
Why are ECG
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram, a recording – a graph of voltage versus time – of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle. Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardia…
Full Answer
Is ECG and EKG the same thing?
There are no considerable differences between the two. ECG and EKG, both are acronyms that carry the same meaning. ECG stands for Electrocardiogram, while EKG is an acronym for the German-translated word Elektro-kardiographie.
What is an EKG machine and how does it work?
What is EKG machine? Electrocardiograph, also called EKG, ECG, or simply cardiograph, is a medical instrument used for detecting and diagnosing common heart abnormalities by measuring heartbeat triggering electric potentials on the body surface and recording electrical currents associated with activity of a heart muscle.
What is the purpose of an EKG?
Your doctor uses the EKG to:
- assess your heart rhythm
- diagnose poor blood flow to the heart muscle (ischemia)
- diagnose a heart attack
- diagnose abnormalities of your heart, such as heart chamber enlargement and abnormal electrical conduction
What are the uses of an ECG?
Uses and Functions of ECG Machine An ECG machine is used for graphically recording and monitoring the electrical activity of various phases of heart beat. This is done with the help of electrodes externally attached to the outer surface of skin, on the chest and limbs of patients with heart diseases.
What is the purpose of the electrode in ECG?
Electrodes (small, plastic patches that stick to the skin) are placed at certain spots on the chest, arms, and legs. The electrodes are connected to an ECG machine by lead wires. The electrical activity of the heart is then measured, interpreted, and printed out. No electricity is sent into the body.
Where are ECG leads placed and why?
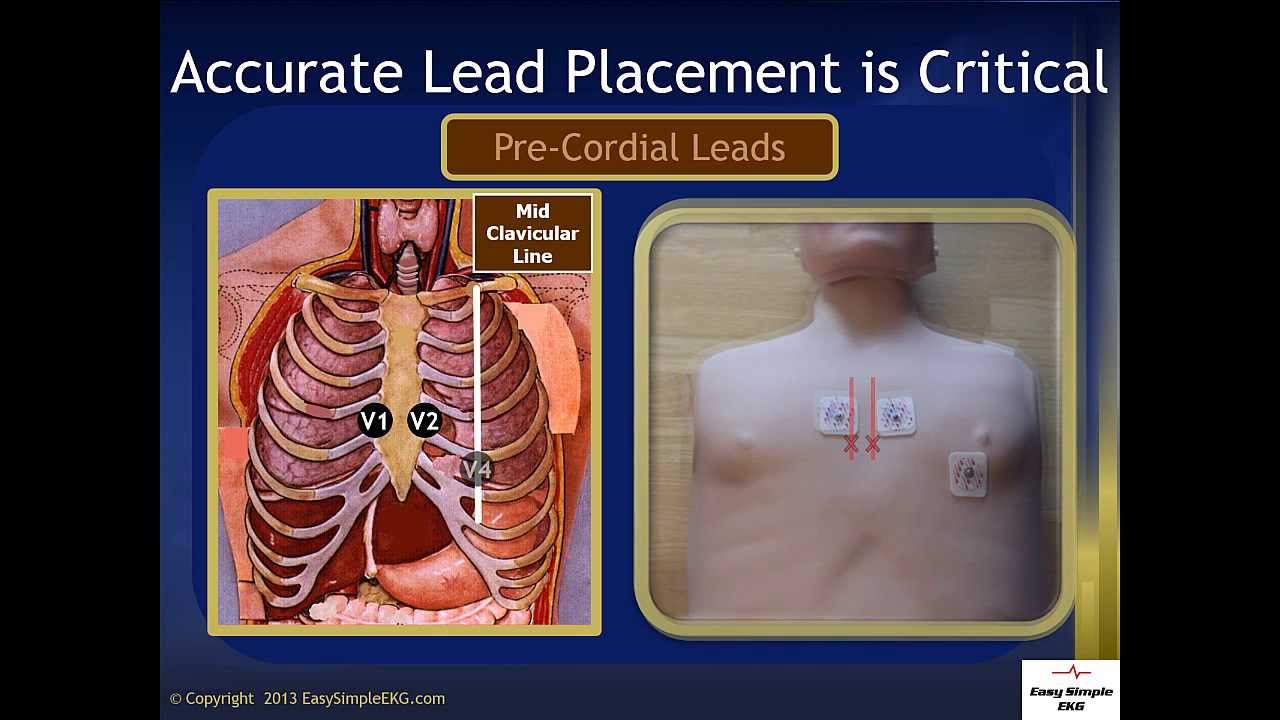
Regardless of a patient's sex, the positioning of the electrodes remains the same: V1 and V2 flank the sternal borders at the fourth intercostal space; V4, V5, and V6 align starting at the fifth intercostal space; and V3 goes on the midway point between V2 and V4.
