
There is not one cause of fallopian tubes and ovarian anomalies. Some may be hereditary, others may be attributed to a random gene mutation or developmental defect. Fallopian tube agenesis, a type of müllerian anomaly, is the absence of one or both fallopian tubes.
What are the ovaries and fallopian tubes?
The ovaries are the small organs on each side of the uterus that contain eggs and produce female hormones. The fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus, where the fertilized embryo implants for pregnancy.
How do fallopian tubes affect fertility?
Each fallopian tube is a channel between your ovaries, where your body makes eggs, and your uterus, where a fertilized egg can develop into a fetus. Fertilization occurs in your fallopian tubes, making it a key part of your reproductive anatomy that affects your fertility. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Can you get pregnant without the ovaries and fallopian tubes?
The ovaries are responsible for releasing an unfertilized egg each month, while the fallopian tubes take the egg from the ovaries and into the uterus for implantation. Without either organ, a woman will not be able to get pregnant in the natural way.
What happens if egg is picked up by accessory fallopian tube?
This extra tube generally has an end that is near the ovary but does not extend into the uterus. Therefore, if an egg is picked up by the accessory fallopian tube, it can not be fertilized and implanted. There is also a risk of an ectopic pregnancy in such an accessory tube, which can be dangerous.
How do the ovaries and fallopian tubes work together?
The ovaries produce the egg cells, called the ova or oocytes. The oocytes are then transported to the fallopian tube where fertilization by a sperm may occur. The fertilized egg then moves to the uterus, where the uterine lining has thickened in response to the normal hormones of the reproductive cycle.
Are ovaries directly connected to fallopian tubes?
As there is no direct connection between the ovaries and fallopian tubes (also known as uterine tubes or oviducts), the egg is transported to the uterus in a peritoneal fluid produced by the fimbriae on the edge of the tube's opening.
Can ovaries be left without fallopian tubes?
A recent University of Colorado Cancer Center review in the International Journal of Gynecologic Cancer suggests a way young, high-risk women can reduce risk while leaving menopause for later: the technique known as salpingectomy removes the fallopian tubes while leaving ovaries intact.
Do fallopian tubes touch ovaries?
The open ends of the fallopian tubes lie very near the ovaries but they are not directly attached. Instead, the fimbriae (Latin for fringe) of the fallopian tubes sweep ovulated eggs into the tubes and towards the uterus.
Where does the egg go if your tubes are tied?
After surgery, each ovary still releases an egg. But the egg's passage through the fallopian tube is now blocked. Sperm also cannot pass through the tube to the egg. When egg and sperm can't meet, pregnancy cannot happen; your body absorbs the egg.
What happens to ovary when fallopian tube removed?
In addition, whether a doctor removes one or both fallopian tubes, it can impede blood flow to one or both ovaries. As a result, the ovaries may not be able to adequately transmit the hormones that they produce, and this can lead to early onset menopause.
How do ovaries stay in place after fallopian tube removal?
How Do the Ovaries Stay in Place? The fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus. Ligaments that extend from the upper part of the uterus to the lower part of the ovaries hold them in place. If you want to preserve your ovaries, your surgeon can reattach them after they've separated them from your uterus.
Do fallopian tubes grow back if removed?
Can my fallopian tubes grow back after getting a salpingectomy? No, your fallopian tubes can't grow back. Your fallopian tubes are formed during fetal development. They can't grow back after they are completely removed.
What are ovaries attached to?
Your ovaries are on the right and left sides of the uterus in your lower abdomen. Your ovaries are held in place by several muscles and ligaments in your pelvis. The ovarian ligament connects your ovaries to your uterus; however, your uterus and ovaries don't touch.
Can a fallopian tube move from ovary to ovary?
Amazing and little-known fact: Fallopian tubes are mobile and active parts of your reproductive tract. When one tube isn't there or is “broken” the other tube can actually move over to the opposite ovary and “pick up” an available egg.
Can left fallopian tube catch egg from right ovary?
The side we ovulate from does not strictly matter as an egg from one ovary can travel down the Fallopian tube on the other side.
Why do I have a sharp pain near my ovaries?
What causes pain in the ovaries? There are many reasons someone may experience ovary pain, including ovarian cysts, ovulation pain, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease or ovarian cancer.
