
What is the function of the mitochondria in a plant cell?
The most important function of the mitochondria is to produce energy. The simpler molecules of nutrition are sent to the mitochondria to be processed and to produce charged molecules. These charged molecules combine with oxygen and produce ATP molecules. This process is known as oxidative phosphorylation.
Are mitochondria found in plant or animal cells?
The mitochondrion is a double-membraned, rod-shaped structure found in both plant and animal cell. Its size ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometre in diameter. The structure comprises an outer membrane, an inner membrane, and a gel-like material called the matrix.
How many mitochondria per cell?
There are 10 to 20 mitochondria in a cell; one ATP synthase complex generates 100 to 150 ATP molecules each second. I am missing the information about the average number of ATP...
What diseases are in the mitochondria?
Types of Mitochondrial Diseases. Alper's Disease. Autosomal Dominant Optic Atrophy (ADOA) Barth Syndrome. Carnitine Deficiency. Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) Co-Enzyme Q10 Deficiency. Creatine Deficiency Syndromes. Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders.
Why are mitochondria unique?
What organelle makes food?
What are the structures of mitochondria?
How are mitochondria separated from the cytoplasm?
What is the last step of cellular respiration?
What is the mitochondria?
Where does cellular respiration begin?
See 4 more
About this website
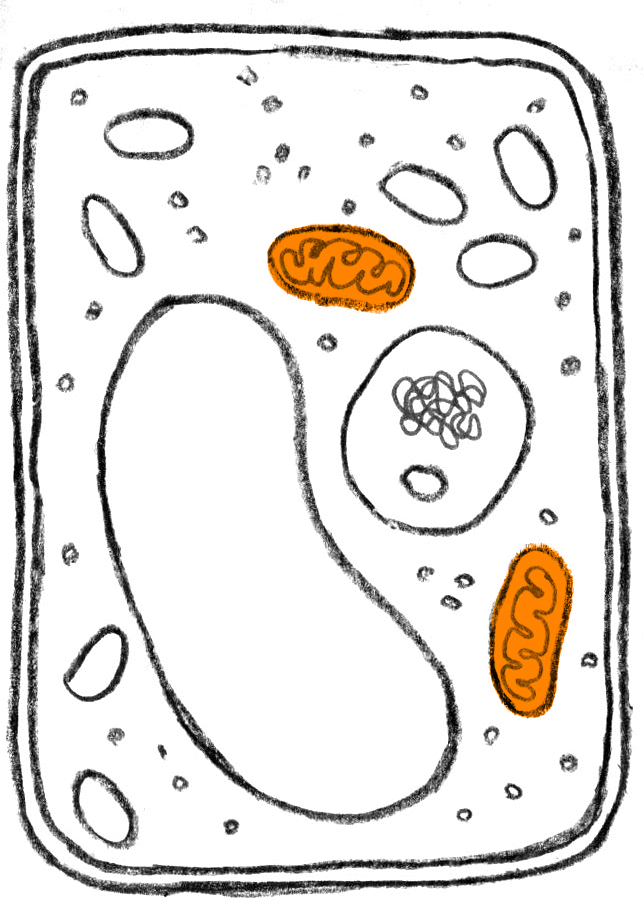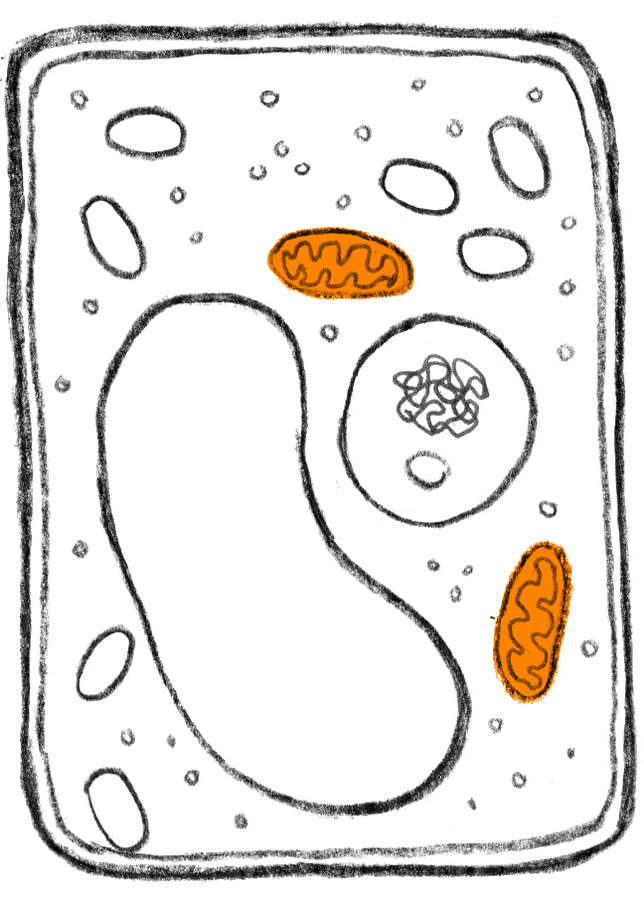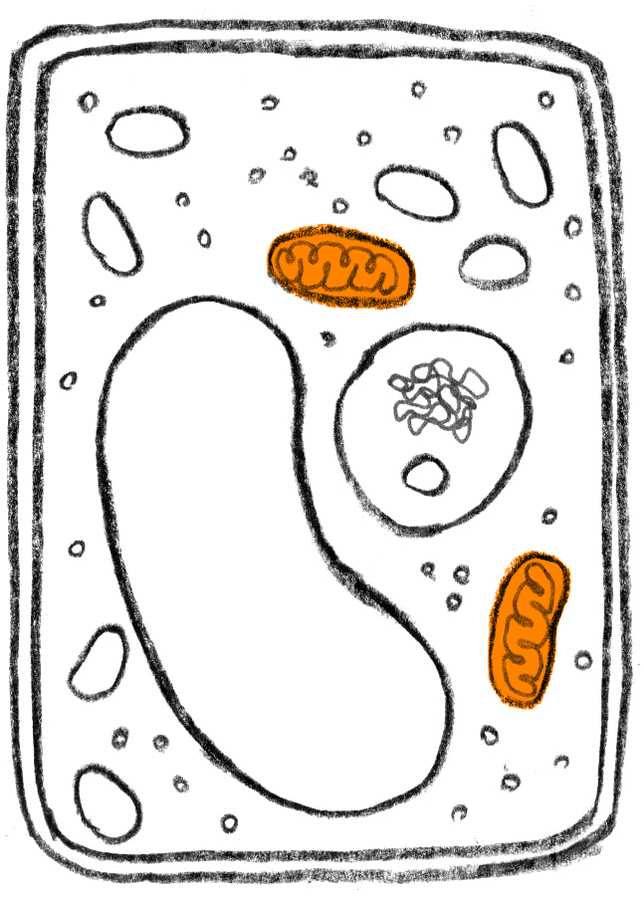
