Answer: Glycoproteins
Glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins that contain oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently attached to polypeptide side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secrete…
What do membrane proteins and glycoproteins do?
- They aid in stabilizing and protecting a few proteins
- They are vital for blood grouping
- The give rise to the production of various types of glycoproteins
- They allow a few proteins in the body to perform the functions efficiently
What is the function of integral proteins in cell membranes?
Integral proteins are embedded in the plasma membrane and may span all or part of the membrane. Integral proteins may serve as channels or pumps to move materials into or out of the cell. Peripheral proteins are found on the exterior or interior surfaces of membranes, attached either to integral proteins or to phospholipid molecules.
Is producing cellular nutrients a function of cell membrane?
Perfect cell membrane function allows nutrition in and keep toxins out. So even if you eat healthy, you still need optimum cell membrane function for cellular nutrition, assimilation and detoxification at the cellular level. Simply put, your cell membranes are the foundation for great health.
What functions does the cell membrane perform?
What are the 7 functions of the plasma membrane?
- A Physical Barrier. …
- Selective Permeability. …
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis. …
- Cell Signaling. …
- Phospholipids. …
- Proteins. …
- Carbohydrates. …
- Fluid Mosaic Model.

What is the major function of glycoproteins and glycolipids in cell membrane?
Main Function Functionally, glycolipids facilitate cellular recognition while glycoproteins serve as receptors for chemical signals.
Why are glycolipids important in the cell membranes?
Generally, glycolipids are found on the outer leaflet of cellular membranes where it plays not only a structural role to maintain membrane stability but also facilitates cell-cell communication acting as receptors, anchors for proteins and regulators of signal transduction [1].
What is the function of the glycoproteins?
They are heavily involved in the immune system, where they allow white blood cells to move around the body, initiate immune responses, and identify other cells. They are also involved in creating mucus to protect various organs in our body. Glycoproteins are essential for keeping our bodies healthy and functional!
What is a glycoprotein and what does it do?
Glycoproteins are molecules that comprise protein and carbohydrate chains that are involved in many physiological functions including immunity. Many viruses have glycoproteins that help them enter bodily cells, but can also serve to be important therapeutic or preventative targets.
What are the main functions of phospholipids and glycolipids in the body?
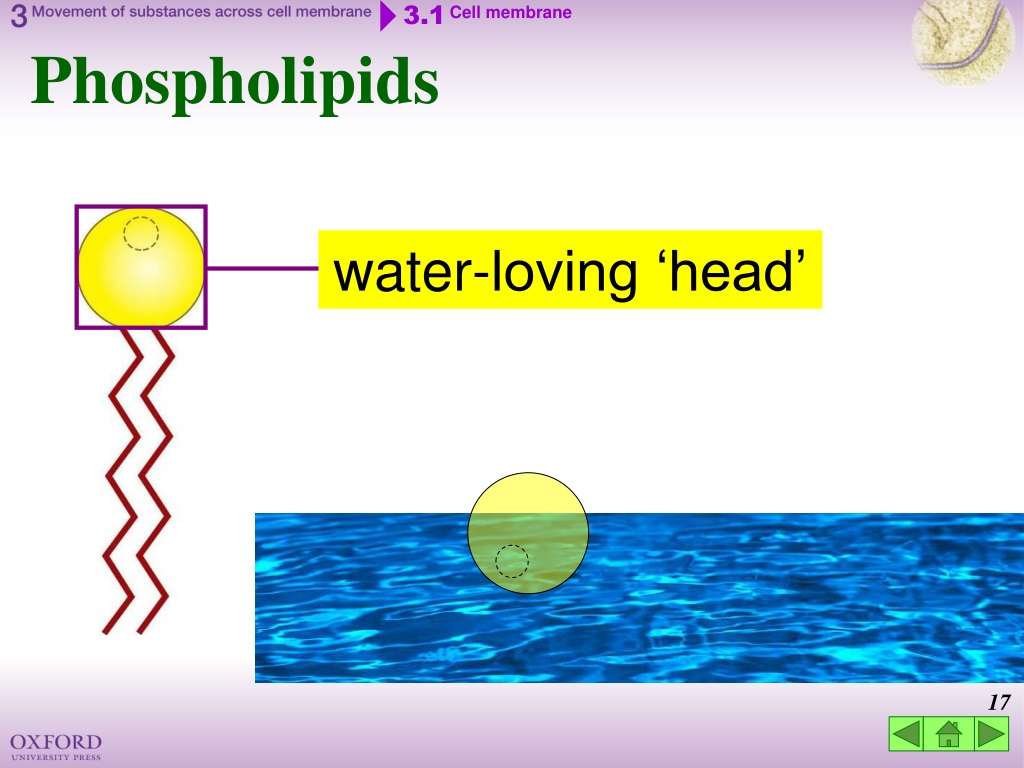
Phospholipids provide barriers in cellular membranes to protect the cell, and they make barriers for the organelles within those cells. Phospholipids work to provide pathways for various substances across membranes.
