Are there any Asymmetrical Animals?
Yes, there are asymmetrical animals. and No, there are not many biological advantages. Of course, with all science there are exceptions. Here’s a short list of some asymmetrical animals : Fiddler crabs have one big claw and one small claw. The crossbill has an unusual beak in which the upper and lower tips cross each other.
What are examples of animals with no symmetry?
what is radial symmetry in animals
- Animal kingdom/ Symmetry/ Radial Symmetry/ NEET/ AIIMS
- Symmetry in Animals
- The science of symmetry – Colm Kelleher
- SYMMETRICAL AND ASYMMETRICAL ANIMALS
What are types of symmetry do animals have?
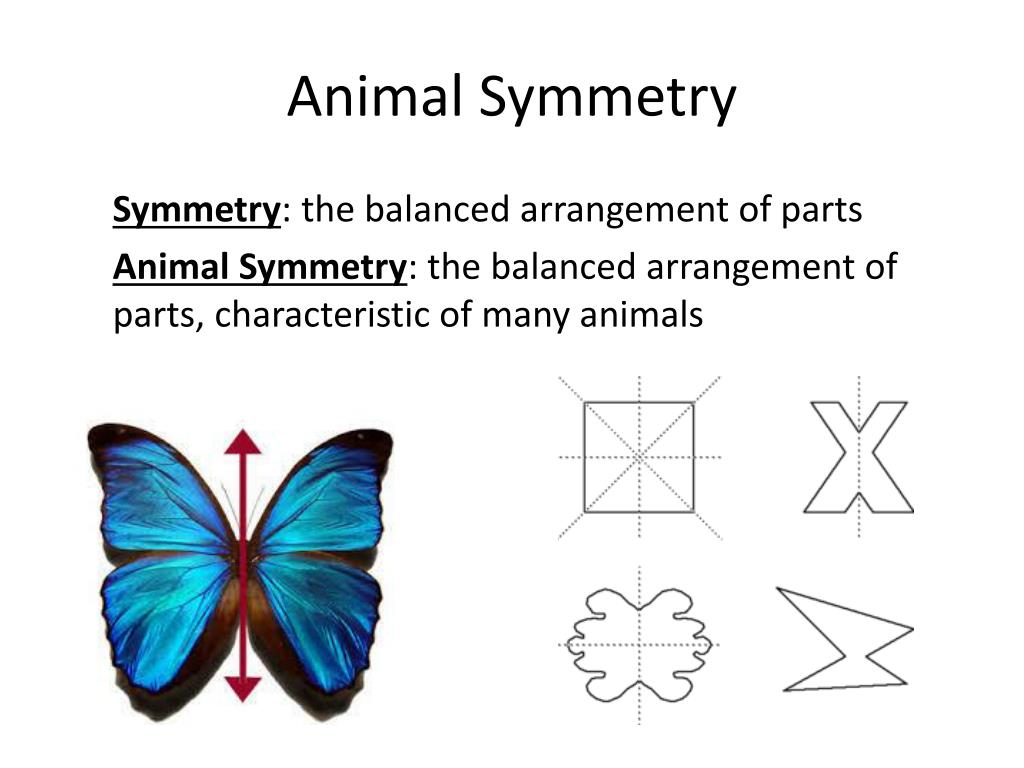
- Symmetry Introduction. Arrangement of body parts in a balanced geometrical design, divisible into equal parts by planes of division is called symmetry.
- Types of Symmetry. ...
- Bilateria and Radiata. ...
- Difference between Bilateria and Radiata
- Theories to explain the origin of Bilateria from Radiata. ...
What are the advantages of bilateral symmetry in animals?
No, all animals are not symmetrical, and here are some of the more well-known examples:
- Various crabs. Most famously, Fiddler Crabs. …
- Antlered animals. Quite often the rack on a moose, elk or deer is different on one side than the other. …
- Flat fish, like Flounder. …
- Narwhals. …
- Crossbill & Wrybill.
Why is symmetry so common in nature?
According to one, a body that is bilaterally symmetrical is easier for the brain to recognize while in different orientations and positions, thus making visual perception easier. Another popular hypothesis is that symmetry evolved to help with mate selection.
How are animals symmetrical?
People, dogs, cats, and elephants all have bilateral symmetry. Animals with radial symmetry have body parts arranged around a central point. Any line drawn from one side through the center to the opposite side will divide the animal into two symmetrical halves. Animals with radial symmetry have many lines of symmetry.
Do most animals have symmetry?
While sponges and placozoans represent two groups of animals which do not show any symmetry (i.e. are asymmetrical), the body plans of most multicellular organisms exhibit, and are defined by, some form of symmetry. There are only a few types of symmetry which are possible in body plans.
What is symmetry and how is it important to animals?
symmetry, in biology, the repetition of the parts in an animal or plant in an orderly fashion. Specifically, symmetry refers to a correspondence of body parts, in size, shape, and relative position, on opposite sides of a dividing line or distributed around a central point or axis.
Why do most animals look the same?
It was previously “The genetic 'switch' that makes many animals look alike as embryos”. An international team of researchers, led by Dr Ozren Bogdanovic and Professor Ryan Lister from the University of Western Australia, have found the genetic “switch” that causes one species of animal to look similar to another.