Is the mitochondria found in most plant cells?
Mitochondria are found in the cells of nearly every eukaryotic organism, including plants and animals. Cells that require a lot of energy, such as muscle cells, can contain hundreds or thousands of mitochondria.
Why are mitochondria found in most animal cells?
Without mitochondria (singular, mitochondrion), higher animals would likely not exist because their cells would only be able to obtain energy from anaerobic respiration (in the absence of oxygen), a process much less efficient than aerobic respiration.
Are mitochondria found in most plant and animal cells explain why?
Both animal and plant cells have mitochondria, but only plant cells have chloroplasts. Plants don't get their sugar from eating food, so they need to make sugar from sunlight. This process (photosynthesis) takes place in the chloroplast.
Are mitochondria found in plant cells?
Furthermore, it is no surprise that mitochondria are present in both plants and animals, implying major commonalities in regulation, energy production, substrates employed, etc. This common presence of mitochondria, with similar functions and structure, underscores how close our life forms are.
Where are mitochondria found the most?
What cells have the most mitochondria? A. Your heart muscle cells – with about 5,000 mitochondria per cell. These cells need more energy, so they contain more mitochondria than any other organ in the body!
Why do plants animals require mitochondria?
The main role of mitochondria is to ensure a steady supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is every cell's main energy-carrying molecule. -Chloroplasts are also found in some algae.