Why are ECG electrodes placed on limbs?
The limb leads, of which there are six (I, II, III, aVF, aVR and aVL), have the exploring electrode and the reference point placed in the frontal plane. These leads are therefore excellent for detecting vectors traveling in the frontal plane.
Where are electrodes placed for ECG?
During an electrocardiogram, small pads or patches (electrodes) are attached to the skin on the chest, arms, and legs. The electrodes are also connected to a machine that translates the electrical activity into line tracings on paper.
Why is ECG connected to left ankle?
A standard ECG is obtained by attaching three electrodes- one to each wrist and another to the left ankle. This is done in order to minimize any noise detection by the activity of action potentials generated by the skeletal muscles.
Does ECG lead placement matter?
Proper, standard ECG leads placement is essential in providing accurate information from the recordings.
Why are limb leads placed on torso?
Placing limb leads on the torso has the major advantages of ease and speed of application, and in an emergency may be applied with minimal undressing. Limb movement artefact is also reduced, or prevented as seen in our series.
Why does a 12-lead ECG have 10 electrodes?
A lead is a glimpse of the electrical activity of the heart from a particular angle. Put simply, a lead is like a perspective. In 12-lead ECG, there are 10 electrodes providing 12 perspectives of the heart's activity using different angles through two electrical planes - vertical and horizontal planes.
How many electrodes are on an ECG?
10 electrodesAlthough it is called a 12-lead ECG, it uses only 10 electrodes. Certain electrodes are part of two pairs and thus provide two leads. Electrodes typically are self-adhesive pads with a conducting gel in the centre. The electrodes snap onto the cables connected to the electrocardiograph or heart monitor.
What is electrode placement?
Conventionally, recording Lead I is the most popular electrode configuration for a standard ECG recording and is as follows: positive electrode on left upper limb, negative electrode on the right upper limb, and ground electrode on the tail or on left lower leg.
What happens if ECG leads are put on incorrectly?
The analysis of ECG signals recorded from misplaced electrodes can lead to misinterpretation or even to significant diagnostic errors like incorrect recognition of anterior infarction, anteroseptal infarction, ventricular hypertrophy [9, 14], false diagnosis of ischemia, or Brugada syndrome [16, 24].
What are the 3 types of ECG?
There are 3 main types of ECG: a resting ECG – carried out while you're lying down in a comfortable position. a stress or exercise ECG – carried out while you're using an exercise bike or treadmill.
Why do 12 lead ECGS have 10 leads?
Therefore, the ten electrodes in the 12 Lead ECG give 12 perspectives of the heart's electrical activity at a given time, using various angles. This is all done via two electrical planes called the horizontal and vertical planes discussed in the next section.
What happens if ECG leads are put on incorrectly?
The analysis of ECG signals recorded from misplaced electrodes can lead to misinterpretation or even to significant diagnostic errors like incorrect recognition of anterior infarction, anteroseptal infarction, ventricular hypertrophy [9, 14], false diagnosis of ischemia, or Brugada syndrome [16, 24].
In which anatomical location should the limb leads be placed?
Limb leads are made up of 4 leads placed on the extremities: left and right wrist; left and right ankle. The lead connected to the right ankle is a neutral lead, like you would find in an electric plug. It is there to complete an electrical circuit and plays no role in the ECG itself.
