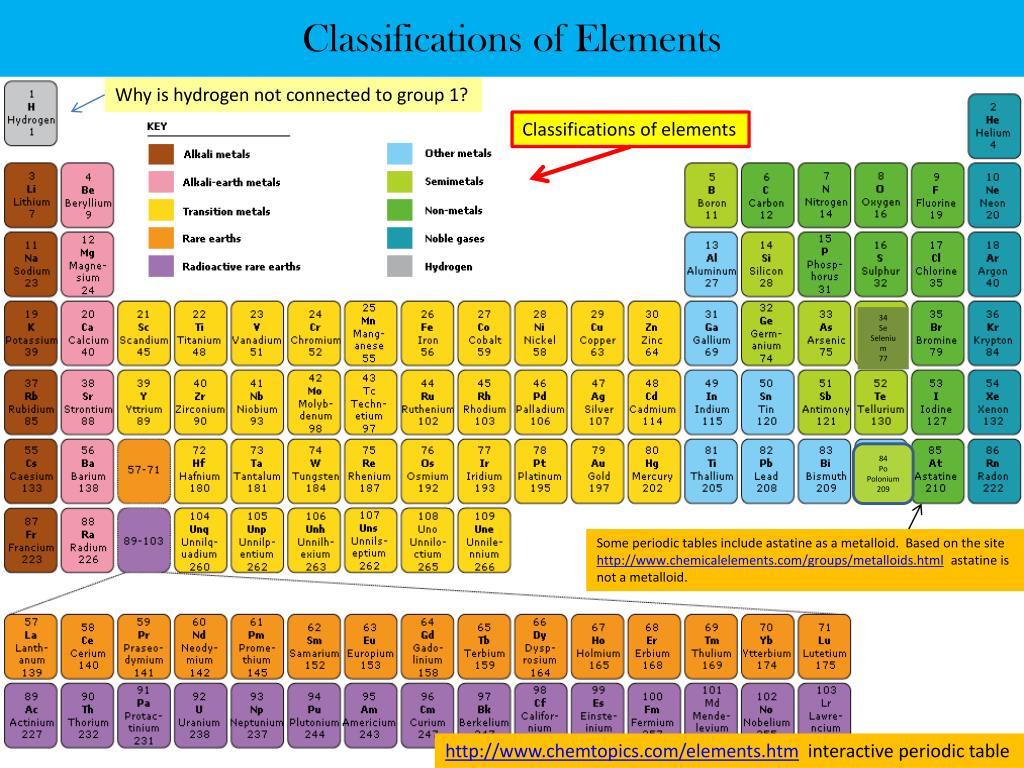
Silicon has 4 electrons in its outer orbitals which it can donate like a metal or it can also accept 4 electrons like a non metal. So, it shows both the properties of metals and non metals. Hence, it is called a metalloid or semi conductor. Boron
Boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. Produced entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovae and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in the Solar system and in the Earth's crust. Boron is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of it…
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its group neighbours silicon and tin. Pure germanium is a semiconductor with an appearance similar to elemental silicon. Like …
Antimony
Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite. Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by …
What is a metalloid?
Do non metals have carbonates?

Why are germanium and silicon metalloids?
Silicon and Germanium both possess the properties of metals and non-metals. Therefore, they are called metalloids.
Why is silicon classified as a metalloid?
Why is Silicon Classified as a Metalloid? Silicon is classified as a metalloid since some of its properties are similar to those of metals and some of its properties are similar to those of nonmetals. For example, silicon is known to have a bluish-grey metallic lustre but is not an amazing conductor of electricity.
Why is germanium a metalloid?
Germanium has conductivity between metals and non-metals. Therefore it cannot be grouped under metals or non-metals. Such elements are grouped under metalloids.
Are germanium and silicon metalloids?
Boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium are commonly recognised as metalloids.
How do you classify metalloids?
1 Answer. The common classification for Metalloids are, possess some characteristics of metals and some of non-metals, semi-conductive, and are metallic lustre.
What properties make silicon a metalloid?
SummaryMetalloids are elements with properties intermediate between those of metals and non-metals.Silicon is a metalloid because it has luster, but is brittle.Boron, arsenic, and antimony are metalloids with a variety of uses.
Why is it called metalloid?
The origin and usage of the term metalloid is convoluted. Its origin lies in attempts, dating from antiquity, to describe metals and to distinguish between typical and less typical forms. It was first applied to metals that floated on water (lithium, sodium and potassium), and then more popularly to nonmetals.
What defines a metalloid?
metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having properties intermediate between those of a typical metal and a typical nonmetal.
Why metalloids are called metalloids?
They are called metalloids because they exhibit characteristics of both metals and non-metals.
What are the characteristics of the metalloids?
This article will describe the six most important properties of metalloids and list some key metalloids characteristics.Metalloids Are Solids. ... Metalloids Have a Metallic Luster and Appear to be Metals. ... Metalloids Are Brittle and Easily Broken. ... Metalloids Have the Ability To Conduct Electricity, but Not As Well as Metals.More items...
Why silicon and germanium are known as semiconductors?
Conduction of heat and electricity silicon, germanium, and tellurium conduct electricity under the right conditions. They are semiconductors. Metalloids conduct less heat than metals.
What are 5 characteristics of metalloids?
Characteristic Properties of MetalloidsMetalloids are solids.They have a metallic luster, and generally look like metals.They are brittle, and easily shattered.Metalloids can conduct electricity, but not as well as metals.More items...•
Is silicone a metalloid?
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor.
Does silicon belong to metalloids?
Like silicon, germanium is used as a semiconductor, and is widely used in the computer industry. Silicon and germanium are both metalloids, having some characteristics of both metals and nonmetals.
What kind of metalloid is silicon?
tetravalent metalloidThe element Silicon is a chemical element with the chemical symbol and the atomic number of 14,which is also a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster. It is known as a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor.
Why are silicon and boron called metalloids?
The elements boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. These elements, called metalloids or sometimes semimetals, exhibit properties characteristic of both metals and nonmetals.
What is a metalloid?
A metalloid is an element which exhibits some properties of both metal and non-metal. Since silicon shows the properties of both metals and non-metals, it is classified as a metalloid. It is used in semi-conductor devices. Other examples of metalloids include boron, germanium, arsenic etc.
Do non metals have carbonates?
Non metals have their carbonates and hydrogencarbonates. If yes , Then give example of : 1.A non metal carbonate And 2.A non metal hydrogencarbonate If No , Then give suitable reasons supporting your answers.
Why haven't semiconductors replaced silicon?
That said, there are various reasons why these semiconductors have not replaced silicon, which is plentiful, usable to beyond 400 K, resistant to degradation by air, and has an established fabrication technology, for the majority of electronic uses.
Is phosphorus a semiconducting photodetector?
Phosphorus, in the form phosphorene, structurally similar to graphene, has been used as a semiconducting photodetector.
What is a metalloid?
A metalloid is an element which exhibits some properties of both metal and non-metal. Since silicon shows the properties of both metals and non-metals, it is classified as a metalloid. It is used in semi-conductor devices. Other examples of metalloids include boron, germanium, arsenic etc.
Do non metals have carbonates?
Non metals have their carbonates and hydrogencarbonates. If yes , Then give example of : 1.A non metal carbonate And 2.A non metal hydrogencarbonate If No , Then give suitable reasons supporting your answers.