Why is it important for organisms to have symmetry?
The equal distribution of body parts and sense organs make them better able to react to environmental stimuli coming from all around their bodies. As shapes of organs and cells are strictly connected to their activities and functions, symmetry is an important matter also at those scales.
Why are cats so symmetrical?
But the reason behind why she looks like this is possibly even more interesting - as it is believed each different coloured side has different DNA on each side. Her unique markings are extremely rare and are thought to be the result of two embryos fusing together - the merging of two nonidentical twins.
How is symmetry of animals used for their classification?
Animals have been traditionally classified according to two characteristics: body plan and developmental pathway. The major feature of the body plan is its symmetry: how the body parts are distributed along the major body axis. Symmetrical animals can be divided into roughly equivalent halves along at least one axis.
What is the advantage of bilateral symmetry in animals?
In addition to having a more developed nervous system, bilaterally symmetrical animals can move more quickly than animals with other body plans. This bilaterally symmetrical body plan may have evolved to help animals better find food or escape predators.
How many animals have bilateral symmetry?
In fact, about 99 percent of animals have bilateral or two-sided symmetry, says my friend Erica Crespi. She’s a biologist at Washington State University who studies frogs and asks a lot of big questions about how animals develop.
How is DNA similar to other animals?
Even though DNA is what makes us all different, your DNA is actually pretty similar to that of other humans. You share quite a bit of DNA with other animals, as well. When scientists look at DNA they find that humans and slugs are about 70 percent similar. Chimpanzees and humans are about 98 percent similar.
What is two sided symmetry?
It turns out two-sided symmetry is just one kind of symmetry we see in nature, Crespi says. Take the starfish. In the early stages of its life, when it’s just a little blobby thing floating in the ocean, the starfish has bilateral symmetry.
How similar are chimpanzees to humans?
Chimpanzees and humans are about 98 percent similar. The DNA for establishing body symmetry, one of the basic traits of animals, are the same. Symmetry can sometimes be less visible as animals get older or if they live in stressful environments, Crespi adds.
What are the first features of an animal?
Crespi explained animals tend to develop in a particular order. The parts that will become the head or tail and the left or right side are among the first features that develop in all animals. This happens well before things like your hair, arms or legs have developed.
What is the process of a jellyfish's body changing shape?
That is, until it goes through a natural process called metamorphosis which completely changes its body shape. Now, with five legs stretched out around a middle point, it has what’s called radial symmetry. We see this in animals like urchins, anemones, and jellyfish, too.
Do jellyfish have symmetry?
We see this in animals like urchins, anemones, and jellyfish, too. Then there are a small number of animals on our planet that do not have symmetry. They are asymmetrical, like the sea sponges that live in the ocean. Crespi explained animals tend to develop in a particular order.
Asymmetry
An organism which is said to exhibit asymmetry has no symmetry whatsoever, regardless of how it would be cut on any axis or plane. Asymmetrical animals include some species of sponges, which are considered one of the most primitive members of the animal kingdom.
Bilateral Symmetry
Organisms which display bilateral symmetry have nearly (not totally) identical left and right sides. Bilateral symmetry is an evolutionary adaptation which evolved along with cephalization. Cephalization refers to the concentration of sensory and nervous tissues within a head-like structure of an organism.
Biradial Symmetry
Biradial symmetry is a type of symmetry exhibited in organisms that display both bilateral and radial types of symmetry and is very rare in the animal kingdom. These animals typically have an oval-shaped body and are either weak swimmers, floaters, or sessile (do not move).
What percentage of animals have symmetry?
We see this kind of symmetry in lots of animals, from cats and birds to worms and frogs. In fact, about 99 percent of animals have bilateral or two-sided symmetry, says my friend Erica Crespi.
Which animal is symmetrical?
Jellyfish, which are enormously abundant, are radially symmetrical; so are coral polyps, which are very common. Starfish have five-fold symmetry. And so on. Even animals that appear to be bilaterally symmetrical are not nearly as tidy on the inside as they are outside. Many organs are asymmetrical.
Why is radial symmetry important?
Radial symmetry is great because it allows an animal to act equally in all directions. For example, the starfish can crawl in any direction with equal efficiency, while a hydra can catch food coming from any direction. Radial symmetry is most common in sessile, attached or otherwise not so mobile animals.
What is radial symmetry?
Radial symmetry is when body parts of an animal are repeated many times around a line (in starfish above, the line is perpendicular to the image, thus it looks like a point).
Why are automobiles symmetrical?
If you look at automobiles, they are symmetrical. This is because they are designed for aerodynamic and mechanical stability as well as aesthetics. In symmetric organisms like humans, the duplicate organs are arranged symmetrically along the vertical axis, roughly the spine.
What are the advantages of bilateral symmetry?
One advantage of bilateral symmetry is that it provides redundancy. If you lose one eye, or one hand or one leg, you can still manage although with difficulty. If you only had one of each, it would make life almost impossible if you lost it. If you're an amphibian such as a salamander, y.
Why do we have bilateral symmetry?
Continue Reading. We have bilateral symmetry because our ancestors had it and we're so adapted to it that deviating from it would be bad for us. It (probably; we can never be certain) originally evolved because it makes movement easier.