Where do the leads go on a heart monitor?
Place the right arm (RA) electrode near the right shoulder, close to the junction of the right arm and torso. Place the left arm (LA) electrode near the left shoulder, close to the junction of the left arm and torso. Place the right leg (RL) electrode below the level of the lowest rib on the right abdominal area.
What is an ECG?
The electrocardiogram (ECG) allows medical personnel to both monitor the electrical signals produced by the heart and interpret their meaning. The quality and accuracy of the prehospital ECG are directly related to the quality and condition of the electrodes. At the beginning of the shift, paramedics must insure that electrode packages have current ...
Where are the left and right arm electrodes placed?
Owing to the fact that Einthoven's law makes no assumptions about geometric placement of the three electrodes [2], the care team placed the left and right arm electrodes on the patient’s left and right cheek , respectively. Physicians noted the morphology of the resulting ECG tracing was acceptable for rhythm interpretation, but caution against substituting interval measurements obtained from modified electrode placement for those obtained with conventional placement.
How many centimeters does a precordial electrode have?
Generally speaking, precordial electrode placement that varies less than one centimeter from the recommended location produces negligible alterations in morphology or interval measurements. However, placement variation of more than two centimeters results in significant morphology changes [3].
What to do if transdermal medication patch interferes with electrode placement?
If the location of a transdermal medication patch interferes with electrode placement, rescuers should quickly remove the patch and wipe the area before attaching the electrode.
How to apply a conduction gel electrode?
As you peel the electrode from its protective cover, insure the conducting gel is intact. Apply the electrode flat on the patient’s skin, smoothing the electrode from the center towards the edges, and avoid pressing on the center of the electrode as this can disrupt the integrity of the conduction gel reservoir.
Which organization recommends the placement of defibrillation electrodes?
The American Heart Association also makes some very specific recommendations regarding the placement and use of defibrillation electrodes [4].
Which position is the best for a defibrillator?
The American Heart Association acknowledges the reasonableness of placing the defibrillation electrodes in any one of four pad positions: anterolateral, anteroposterior, anterior-left infrascapular, and anterior-right- infrascapular [4]. One position has not proven superior to any others.
Why do electrodes matter?
It is the interface between the body and the measuring equipment that allows us to measure and record the ECG. When recording the ECG, we experience artifacts which can be caused by mains noise, motion and potentials from other muscles.
Why do muscle potentials interfere with ECG?
These potentials can interfere with the ECG produced due to an overlap in frequency content. As the ECG and EMG (electrical activity of the muscles) fall within a similar frequency range, it is these muscle potentials that typically cause a significant amount of in band noise and interference on the ECG.
What is an ECG artifact?
ECG Artifacts. A change in amplitude, frequency or morphology of the ECG can highlight significant cardiac abnormalities. For the clinician to detect these changes it is important for the signal to be of high quality.
What causes an unreadable ECG?
Excessive motion can also produce an unstable contact between the skin and electrode which will produce an unreadable ECG. Although these problems are inevitable, a choice of high quality materials combined with adequate skin preparation can reduce the effect these have on the ECG. Muscle Interference.
How does a right leg drive work?
Right leg drive is used to further reduce the common-mode interference. The right leg drive system cancels out common-mode interference by using a negative feedback loop. The feedback loop uses a small current opposite to that of the common-mode interference and drives it into the right leg electrode to cancel out the common-mode interference [8].
How to remove artifacts from ECG?
Typically, artifacts are removed using hardware and software filters. However, when filtering to remove artifact we can inevitably lose important parts of the ECG. In some cases, aggressive digital filtering has even been shown to remove P-wave entirely [1]. It would therefore be highly desirable to reduce artifacts as much as possible at the very source of the problem, the electrode interface.
Can common mode interference corrupt ECG?
Ideally, if we had equal impedance across all electrodes , the mains noise would be removed completely by common-mode rejection. However, due to the small impedance differences across the electrodes, common-mode interference can corrupt the ECG.
What is an ECG lead?
