The three largest Muslim empires that extended from the Mediterranean to the Bay of Bengal include the Ottoman, Mughal, and Safavid empires. Each of these empires is unique in their own right, but commonalities exist among the three. Firstly, these are Muslim empires, ruled by individuals practicing the faith of Islam.
- Sasanian empire (224–636 A.D.) ...
- Byzantine empire (about 330–1453) ...
- Umayyad caliphate (661–750) ...
- Spanish Umayyads (756–1031) ...
- Abbasid caliphate (750–1258) ...
- Samanids (819–1005) ...
- Seljuqs of Iran (about 1040–1196)
What are the different types of Islamic empires?
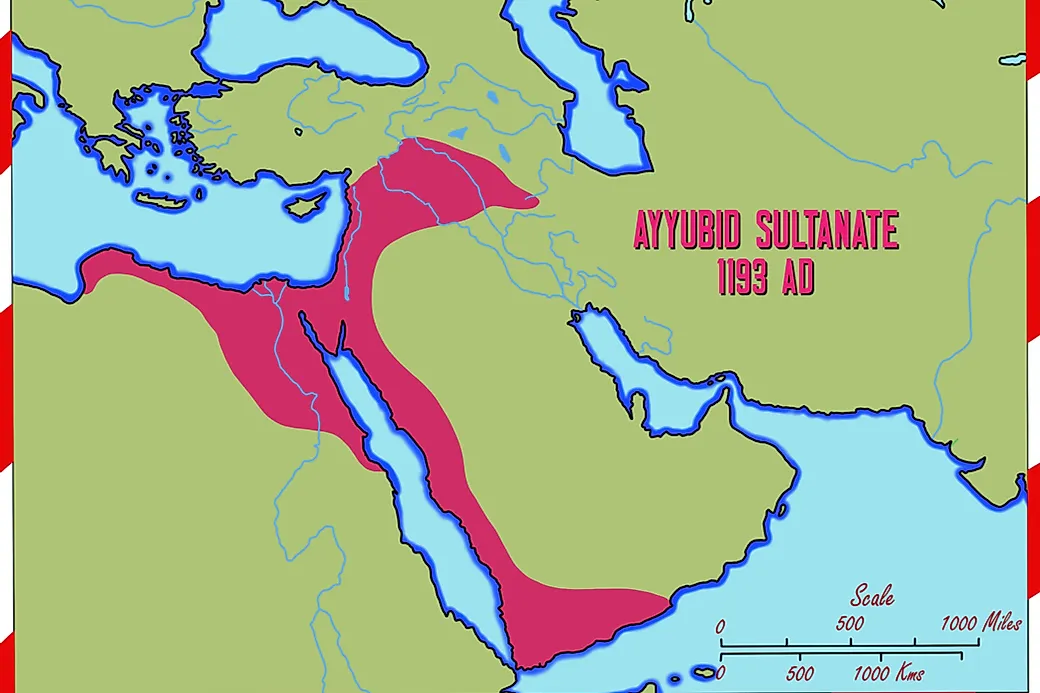
1 Rashidun Caliphate 2 Umayyad Caliphate 3 Abbasid Caliphate 4 Fatimid Caliphate 5 Ghaznavid Empire 6 Ayyubid Sultanate 7 Great Seljuk Empire, Sultanate of Rûm 8 Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt 9 Ilkhanate/Timurid Empire
What were the major Muslim empires in the Middle Ages?
Major Muslim Empires During The Middle Ages. The Middle Ages witnessed the rise of several major Islamic empires in the Old World. The Ayyubid sultanate existed between 1171 and 1246. The Middle Ages was a period that witnessed the rise of some of the greatest Muslim Empires in the Old World.
What were some of the Islamic dynasties that grew into empires?
While the caliphates gradually fractured and fell, other Muslim dynasties rose; some of these dynasties grew into Islamic empires, with some of the most notable being the Ottoman Empire, Safavid dynasty, and Mughal Empire . The Emirate of Septimania, Southern France (Gaul) (719-759) Rule by:
Which period witnessed the rise of several major Islamic empires?
The Middle Ages witnessed the rise of several major Islamic empires in the Old World. The Ayyubid sultanate existed between 1171 and 1246. The Middle Ages was a period that witnessed the rise of some of the greatest Muslim Empires in the Old World.

What were the major Islamic empires?
1 Safavid, Mughal, and Ottoman Empires. The three Islamic empires of the early modern period – the Mughal, the Safavid, and the Ottoman – shared a common Turko-Mongolian heritage. In all three the ruling dynasty was Islamic, the economic system was agrarian, and the military forces were paid in grants of land revenue.
What were the 3 major Islamic empires?
Between 1453 and 1526 Muslims founded three major states in the Mediterranean, Iran and South Asia: respectively the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal empires.
What are Islamic empires called?
Caliphate, the political-religious state comprising the Muslim community and the lands and peoples under its dominion in the centuries following the death (632 ce) of the Prophet Muhammad.
What were the two Islamic empires?
While the primary caliphates gradually fractured and fell, other Muslim dynasties rose; some of these dynasties established notable and prominent Islamic empires, such as the Ottoman Empire centered around Anatolia, the Safavid Empire of Persia, and the Mughal Empire in India.
