff's rule states that adenine pairs with thymine in DNA, and cytosine pairs with guanine. However, in RNA thymine is replaced with uracil. So, adenine pairs with uracil in mRNA. In termination, the RNA polymerase and associated enzymes leave the mRNA molecule and it dissociates from the DNA.
How do ribosomes make proteins?
Ribosomes are organelles that read the mRNA and create the correct protein sequence. Ribosomes are located in the cytoplasm and thus do not have access to the DNA in the nucleus. The process that ribosomes use to read the mRNA and make protein is called translation. During this process, the ribosome sandwiches its two subunits around the mRNA. The ribosome reads the mRNA in groups of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon is read by an additional molecule, called transfer RNA (tRNA). The tRNA brings the correct amino acids based on the codons to the ribosome. The ribosome then catalyzes a peptide bond in between the amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Eventually, the chain is released and can fold into a complete protein.
How is messenger RNA made?
Messenger RNA is made during the process of transcription. During transcription, RNA polymerase accesses DNA in the nucleus. The RNA polymerase reads one strand of DNA and adds complementary ribonucleotides to form the mRNA strand product as well.
What is the process of making proteins?
Protein synthesis is the process that cells use to make protein. During transcription cells copy DNA to messenger RNA (mRNA) in the nucleus. This forms as a copy of the genetic material in DNA that can then be used for the second part of protein synthesis, translation. During translation ribosomes in the cytoplasm read the mRNA and use another molecule called tRNA to bring the appropriate amino acids. The amino acids are linked together through peptide bonds to make a protein. Proteins function as:
What is the purpose of mRNA?
What is the purpose of mRNA? The purpose of mRNA and the role of mRNA is to bring the instructions from the DNA to the ribosome for protein production. The role of mRNA in protein production is essential. So, what is the job of mRNA? The mRNA function is to carry the genetic code from DNA to the ribosome. In eukaryotes, this allows DNA to stay safe inside the nucleus. It also allows for a tighter level of control and more specific regulation of protein production.
What is the difference between RNA and DNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA. RNA is a type of nucleic acid and carries the genetic information for the cell. RNA is similar to DNA but there are several structural differences. RNA uses the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. It also exists as a single strand in cells and only sometimes is double-stranded. DNA in contrast is always double-stranded. RNA uses the bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil, whereas DNA uses adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. DNA is a more permanent structure in the cell and can be found in the nucleus of eukaryotes. In contrast, RNA is more readily created and destroyed and can be found in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The table below explains the difference between DNA and RNA.
What is the RNA that is attached to DNA during transcription?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is attached briefly to DNA during the transcription process. RNA polymerase uses the DNA strand as a template to synthesize mRNA.
What is tRNA?
Transfer ribonucleic acid, or its familiar abbreviated form tRNA, is sort of like that crazy uncle who shows up once a year at family reunions. You tend to forget about him for 364 days out of the year, but he's so crucial to keeping the party alive that one day in summer. In a similar fashion, tRNA's a little crazy, and we tend to forget about it, but it plays a key role in protein synthesis.
How does attaching a tRNA help the ribosome?
By attaching, it frees up the tRNA to transfer the appropriate amino acid to the end of a chain of them being produced by the ribosome. The tRNAs tag team with the ribosome decoding the mRNA codon by codon until the whole strand is complete. In the end, we should see a properly formed chain creating a specific protein!
How does tRNA work?
A good way to think about tRNA's function in the greater scheme is by comparing them to worker bees. Many of them work together to create a single protein from mRNA, and the ribosome is the beehive. When the mRNA makes its way to the ribosome with all of its coded copies of the original DNA segment, the tRNA attaches to a specific codon at ...
What is the role of tRNA in protein?
The molecule has three distinct loops, one of which contains an anticodon that decodes the mRNA in order to transfer a specific amino acid to the end of a long chain being created in the ribosome. The result is a complete protein molecule.
What is the role of tRNA in protein synthesis?
The overall role of tRNA in protein synthesis is to decode a specific codon of mRNA, using its anticodon, in order to transfer a specific amino acid to the end of a chain in the ribosome. Many tRNAs together build upon the amino acid chain, eventually creating a protein for ...
What is the process of making copies of codons?
A full example of the process would be something like this: the mRNA makes copies of specific codons as instructed in the DNA, the mRNA makes its way to the ribosome, many tRNA molecules bind to codons in the mRNA , the tRNAs then transfer the corresponding amino acids to the end of a long chain being developed by the ribosome.
How many loops does tRNA have?
Structure. The way a tRNA molecule is built is downright funky. It's this weird looking, loopy, twisted molecule. It has three distinct loops and is attached to a specific amino acid based on a distinct anticodon which makes up a part of its primary loop.