What is the purpose of a HSG?
Diagnosing a blocked fallopian tube. Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is a type of X-ray used to examine the inside of fallopian tubes to help diagnose blockages. During HSG, your doctor introduces a dye into your uterus and fallopian tubes. The dye helps your doctor see more of the inside of your fallopian tubes on the X-ray.
What causes scarring in the fallopian tubes?
Pelvic inflammatory disease. This disease can cause scarring or hydrosalpinx. Endometriosis. Endometrial tissue can build up in the fallopian tubes and cause a blockage. Endometrial tissue on the outside of other organs can also cause adhesions that block the fallopian tubes.
What is the term for a blockage of the fallopian tube?
This usually happens in a type of blockage called a hydrosalpinx. This is when fluid fills and enlarges a blocked fallopian tube. Conditions that can lead to a blocked fallopian tube can cause their own symptoms. For example, endometriosis often causes very painful and heavy periods and pelvic pain.
Why is my fallopian tube blocked?
If a fallopian tube is blocked, the passage for sperm to get to the eggs, as well as the path back to the uterus for the fertilized egg, is blocked. Common reasons for blocked fallopian tubes include scar tissue, infection, and pelvic adhesions.
What is the function of the fallopian tubes?
Overview. Fallopian tubes are female reproductive organs that connect the ovaries and the uterus. Every month during ovulation, which occurs roughly in the middle of a menstrual cycle, the fallopian tubes carry an egg from an ovary to the uterus. Conception also happens in the fallopian tube. If an egg is fertilized by sperm, it moves through ...
Why do you need in vitro fertilization?
This is because it’s harder for a fertilized egg to move through a blockage to the uterus. In these cases, your doctor might recommend in vitro fertilization (IVF), depending on whether treatment is possible.
What to do if HSG doesn't help?
If the HSG doesn’t help your doctor make a definitive diagnosis, they can use laparoscopy for further evaluation. If the doctor finds a blockage during the procedure, they might remove it, if possible.
What is the condition most commonly associated with the fallopian tubes?
Associated Conditions. Ectopic pregnancy is the condition most commonly associated with the fallopian tubes. It occurs when there is a delay in the transport of the fertilized egg towards the uterus. In such cases, the fertilized egg may implant and cause an ec topic pregnancy inside the tube.
How long are fallopian tubes?
In an adult, the fallopian tubes are around 10 to 12 centimeters (cm) long, although this can vary substantially from person to person. They are generally considered to consist of four sections. The short interstitial section connects through the wall of the uterus to the interior of the uterus.
What is it called when a woman implants her uterus?
If a pregnancy implants in the fallopian tubes, or elsewhere outside of the uterus, it's referred to as an ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregna ncy can be very dangerous, with a risk of rupture and even death.
What is the function of the fallopian tubes?
The fallopian tubes carry the eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. The primary role of the fallopian tubes is to transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Procedures to block the fallopian tubes can be used as a form of permanent contraception, or sterilization.
What is the role of the cilia in the menstrual cycle?
They also change throughout the menstrual cycle. The beating movement of the cilia increases near the time of ovulation . 1 This is regulated by estrogen and progesterone production.
Why is it important to have a tube tied to get pregnant?
Successful transport of eggs through the fallopian tubes is necessary for someone to get pregnant without medical intervention. This is why tubal sterilization, which interrupts the function of the tubes, is an effective form of permanent contraception. This is sometimes referred to as getting one's "tubes tied.".
Where does fertilization occur?
When fertilization occurs, it is generally in the fallopian tubes. The sperm travel out from the uterus into the tubes, where they may encounter and fertilize an egg. The fertilized egg then continues its movement towards the uterus.
Can nuclear waste still be used for energy?
As far as I'm aware, waste fuel from nuclear power plants is still radioactive/fissile. Seeing as waste management seems to be the biggest counterpoint to nuclear energy, what can be done with the waste?
Why do antigen rapid tests not work after 15 minutes?
Why is this so? Do the coloring/colored molecules that do the binding no longer work, or weaken, after 15 minutes? Or does a positive turn into a negative?
Are Neutrinos not faster than light?