How do glycolipids provide energy?
Abstract. Glycolipids are membrane lipids which act as cellular markers and also provide energy for the cells. The present study is an attempt to understand whether glycolipids can act as energy sources during fasting.
Why are glycoproteins more hydrophilic than simple proteins?
Because of the -OH groups of sugars, glycoproteins are more hydrophilic than simple proteins. This means glycoproteins are more attracted to water than ordinary proteins. The hydrophilic nature of the molecule also leads to the characteristic folding of the protein's tertiary structure.
What is the glycoprotein categorized according to?
Glycoproteins are categorized according to the attachment site of the carbohydrate to an amino acid in the protein.
How do glycoproteins get their sugar?
Glycoproteins get their sugar from an enzymatic process that forms a molecule that would not function otherwise. Another process, called glycation, covalently bonds sugars to proteins and lipids. Glycation is not an enzymatic process. Often, glycation reduces or negates the function of the affected molecule.
Why is glycophorin important?
Glycophorin A is also important because it's the attachment site for Plasmodium falciparum, a human blood parasite . Glycoproteins are important for reproduction because they allow for the binding of the sperm cell to the surface of the egg. Mucins are glycoproteins found in mucus.
What are some examples of blood clotting?
Examples include human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) and erythropoietin (EPO). Blood clotting depends on the glycoproteins prothrombin, thrombin, and fibrinogen. Cell markers may be glycoproteins. The MN blood groups are due to two polymorphic forms of the glycoprotein glycophorin A.
What is a glycoprotein?
A glycoprotein is a type of protein molecule that has had a carbohydrate attached to it . The process either occurs during protein translation or as a posttranslational modification in a process called glycosylation. The carbohydrate is an oligosaccharide chain (glycan) ...
What is the R group?
The R group is usually the amide side chain of asparagine. The bonding process is called N-glycosylation. N-linked glycoproteins gain their sugar from the endoplasmic reticulum membrane and then are transported to the Golgi complex for modification.
Where are glycoproteins found?
Glycoproteins are found in connective tissues, cell walls and blood plasma. Depending on where they are located in the body, they will display structural differences. Glycoproteins play a major role in reproduction since they are located on the surface of sperm. Glycoproteins change the plasma membrane permeability making it easier for ...
What is the process of forming glycoproteins?
Non-enzymatic Glycoproteins This creates glycoproteins when sugar is added to polypeptides in a process called glycosylation.
How are carbohydrates modified?
The carbohydrates that are inside the glycoprotein are modified by enzymes that also takes away some of the sugars. It then attaches other sugars so that it forms new glycoproteins. O-linked Glycoproteins These types of glycoproteins are created by adding sugar to the hydroxyl chain and polypeptides. They are different from the N-linked ...
What is the order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain?
