Why do double bonds cause Kinks in fatty acids?
If they are unsaturated, however, double bonds are introduced, and these double bonds introduce kinks into the structure of the fatty acid molecule. In a different question on this site, it was suggested that the reason why double bonds cause kinks to form is that they interrupt the zig zag shape of the molecule.
What is the difference between cis and unsaturated fats?
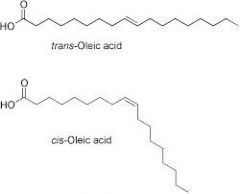
Saturated fatty acids do not have carbon-carbon double bonds, while unsaturated fatty acids have double bonds between carbon atoms. When a double bond occurs in the middle of the chain, it can either be cis or trans. In cis fats, the double bond forms with the two hydrogen atoms on the same side of the double bond.
What is the difference between cis and trans fatty acids?
The key difference between cis and trans fatty acids is that the cis fatty acids have two hydrogen atoms attached to the double bond in the same side of the carbon chain whereas the trans fatty acids have the two hydrogen atoms bonded to the double bond in the opposite sides of the carbon chain.
What is the structure of cis fatty acids?
Cis fatty acids are carboxylic acids containing long aliphatic carbon chains having the two hydrogen atoms attached to double bond in the same side of the carbon chain.

Why are fatty acids cis?
When the two hydrogen atoms stick out on the same side of the chain, the fatty acid is said to be in a cis configuration. This results in a kink due to the two hydrogen atoms repelling each other slightly. The more double bonds in the cis configuration, the less flexible is the fatty acid.
Do fatty acids have cis double bonds?
Fatty acids with one double bond are the most prevalent in the human body, comprising about half of the total. Fatty acids with two or more double bonds occur in lesser quantities, but are extremely important. When double bonds occur they are almost always cis.
Why unsaturated fatty acids are cis?
In an unsaturated fatty acid, the carbon atoms on either side of the double bond can be in either a cis or a trans configuration. The higher the concentration of trans fatty acids, the more solid the fat, so oils are generally high in cis fatty acids, and margarine and lard are high in trans fatty acids.
What is the role of a cis configuration of double bonds in the fatty acid component of a phospholipid molecule in the cell membrane?
In the cis configuration, the two hydrogens associated with the bond are on the same side, while in a trans configuration, they are on opposite sides (see below). A cis double bond generates a kink or bend in the fatty acid, a feature that has important consequences for the behavior of fats.
Why do saturated fatty acids have straight structures?
In saturated fatty acids, carbon atoms are bonded to as many hydrogen atoms as possible. All the carbon-to-carbon atoms share just single bonds between them. This causes the molecules to form straight chains, as shown in Figure 2.6.
What is a cis isomer of a fatty acid?
Unsaturated fatty acids may occur in two distinct structural configurations – cis and trans isomers. Cis: The hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon double bond are on the same side. Trans: The hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon double bond are on different sides.
Why do double bonds cause kinks?
The carbons that share a double bond between them have only one hydrogen each. If the hydrogens are on the same side of the double bond, then the molecule kinks at the bond, forming an angle. If the hydrogens are on opposite sides, then the molecule has no kinks, and it is straight.
Why does a cis fatty acid have a kinked shape?
If hydrogens are present in the same plane, it is referred to as a cis fat; if the hydrogen atoms are on two different planes, it is referred to as a trans fat. The cis double bond causes a bend or a “kink” that prevents the fatty acids from packing tightly, keeping them liquid at room temperature.
How does the presence of a double bond influence the shape of a fatty acid?
How does the double bond influence the dispersion forces that can form between the hydrocarbon chains of fatty acids? In unsaturated fatty acids, the cis double bonds cause the carbon chain to bend or "kink", which gives the molecules an irregular shape.
What is the classification of fatty acids with one or more double bonds within their carbon chain?
Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. The term unsaturated indicates that fewer than the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms are bonded to each carbon in the molecule.
Why do phospholipids form a bilayer?
Because their fatty acid tails are poorly soluble in water, phospholipids spontaneously form bilayers in aqueous solutions, with the hydrophobic tails buried in the interior of the membrane and the polar head groups exposed on both sides, in contact with water (Figure 2.45).
Where are cis fatty acids found?
Table 1. Some vegetable oils, such as olive oil (≈75 %), mid-oleic sunflower oil (≈70 %), and rapeseed oil (≈65 %), consist of more than 50 % of cis-MUFA, followed by other products such as palm oil, nuts and seeds, avocados, and animal fats [9].
Why does a cis fatty acid have a kinked shape?