Scientists keep proving that neutrinos do not travel faster than the speed of light . Well if that is the case, in case of a cosmic event like a supernova, why do neutrinos reach us before light does? What is obstructing light from getting to us the same time?
How do fallopian tubes and ovaries differ?
The fallopian tubes and the ovaries are two developmentally different systems. The fallopian (or uterine) tubes are the remnant of a structure called the paramesonephric duct. The duct in an embryo basically just opens up into the future abdominal cavity. The gonads, on the other hand form from a ridge-like structure along the back part of the future abdomen. Eventually, things called germ cells migrate into that ridge and eventually will become the eggs. Unfortunately these two things are separate, so in order to get the egg to where they're going to meet the sperm, you need a collecting duct, which is the fallopian tube. So, through a process of folding ridges that is kind of complicated, the ends of the paramesonephric duct end up in close association to the developing ovary. Then the fimbriae (finger-like extensions on the end of the tube) form, and during ovulation, they kind of grab the ovum to ensure that the egg doesnt miss its target.
What happens when an egg leaves the ovary?
When the egg leaves the ovary, it herniates through the wall into the celom (body cavity). The uterine (fallopian) tube is sort of like the drain for the celom in this region. So if it were connected to the ovary, it would have no way of draining the space around it.
Why do we do experiments on new compounds and drugs?
We always do experiments on new compounds and drugs to ascertain certain properties and determine behavior, safety, and efficacy. But if we know the structure, can’t we determine how it’ll react in every situation?
Why remove ovaries & fallopian tubes?
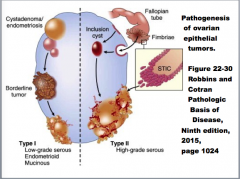
Women with ovarian cancer may have their ovaries and fallopian tubes removed as part of a cancer treatment. Originally, experts believed that ovarian cancer always originated in the tissues of the ovary. New research, however, has suggested that some ovarian cancers may actually start in the fallopian tube, which has prompted some patients to only have their fallopian tubes removed.
What is a salpingo oophorectomy?
A unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy removes one of the ovaries and the connected fallopian tube. Prophylactic ovary removals extract healthy, noncancerous ovaries in women who have elevated risk (BRCA genetic mutation) of ovarian and fallopian tube cancer. Typically, these types of procedures are performed after a woman is done having children.
What is the ovaries?
The ovaries are the small organs on each side of the uterus that contain eggs and produce female hormones. The fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus, where the fertilized embryo implants for pregnancy. Ovary and fallopian tube removal procedures are performed either with a large open incision in the abdomen to access ...
What is ovary and fallopian tube removal?
What is ovary & fallopian removal? Ovary and fallopian tube removal involves the surgical removal of one or both ovaries and one or both fallopian tubes, which is generally done when ovarian cancer is present. The ovaries are the small organs on each side of the uterus that contain eggs and produce female hormones.
How many incisions are needed for fallopian tube removal?
Ovary and fallopian tube removal procedures are performed either with a large open incision in the abdomen to access the ovaries or laparoscopically, which is a minimally invasive surgery that involves three to four small incisions on the abdomen.
What is the difference between oophorectomy and salpingo oophorectomy?
An oophorectomy removes one or both of the ovaries and a bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy removes both the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Women with the BRCA genetic mutation may preemptively have their ovaries and fallopian tubes removed to prevent possibly developing ovarian cancer.
Why do they remove the ovaries?
Ovary and fallopian tube removal involves the surgical extraction of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, sometimes due to the presence of ovarian mass or cancer.
Why do you need to remove both ovaries?
In hysterectomies to treat benign conditions , removing both of the ovaries in addition to the fallopian tubes has been used as a way to reduce ovarian cancer risk.
Where does ovarian cancer come from?
New evidence suggests that ovarian cancer often originates from the fallopian tube, rather than from the ovaries. This led the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) to issue a statement in 2015 suggesting that the practice of bilateral salpingectomy with ovarian conservation — surgical removal of both fallopian tubes ...
Can you remove fallopian tubes during hysterectomy?
During hysterectomies for non-cancerous conditions, removing both fallopian tubes while keeping the ovaries may help protect against ovarian cancer while preserving hormonal levels, but few women receive this surgical option, according to a new study by Yale School of Medicine researchers.