The order of the amino acids in the polypeptide chain is crucial to its function. This order is called the amino acid sequence. The import of this is found when one considers that if the amino acids were ordered in a different sequence, they would not have the same function.
What changes the permeability of the plasma membrane?
Glycoproteins change the plasma membrane permeability making it easier for the attraction of eggs to the sperm cells. N-linked Glycoproteins These types of glycoproteins are modified and synthesized inside the membrane organelles of a cell. The protein part of the glycoprotein is created on the surface by other amino acids.
How many different types of glycoproteins are there?
Here, they work as membrane proteins sometimes facilitating some of the body's important processes like reproduction. There are three different types of glycoproteins that are determined differentiated through their synthesis mechanism and structure.
Does glycosylation increase blood sugar?
People, who have higher amounts of circulating glucose, experience higher levels of glycosylation. Additionally, older proteins also have a higher incidence of glycosylation. This is the primary basis of the glycosylated hemoglobin diagnostic test that is used for checking on the blood sugar levels for diabetics.
How do glycoproteins help cells recognize other cells?
Here, glycoproteins play an important role in cell to cell recognition given that the glycoprotein of one cell can identify and respond to the oligosacchar ide patterns (of glycoproteins) of another cell. It's also through this process that binding (adhesion occurs).
What are Glycoproteins?
As mentioned, glycoproteins are protein molecules (polymers) with covalently linked carbohydrates. Here, glycosylation has been shown to occur following the production/synthesis of proteins (post-transitional) which means that the carbohydrate component of glycoproteins is added following protein synthesis. However, carbohydrates can be added as the protein molecule continues growing in some cases.
What is glycoprotein in biology?
Definition. Glycoprotein refers to proteins in which oligosaccharide chains (glycans) are covalently attached/bound to the amino acid side chains (polypeptide backbones). In different types of organisms, these molecules are formed through a process known as glycosylation. Here, the number and type of sugar molecules added to ...
Where does glycosylation occur in eukaryotic cells?
In eukaryotic cells, this process starts in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and continues in the Golgi apparatus.
How are O-linked glycoproteins formed?
O-linked glycoproteins - Unlike N-linked glycoproteins, O-linked glycoproteins are formed through a process known as O-linked glycosylation. The carbohydrate is linked to the oxygen atom on the side chain (located in the hydroxyl group) of serine of threonine amino acid. As is the case with N-linked glycosylation, ...
What are carbohydrates in glycoproteins?
Carbohydrates found in glycoproteins are referred to as oligosaccharides; polymers that consist of between 3 and 10 monosac charides. Generally, oligosaccharides are not found freely in cells. Rather, they exist as complex molecules linked to proteins (N-linked or O-linked). In human beings, there are several types of sugars (monosaccharides) ...
What are some examples of glycoprotein markers?
Some of the best examples of glycoprotein markers are Glycophorins A and B . Generally, these are classified as sialoglycoprotein which means that the glycoprotein also consists of sialic acid. Found in the membrane of human erythrocytes, the molecule is used for MN blood grouping.
What are glycoproteins involved in?
Glycoproteins are involved in nearly every process in cells! They have diverse functions such as in our immune system, protection of our body, communication between cells, and our reproductive systems. Let's examine these functions more closely.
Why are glycoproteins important for blood?
If you have type A blood, you have A antigens, or A glycoproteins, on your red blood cells. This helps the body to identify that your blood is part of you and tells it not to attack it. Glycoproteins also help to stimulate the process of coagulation of platelets to clot blood when you get cut. People who are missing important proteins on platelets can't clot their blood and have a disease called hemophilia, where any cut continues to bleed indefinitely.
What Are Glycoproteins?
Glyco is a prefix in science that means 'sugar.' Glycoproteins are simply proteins with a sugar attached to them.
What is the purpose of mucus in the body?