If hydrogens are present in the same plane, it is referred to as a cis fat; if the hydrogen atoms are on two different planes, it is referred to as a trans fat. The cis double bond causes a bend or a “kink” that prevents the fatty acids from packing tightly, keeping them liquid at room temperature.
Are cis fatty acids found in nature?
In nature, cis-fatty acids are the most common compared to trans fat, which are formed mainly due to certain artificial treatments. Naturally occurring trans fats such as those found in grass-fed meat, are quite different and exist at a very low concentration compared to industrially produced trans fats.
What is the difference between unsaturated and saturated fatty acids?
The difference between saturated and unsaturated fat lies in the number of double bonds in the fatty acid chain. Saturated fatty acids lack double bonds between the individual carbon atoms, while in unsaturated fatty acids there is at least one double bond in the fatty acid chain.
What changes in the fatty acid composition of membranes result in an increased ratio of unsaturated fatty acids?
Generally, during shifts to low temperatures, changes in the fatty acid composition of membranes result in an increased ratio of unsaturated fatty acids, cis-double bonds, methyl branching, and shortening of the fatty acid chains ( Gounot and Russell, 1999 ). Unsaturation of membrane lipids correlates with low-temperature sensitivity ( Singh et al., 2002; Nishida and Murata, 1996 ). A specific membrane phospholipid containing branched very-long-chain fatty acids that could improve cold tolerance was detected in polar Calothrix sp. samples ( Řezanka et al., 2009 ).
What is a trans fatty acid?
Trans Fatty Acids. Trans fatty acids are isomers of the normal cis fatty acids, produced when PUFAs are hydrogenated, such as in the production of margarine and vegetable shortening. Hydrogenated vegetable oils were developed mainly as an alternative to animal fats and tropical oils used in frying, baking, and spreads.
How much energy does trans fat give?
Trans fatty acids, formed in the process of hardening polyunsaturated fats in the manufacture of margarines and shortening , contribute 2% to 4% of energy in a typical diet in the United States. 149 These fatty acids have properties intermediate between cis unsaturated and saturated fatty acids and can increase blood cholesterol. 150
Why are transfatty acids not recommended?
Because transfatty acids have the greatest atherogenic potential in comparison to all fatty acids in the diet, their consumption is not recommended by any international guidelines [ 10–12 ].
What is trans fat?
Trans fat is the final product of a chemical process called hydrogenation which is used to transform healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated vegetable oils into solid and prevent them from becoming rancid. Trans fats were created by the food industry because they are more stable fats and have a longer shelf life. Hydrogenation also makes them more easily spreadable and modifies the flavor of baked goods. The industrial process of hydrogenation consists of heating oils in the presence of hydrogen and a heavy-metal catalyst, such as palladium, nickel, cobalt, copper, or iron, changing the chemical structure of oils and causing the oil to become a solid. On food label ingredient lists, this manufactured substance is typically listed as “partially hydrogenated oil.” The amount of trans fat in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils is substantial accounting for about 30%–60% of trans fat.
What is the worst type of fat?
The worst type of dietary fats and widely accepted as being unhealthy for good reason is the so-called trans fat, which has one or more double bonds in a trans position, rather than the natural cis position ( Fig. 3.7 ). In nature, cis -fatty acids are the most common compared to trans fat, which are formed mainly due to certain artificial treatments. Naturally occurring trans fats such as those found in grass-fed meat, are quite different and exist at a very low concentration compared to industrially produced trans fats.
What percentage of trans fat is hydrogenated?
The amount of trans fat in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils is substantial accounting for about 30%–60% of trans fat.
What is the Difference Between Cis and Trans Fatty Acids?
Cis fatty acids are carboxylic acids containing long aliphatic carbon chains having the two hydrogen atoms attached to double bond in the same side of the carbon chain whereas the trans fatty acids are carboxylic acids containing long aliphatic carbon chains having the two hydrogen atoms attached to double bond in the opposite sides of the carbon chain. This is the key difference between cis and trans fatty acids. Furthermore, when considering their occurrence, cis configuration is much common in nature while the trans configuration is not common in nature. Because, the trans fatty acids mainly form as a result of different industrial processes such as hydrogenation. Moreover, another difference between cis and trans fatty acids is that the cis configuration causes the fatty acid molecule to bend while the trans configuration does not cause the molecule to bend much.
What happens when there are many double bonds in a carbon chain?
If there are many double bonds in the chain, it lessens the flexibility of the chain. Moreover, if there are more cis configurations along the carbon chain, it makes the chain quite curved in its most accessible conformations. Examples include cis-oleic acid and cis-linoleic acid.