Is there more mitochondria in plant or animal cells?
Animal cells have more mitochondria than plant cells because.
Why do plants do possess mitochondria and chloroplast?
Plant cells are remarkable in that they have two organelles specialized for energy production: chloroplasts, which create energy via photosynthesis, and mitochondria, which generate energy through respiration, a particularly important process when light is unavailable.
Are mitochondria found in animal cells explain quizlet?
Are mitochondria found in animal cells? Yes, because all animal cells carry out cellular respiration. Write a grammatically correct sentence that compares the reactants and products of photosynthesis with the reactants and products of respiration.
Do both animal and plant cells have mitochondria because they both?
Answer and Explanation: The correct answer is a. carry on respiration. Both plant and animal cells have mitochondria because they both carry on respiration.
Can you see the mitochondria in both animal and plant cells?
Mitochondria are present in both animal and plant cells. Cell wall and chloroplasts are present in only in plant cells.
Are chloroplasts found in animal cells explain why or why not?
Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protists such as algae. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells.
Plant Cell Mitochondria: Structure & Role - Study.com
In plants, the mitochondria enable respiration and energy production. Learn about the structure and role of plant cell mitochondria to understand...
Plant mitochondria - past, present and future - PubMed
The study of plant mitochondria started in earnest around 1950 with the first isolations of mitochondria from animal and plant tissues. The first 35 years were spent establishing the basic properties of plant mitochondria and plant respiration using biochemical and physiological approaches. A number …
The Role of Mitochondria in Reproductive Function and Assisted ...
Mitochondria are fascinating cytoplasmic organelles crucial to life because of their production of energy. Abnormalities in mitochondrial function may be responsible for cellular and organismal aging and can be reversed to some extent by mitochondrial nutrients such as coenzyme Q10.
Answer
Yes because plant cell is eukaryotic and it is also in animal cell too.
New questions in Biology
MASA EN KILOGRAMOS (Kg)MASA EN GRAMOS (g)ARTICULOLata de FrijolesBolsa de SopaLata de AtúnFrasco de Consomé en polvoPaquete de PanPaquete de GalletasB … olsa de AzúcarLata de ChilesFrasco de CaféPaquete de Botana
Why are mitochondria unique?
Mitochondria are unique due to their double membrane. This structure provides insight into the development of mitochondria. Mitochondria were thought to originally be prokaryotes that were engulfed by larger cells. The mitochondria lived in symbiosis with the cell, providing energy to the main cell and the cell providing nutrients ...
What organelle makes food?
Makes own food through photosynthesis. Uses cellular respiration to make energy. Lesson Summary. The mitochondria is a membrane-bound organelle that makes energy for eukaryotic cells like plants and animals. The mitochondria does this through the process of cellular respiration, which has three steps: Glycolysis.
What are the structures of mitochondria?
The mitochondria is a membrane-bound organelle. It contains several structures that allow it to do its job in the cell, including: 1 Outer membrane 2 Inner membrane 3 Intermembrane space 4 Cristae 5 Matrix
How are mitochondria separated from the cytoplasm?
The mitochondria is separated from the cytoplasm by the outer membrane. The outer membrane is more permeable than the inner membrane. The outer membrane is separated from the inner membrane by the intermembrane space. This space is important for the mitochondria's role in cellular respiration, the process that cells use to make energy.
What is the last step of cellular respiration?
During the last step in cellular respiration, called oxidative phosphorylation, a hydrogen ion gradient is created in the intermembrane space, which provides stored energy to make ATP. The inner membrane is folded into a convoluted structure called cristae.
What is the mitochondria?
Mitochondria in Plant Cells: Overview. The mitochondria is a membrane-bound organelle that is the site of energy production in cells. Mitochondria are enclosed by two membranes and are only found in eukaryotic cells, such as plants, animals and fungi. Bacteria and archaea are prokaryotic cells and do not have membrane-bound organelles ...
Where does cellular respiration begin?
This is because all cells need energy to carry out their functions. Cellular respiration begins in the cytoplasm where glucose is converted to pyruvate in a process called glycolysis. Pyruvate is converted to Acetyl-CoA and enters the mitochondrial matrix to go through the Krebs cycle.