In the stomach, this mucus helps protect your stomach lining from the harsh acids needed to digest food. In the lungs, the mucus helps to trap bacteria, keeping your lungs clean and healthy! Glyoproteins are also involved in keeping our skin healthy.
Where are sugars found in the cell?
The sugars can be attached to a protein in two locations in the cell, the endoplasmic reticulum , which produces N-linked sugars, and the Golgi apparatus, which produces O-linked sugars. The N-linked glycoproteins have a sugar attached to a nitrogen atom, and O-linked glycoproteins have a sugar attached to an oxygen atom. The different structure of N- and O-linked sugars give them different functions.
Why do MHC molecules bind with white blood cells?
8. MHC molecules bind with white blood cells to allow them to communicate with the T-cells.
Where are N and O glycoproteins found?
The different structure of N- and O-linked sugars give them different functions. Glycoproteins are always found on the outside of the plasma membrane, with the sugar facing out.
Why are glycoproteins soluble?
As glycans are hydrophilic, the formation of a glycoprotein can make the molecule more soluble. The covalent bond between the polypeptide chain and glycan also forms a highly-stable molecule that prevents peptide bonds from breaking down during a process called proteolysis.
What is a glycoprotein?
Definition. A glycoprotein is part of an extremely diverse group of linked amino acid and carbohydrate chains. Glycoproteins are found throughout nature and have a similarly diverse range of functions. They are one of two glycoconjugates – the other group is composed of glycolipids. Glycoprotein examples include fibrillins, mucins, ...
What is the name of the amino acid that replaces the lost OH of the glycosyl group?
The hydroxyl group of the associated amino acid replaces the lost –OH of the glycosyl group. Adding glycosyl to a peptide chain, protein, or lipid is called glycosylation. More than half of the proteins in the human body are glycosylated. In eukaryotic cells, glycosylation occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.
How many glycoproteins are in the zona pellucida?
The human zona pellucida has four glycoproteins (ZP1 through to 4) and these are known to contribute to egg/sperm interaction. Recent studies show that infertile females often have a mutation in the gene that encodes for ZP1.
What is the structure of a glycoprotein?
Glycoprotein Structure. Glycoprotein structure is described in its name – a sugar portion (glyco) attached to a protein. The two components attach by way of a covalent bond. Most scientists refer to the carbohydrate (sugar) part of a glycoprotein structure as a glycan. Glycans are oligosaccharides and can form between one and eighty percent ...
What is the sugar molecule that is removed from a monosaccharide called?
Before binding to a protein, this sugar molecule is called a glycosyl group. Mucin structure. The removal of a hydroxyl group (-OH) from a monosaccharide in a polysaccharide chain forms a glycosyl group with a vacant spot that makes it unstable.
How do amino acids become functional?
Once amino acid chains have been produced through intracellular protein synthesis, they must undergo further reactions to become biologically functional. As we have just seen, adding glycosyl to certain inactive amino acid chains (polypeptides) produces functional, folded glycoproteins.

O-Linked and N-Linked Glycoproteins
Glycoprotein Examples and Functions
- Glycoproteins function in the structure, reproduction, immune system, hormones, and protection of cells and organisms. Glycoproteins are found on the surface of the lipid bilayer of cell membranes. Their hydrophilic nature allows them to function in the aqueous environment, where they act in cell-cell recognition and binding of other molecules. Cel...
Glycosylation Versus Glycation
- Glycoproteins get their sugar from an enzymatic process that forms a molecule that would not function otherwise. Another process, called glycation, covalently bonds sugars to proteins and lipids. Glycation is not an enzymatic process. Often, glycation reduces or negates the function of the affected molecule. Glycation naturally occurs during aging and is accelerated in diabetic pati…
Sources
- Berg, Jeremy M., et al. Biochemistry.5th ed., W.H. Freeman and Company, 2002, pp. 306-309.
- Ivatt, Raymond J. The Biology of Glycoproteins. Plenum Press, 1984.