What is Trans Fatty Acids?
Trans fatty acids are carboxylic acids containing long aliphatic carbon chains having the two hydrogen atoms attached to double bond in the opposite sides of the carbon chain. Therefore, this does not cause the carbon chain to bend much.
What are the two forms of unsaturated fatty acids?
Cis and trans fatty acids are two forms of unsaturated fatty acids.
Why do unsaturated fatty acids bend?
We name this as the “cis configuration of unsaturated fatty acids”. Since the hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the carbon chain, it causes the chain to bend. This restricts the conformational freedom of the fatty acid. If there are many double bonds in the chain, it lessens the flexibility of the chain.
Is cis common in nature?
Furthermore, when considering their occurrence, cis configuration is much common in nature while the trans configuration is not common in nature. Because, the trans fatty acids mainly form as a result of different industrial processes such as hydrogenation. Moreover, another difference between cis and trans fatty acids is ...
Is a fatty acid a carboxylic acid?
Fatty acids are carboxylic acids containing long aliphatic carbon chains that are either saturated or unsaturated. This means, the aliphatic chain may or may not contain double bonds between the carbon atoms. Cis and trans fatty acids are two forms of unsaturated fatty acids.
Why do unsaturated fats have lower melting point than saturated fats of the same MW?
This is why unsaturated fats such as vegetable oil have lower melting point than saturated fats of the same MW (the cis double bonds lead to a more compact molecule which gets less tangled with its neighbours.) The reason nature produces cis bonds is due to the enzymatic mechanism in which these bonds are produced.
What happens when fat is hydrogenated?
When fat is artificially hydrogenated with a metal catalyst (for example nickel) to increase its viscosity/raise its melting point (to turn vegetable oil into margarine) some of the cis double bonds that escape being hydrogenated are able to change from cis to the more thermodynamically stable trans.
Is trans fat bad for you?
These trans fats are unnatural and are therefore widely claimed to be unhealthy. But in biological systems, polyunsaturated fatty acids are cis, and for an animal to oxidize them, they first have to be converted to trans, which takes energy.
Does vegetable oil have a lower melting point than saturated fat?
Nature produces cis fats exclusively (someone may prove me wrong with some weird example.) This is why unsaturated fats such as vegetable oil have lower melting point than saturated fats of the same MW (the cis double bonds lead to a more compact molecule which gets less tangled with its neighbours.)
Do polyunsaturated fatty acids have trans?
0. But in biological systems, polyunsaturated fatty acids are cis, and for an animal to oxidize them, they first have to be converted to trans, which takes energy. So I think it depends on whether you are discussing in vitro or in vivo polyunsaturated fats. Share. Improve this answer.
Is trans fat more stable than cis fat?
I've been studying organic chemistry and I think trans fats are actually more stable than cis fats. This is because the steric hindrance (for trans) would be lower and the molecule energy would be lower too (more stable).
What is the double bond in cis fat?
In cis fats, the double bond forms with the two hydrogen atoms on the same side of the double bond. In trans fats, the double bond forms with the two hydrogen atoms on opposite sides of the double bond.
What happens to cis bonds during hydrogenation?
During hydrogenation, some of the cis bonds in fatty acids are transformed into trans bonds, resulting in trans fatty acids. Figure 01: Cis and Trans Fat.
What is Cis Fat?
Cis fat is a form of unsaturated fatty acids. In cis fats, two hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the double bond of the fatty acid’s carbon chain backbone. Cis fats are bent chains. Therefore, they are less stable compared to trans fats. Moreover, cis bonds form high energy configuration. During hydrogenation, some of the cis bonds in fatty acids are transformed into trans bonds, resulting in trans fatty acids.
What is the Difference Between Cis and Trans Fat?
So, on the chemical aspect, this is the key difference between cis and trans fat. Moreover, another important difference between cis and trans fat is that trans fats are thermodynamically more stable than cis fats. Furthermore, trans fats have a higher melting point than cis fats.
What are the two subtypes of fatty acids?
Cis and trans fat are two subtypes of fatty acids.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids?
These long aliphatic chains are either saturated or unsaturated. Saturated fatty acids do not have carbon-carbon double bonds, while unsaturated fatty acids have double bonds between carbon atoms. When a double bond occurs in the middle of the chain, it can either be cis or trans. In cis fats, the double bond forms with the two hydrogen atoms on the same side of the double bond. In trans fats, the double bond forms with the two hydrogen atoms on opposite sides of the double bond.
Why is it important to minimize trans fat intake?
Trans fats contribute to the increase of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, which can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Hence, it is necessary to minimize the intake of trans fats.