
Water is absorbed mainly in the large intestine, which turns undigested food into a coherent mass of feces. The colon absorbs water from the undigested food. Due to the presence of Haustra the water-absorbing surface of the colon increases and it efficiently increases absorption of water.
How much water does the large intestine absorb?
On top of that, another 6 to 7 liters of fluid is received by the small intestine daily as secretions from salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, liver and the small intestine itself. By the time the ingesta enters the large intestine, approximately 80% of this fluid has been absorbed.
How does the large intestine help conserve water?
How does the large intestine help maintain a water balance in the body? The large intestine helps maintain the water balance in the body by digesting and removing water from the remains of food (feces) after which it will go through the rectum. Related questions. QUESTION.
What is primarily absorbed in the large intestine?
Water and Ion Absorption. In the large intestine, there is a net absorption of sodium ions and chloride ions are actively absorbed. Sodium – this ion may be absorbed by various methods: Sodium-hydrogen antiporter on the luminal membrane; Epithelial sodium channels; Enhanced by absorption of short-chain fatty acids in the colon via specialised symporters
What kind of absorption occurs in large intestine?
The purpose of the large intestine is to absorb water and salts from the material that has not been digested as food, and get rid of any waste products left over. By the time food mixed with digestive juices reaches your large intestine, most digestion and absorption has already taken place.
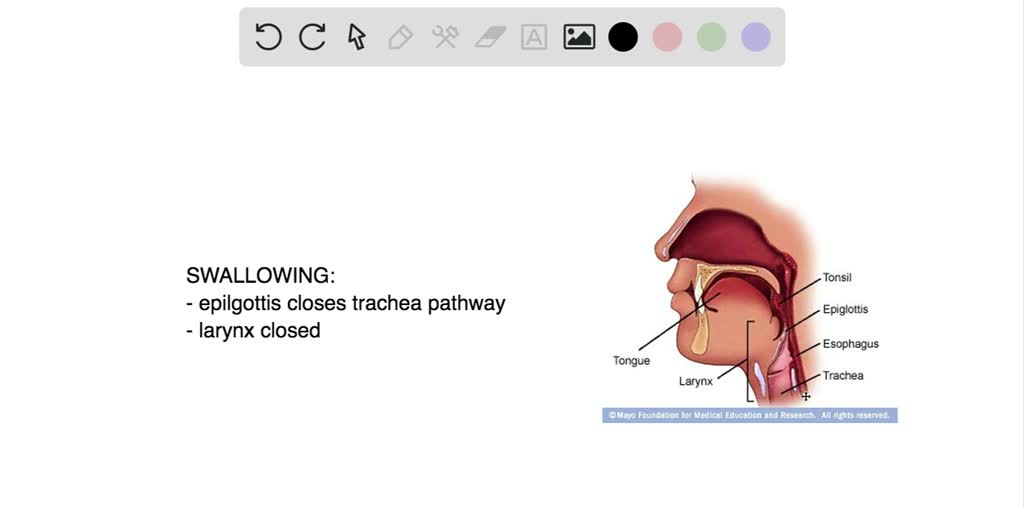
What does the rectum eliminate?
The rectum eliminates stool created within the intestines. Stool is composed of unneeded material such as unusable plant fiber and non-nutritional...
How does large intestine work?
The large intestine works to move stool through two types of movements. Haustral movements are gradual and continual, while mass movements are gran...
What is the rectum?
The rectum is the final portion of the large intestine. It holds stool created by the colon before it is excreted via the anus.
Which ions are absorbed in the large intestine?
In the large intestine, there is a net absorption of sodium ions and chloride ions are actively absorbed.
How is absorption regulated in the colon?
Regulation of Absorption. Absorption in the gastrointestinal tract is regulated by neuroendocrine mechanisms. In the colon endocrine mechanisms used include: Aldosterone – increases the net absorption of water and electrolytes by stimulating the basolateral sodium-potassium ATP-ase.
How is potassium absorbed in the colon?
In the colon potassium may be absorbed or secreted depending on the remaining concentration in the lumen and the electrochemical gradient created by the active absorption of sodium. Secretion usually occurs when the luminal concentration of potassium ions is below 25mM.
How does the colon help the chyme?
The colon helps to absorb a small volume of water from the lumen (400ml/day). As the chyme is very concentrated by the time it reaches here, the colon must work against a larger osmotic pressure gradient than in the rest of the GIT. In other words, it must move water against the gradient for osmosis.