What was the last Islamic empire?
'office of the caliphate') was the claim of the heads of the Turkish Ottoman dynasty to be the caliphs of Islam in the late medieval and the early modern era....Ottoman Caliphate.Ottoman Caliphate خلافت مقامى Hilâfet makamı• 1922–1924Abdulmejid II (last)Established• Al-Mutawakkil III formally surrenders his title over to Selim I151717 more rows
Who were the 4 gunpowder empires?
Who were the four Gunpowder Empires? Russia, the Ottoman, the Safavid, and the Mughal Empires.
Who are the 4 caliphs in Islam?
Rashidun, (Arabic: “Rightly Guided,” or “Perfect”), the first four caliphs of the Islamic community, known in Muslim history as the orthodox or patriarchal caliphs: Abū Bakr (reigned 632–634), ʿUmar (reigned 634–644), ʿUthmān (reigned 644–656), and ʿAlī (reigned 656–661).
What was the biggest Islamic empire?
1. Ottoman Empire (1299–1922) The Ottoman Empire can undoubtedly be called the greatest Muslim empire of all time because it stayed on the face of the globe for nearly 700 years. The empire was one of the largest and the longest ruling empire in history.
Who started the Islamic empire?
The early Islamic empire stretched from al-Andalus (Muslim Iberia) to the Punjab region under the reign of the Umayyad dynasty. After Muhammad's death, Abū Bakr, one of his closest associates, was chosen as the first caliph ("successor").
Which is the biggest empire in history?
Empires at their greatest extentEmpireMaximum land areaMillion km2Million sq miBritish Empire35.513.71Mongol Empire24.09.27Russian Empire22.88.8090 more rows
What were the Islamic empires in medieval times?
Major Muslim Empires During The Middle AgesRankNameDuration1Rashidun Caliphate632–6612Umayyad Caliphate661–7503Abbasid Caliphate750–12584Fatimid Caliphate909–11715 more rows•May 17, 2018
Which is the biggest empire in history?
Empires at their greatest extentEmpireMaximum land areaMillion km2Million sq miBritish Empire35.513.71Mongol Empire24.09.27Russian Empire22.88.8090 more rows
What were three places Islam spread to through trade?
Name three places Islam spread through trade, and the goods the acquired from these places. China: paper and gunpowder. Africa: ivory, cloves, and slaves. India: cloth goods.
What were the Arab empires?
Like all other empires, the first Arab Muslim empires were built within the context of the political realities of their neighboring societies. A painting depicting five men, one of whom has his face covered. A depiction of Mohammed (top, veiled) and the first four Caliphs.
What was the first Arab empire?
The first Arab Muslim empire. During the seventh century, after subduing rebellions in the Arabian peninsula, Arab Muslim armies began to swiftly conquer territory in the neighboring Byzantine and Sasanian empires and beyond. Within roughly two decades, they created a massive Arab Muslim empire spanning three continents.
What empires were able to conquer the east and west?
With the Byzantine and Sasanian Empires on the decline and strategically disadvantaged, Arab Muslim armies were able to quickly take over vast territories that once belonged to the Byzantines and Sasanians and even conquer beyond those territories to the east and west.
How did the Abbasids change the social hierarchy?
However, they changed the social hierarchy by constructing a more inclusive government in a more cosmopolitan capital city, Baghdad. The distinction between Arab Muslims and non-Arab Muslims diminished, with Persian culture exerting a greater influence on the Abbasid court.
How did Islam spread?
Islam spread through military conquest, trade, pilgrimage, and missionaries. Arab Muslim forces conquered vast territories and built imperial structures over time. Most of the significant expansion occurred during the reign of the Rashidun from 632 to 661 CE, which was the reign of the first four successors of Muhammad.
Which dynasty spread the Islamic culture?
It was not until the Umayyad Dynasty —from 661 to 750—that Islamic and Arabic culture began to truly spread. The Abbasid Dynasty —from 750 to 1258—intensified and solidified these cultural changes. A dome situated in the courtyard of a mosque. Dome of the Clocks, Umayyad Mosque, Damascus, Syria.
Did Islam spread through their conquests?
The Rashidun can be credited for military expansion, but did Islam truly spread through their conquests? Significant conversion and cultural exchange did not occur during their short rule, nor were complex political institutions developed. It was not until the Umayyad Dynasty —from 661 to 750—that Islamic and Arabic culture began to truly spread. The Abbasid Dynasty —from 750 to 1258—intensified and solidified these cultural changes.
Which Islamic country was the Umayyad Caliphate?
The Umayyad Caliphate of Cordobain Islamic Spain(756-929-1031)
Which dynasty was the Persian Empire under?
The Persian Empire, under the Safavid dynasty (1502–1736), Afsharid dynasty, and Qajar dynasty
What dynasty was in Delhi?
The Mamluk dynasty of Delhi(1206–1290)
What dynasty was in Morocco?
The Almohad dyna sty(1121–1269) of Morocco
Where was the Umayyadof Spain?