An ECG lead is a graphical description of the electrical activity of the heart and it is created by analysing several electrodes.
How does an electrocardiograph generate an ECG lead?
Figure 16. The electrocardiograph generates an ECG lead by comparing the electrical potential difference in two points in space. In the simplest leads these two points are two electrodes (illustrated in this figure). One electrode serves as exploring electrode (positive) and the other as the reference electrode. The electrocardiograph is constructed such that an electrical current traveling towards the exploring electrode yields a positive deflection, and vice versa.
What is the order of the leads in the Cabrera system?
In the Cabrera system, the leads are placed in their anatomical order. The inferior limb leads (II, aVF and III) are juxtaposed, and the same goes for the lateral limb leads and the chest leads. As mentioned earlier, inverting lead aVR into –aVR improves diagnostics additionally.
Where are the limb leads placed?
Leads I, II, III, aVF, aVL and aVR are all derived using three electrodes, which are placed on the right arm, the left arm and the left leg. Given the electrode placements, in relation to the heart, these leads primarily detect electrical activity in the frontal plane.
What is the difference in electrical potential?
Electric potential difference is defined as a difference in electric potential between two measurement points. In electrocardiology these measurement points are the skin electrodes. Thus, the electrical potential difference is the difference in the electrical potential detected by two (or more) electrodes.
Can 12 lead ECG be missed?
There are conditions that may be missed when utili zing the 12-lead ECG. Fortunately, researchers have validated the use of additional leads to improve diagnostics of such conditions. These are now discussed.
Why is it important to place electrodes correctly?
Exact placement of each electrode on the patient is important. Incorrect placement can lead to false or misleading diagnosis.
What is an ECG?
What is Electrocardiogram. As a non-invasive yet most valuable diagnostic tool, the 12-lead ECG records the heart's electrical activity as waveforms. When interpreted accurately, an ECG can detect and monitor a host of heart conditions - from arrhythmias to coronary heart disease to electrolyte imbalance. Since the first telecardiogram recorded in ...
Why do you cross your arms on your stomach?
For patients that do not fit comfortably on the bed or exam table due to size, ask them to cross their arms on their stomach to reduce muscle tension and movement. Unless you're performing a stress ECG test, ask the patient to lie still and quietly until the test is done.
What is a lead ECG?
A lead is a glimpse of the electrical activity of the heart from a particular angle. Put simply, a lead is like a perspective. In 12-lead ECG, there are 10 electrodes providing 12 perspectives of the heart's activity using different angles through two electrical planes - vertical and horizontal planes.
Which leads require a positive electrode?
Leads I, II, and III require a negative and positive electrode (bipolarity) for monitoring. On the other hand, the augmented leads-aVR, aVL, and aVF-are unipolar and requires only a positive electrode for monitoring.
When was the first telecardiogram performed?
Since the first telecardiogram recorded in 1903 , huge strides have been made in the recording and interpretation of ECG. Today, the 12-Lead ECG remains a standard diagnostic tool among paramedics, EMTs, and hospital staff.
Should lead placement and patient positioning be the same for subsequent ECGs on any individual patient?
Lead placement and patient positioning should be the same for subsequent ECGs on any individual patient.
Where are electrodes placed during an EKG?
During an EKG, a technician places electrode leads on the chest, legs and arms, according to the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. These leads carry information on the heart’s electrical output to an EKG machine, which records this information for interpretation and diagnosis.
Why are EKG leads placed?
Reason for Placement. EKG leads record their information as differences in the output between matched positive and negative electrodes, notes the Merck Manuals Online Medical Library. The specific placement of these electrodes allows doctors to acquire accurate vertical and horizontal images of the heart.
What is an EKG?
An electrocardiogram, or EKG, is a procedure designed to measure the heart’s electrical output through a number of electrode leads. The placement of those leads stems from the requirements of a full examination of the heart’s function.
What are the heart problems detected by accurate lead placement?
The MMOML lists heart problems detected by accurate lead placement that include heartbeat irregularities (arrhythmias) and enlargements of the upper heart (atria) and lower heart (ventricles).