What is the large intestine lined with?
The large intestine is lined by mucosa with Crypts of Lieberkühn containing glands and the mucus-producing goblet cells. These protect the intestinal wall from the plethora of anaerobic bacteria in the colon and from the pressure exerted on the walls by the concentrated chyme (soon to become faeces).
What is the role of the large intestine?
The large intestine, or colon, has several roles including water absorption and immunity. The chyme that enters the colon is already very concentrated because most of the water has already been absorbed. Thus, the large intestine is specialised to work in the environment this produces.
How is sodium absorbed?
Sodium – this ion may be absorbed by various methods: 1 Sodium-hydrogen antiporter on the luminal membrane 2 Epithelial sodium channels 3 Enhanced by absorption of short-chain fatty acids in the colon via specialised symporters
What are the forces that help water absorption?
So that absorption depends upon intake, whereas intake is guided by the water content of the body. The main physico-chemical forces which help water absorption are hydrostatic pressure, endosmosis and osmotic pressure.
How are water and salts absorbed?
Water ad salts are absorbed passively and actively. During passive absorption, water and small water-soluble substances traverse the intestinal mucosa along osmotic or electrochemical gradient, the energy moving them being derived from whatever processes established the gradients in the first place.
How much water is absorbed by salt?
It is interesting to note that water absorption is influenced by the presence of salts in it. Pure distilled water is absorbed only up to 59%, but if given in the form of increasing strengths of saline the rate of absorption gradually rises and becomes 95% with a solution containing 0.4 – 0.7% NaCl. But beyond that strength the rate falls, because, increased osmotic pressure draws out fluid from the wall.
What ions are absorbed by the epithelial cells?
The sodium ions after being absorbed inside the epithelial cells produce an electric potential which helps in the movements of chloride ions. Due to this electric potential, chloride ions may move inside the epithelial cells, against the high osmotic pressure Calcium is absorbed in presence of vitamin D, protein and lactose.
What is the function of the large intestine?
The large intestine absorbs all the residual water and forms solid stool. Absorption of water is not influenced by total water content of the body. There is no limit to the amount of water absorbed. Large quantities of fluid may be ingested without developing liquid stool, showing complete absorption. If more water is taken, more will be excreted ...
How is calcium absorbed?
Calcium absorption is effected by active transport mechanism which uses high energy phosphate generated by aerobic metabolism. Iron is absorbed in combination with a special protein called ferritin. Absorption is promoted by ascorbic acid which keeps it reduced.
Which part of the body absorbs water?
Water introduced into the stomach almost immediately passes into the small intestine which is the chief seat of water absorption. The intestinal contents near the ileocecal valve contain the same proportion of water as the upper part of jejunum. But their absolute amount is much smaller. The large intestine absorbs all the residual water ...
How does water absorption occur in the small intestine?
In the small intestine, water absorption is brought about by the creation of suitable osmotic gradients that promote net uptake of water from the intestinal lumen. The absorption of solute, especially that brought about by active carriers, are highly effective in creating the osmotic gradients that promote net water uptake.
How does water absorption occur?
Absorption of ingested water and most solutes occurs in the proximal small intestine, therefore the rate at which beverages are emptied from the stomach is an important factor in determining the rate of water absorption. In the small intestine, water absorption is brought about by the creation of suitable osmotic gradients that promote net uptake of water from the intestinal lumen. The absorption of solute, especially that brought about by active carriers, are highly effective in creating the osmotic gradients that promote net water uptake. The activation of these transporters also increases the permeability of the mucosa which helps absorption. Moderate hypotonicity of the luminal contents potentiates solute-induced water absorption while hypertonicity slows fluid absorption. Dilute hypotonic glucose-sodium solutions are highly effective oral rehydration solutions, and the type of carbohydrate used does not appear to be important. The addition of other actively absorbed solutes gives little benefit in potentiating water uptake. The inclusion of sodium in rehydration solutions may not be required to stimulate water absorption but probably assists the overall rehydration process. The amount of glucose required to stimulate water absorption is relatively small and for rehydration purposes ingestion of an adequate amount of a dilute solution is more beneficial than drinking a smaller volume of a more concentrated beverage.
Does sodium help with rehydration?
The inclusion of sodium in rehydrat ion solutions may not be required to stimulate water absorption but probably assists the overall rehydration process. The amount of glucose required to stimulate water absorption is relatively small and for rehydration purposes ingestion of an adequate amount of a dilute solution is more beneficial ...