The Umayyadof Spain in North-Africa during war with the Fatimid's
What happened after Muhammad's death?
In the centuries after the life of Muhammad, Muslim armies poured out into all surrounding areas, bringing the lands from Persia to Spain under their control.
Which dynasty grew into an Islamic empire?
While the caliphates gradually fractured and fell, other Muslim dynasties rose; some of these dynasties grew into Islamic empires, with some of the most notable being the Safavid dynasty, Ottoman Empire, and Mughal Empire .
When did the Muslim conquests begin?
This article includes a list of successive Muslim states and dynasties from the rise of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and of the Early Muslim conquests which began in 622 CE and continues through to this current day.
What is the history of Islam?
The history of modern Islam has often been explained in terms of the impact of “the West.”. From this perspective the 18th century was a period of degeneration and a prelude to European domination, symbolized by Napoleon I ’s conquest of Egypt in 17 98. Yet it is also possible to argue that the period of Western domination was merely an interlude in ...
What was the Islamic movement in West Africa?
In West Africa a series of activist movements appeared from the 18th century into the 19th. There, as in Arabia, Islamic activism was directed less at non-Muslims than at Muslims who had gone astray. As in many of Islamdom’s outlying areas, emergent groups of indigenous educated, observant Muslims, such as the Tukulor, were finding the casual, syncretistic, opportunistic nature of official Islam to be increasingly intolerable. Such Muslims were inspired by reformist scholars from numerous times and places—e.g., al-Ghazālī, al-Suyūṭī, and al-Maghīlī—and by a theory of jihad comparable to that of the Wahhābīs and by expectations of a mujaddid at the turn of the Islamic century in ah 1200 (1785 ce ). In what is now northern Nigeria, the discontent of the 1780s and ’90s erupted in 1804, when Usman dan Fodio declared a jihad against the Hausa rulers. Others followed, among them Muḥammad al-Jaylānī in Aïr, Shehuh Ahmadu Lobbo in Macina, al-Ḥājj ʿUmar Tal (a member of the reformist Tijānī ṭarīqah) in Fouta Djallon, and Samory in the Malinke (Mandingo) states. Jihad activity continued for a century; it again became millennial near the turn of the next Muslim century, in ah 1300 (1882 ce ), as the need to resist European occupation became more urgent. For example, Muḥammad Aḥmad declared himself to be the Mahdī in the Sudan in 1881.
What were some examples of reforms in Iran?
In some areas leaders attempted to revive existing political systems. In Iran, for example, attempts at restoration combined military and religious reform. About 1730 a Turk from Khorāsān named Nadr Qolī Beg reorganized the Ṣafavid army in the name of the Ṣafavid shah, whom he replaced with himself in 1736. Taking the title Nādir Shah, he extended the borders of the Ṣafavid state farther than ever; he even defeated the Ottomans and may have aspired to be the leader of all Muslims. To this end he made overtures to neighbouring rulers, seeking their recognition by trying to represent Iranian Shīʿism as a madhhab (school of Islamic law) alongside the Sunni madhhab s. After he was killed in 1747, however, his reforms did not survive and his house disintegrated. Karīm Khan Zand, a general from Shīrāz, ruled in the name of the Ṣafavids but did not restore real power to the shah. By the time the Qājārs (1779–1925) managed to resecure Iran’s borders, reviving Ṣafavid legitimacy was impossible.
How did Islamdom inhibit the power of merchants?
In Islamdom the power of merchants had been inhibited by imperial overtaxation of local private enterprise, appropriation of the benefits of trade, and the privileging of foreign traders through agreements known as the Capitulations.
What was the restoration of the Ottoman Empire?
In the Ottoman Empire restoration involved selective imitation of things European. Its first phase, from 1718 to 1730, is known as the Tulip Period because of the cultivation by the wealthy of a Perso-Turkish flower then popular in Europe. Experimentation with European manners and tastes was matched by experimentation with European military technology. Restoration depended on reinvigorating the military, the key to earlier Ottoman success, and Christian Europeans were hired for the task. After Nādir Shah’s defeat of the Ottoman army, this first phase of absolutist restoration ended, but the pursuit of European fashion had become a permanent element in Ottoman life. Meanwhile, central power continued to weaken, especially in the area of international commerce. The certificates of protection that had accompanied the Capitulations arrangements for foreign nationals were extended to non-Muslim Ottoman subjects, who gradually oriented themselves toward their foreign associates. The integration of such groups into the Ottoman state was further weakened by the recognition, in the disastrous Treaty of Küƈük Kaynarca (1774), of the Russian tsar as protector of the Ottoman’s Greek Orthodox millet.
What did the Sufis study?
Sufis often encouraged the study of tales about the Prophet Muhammad (Hadith), which they used to establish him as a model for spiritual and moral reconstruction and to invalidate many unacceptable traditional or customary Islamic practices.
When did jihad become millennial?
Jihad activity continued for a century; it again became millennial near the turn of the next Muslim century, in ah 1300 (1882 ce ), as the need to resist European occupation became more urgent. For example, Muḥammad Aḥmad declared himself to be the Mahdī in the Sudan in 1881.
