Do all cells need ribosomes?
Thus, all cells have ribosomes. While a structure such as a nucleus is only found in eukaryotes, every cell needs ribosomes to manufacture proteins. Since there are no membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotes, the ribosomes float free in the cytosol.
What are the main function of ribosomes?
What are the six cell organelles?
- Nucleus. nucleus; animal cell.
- Ribosomes. Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cell.
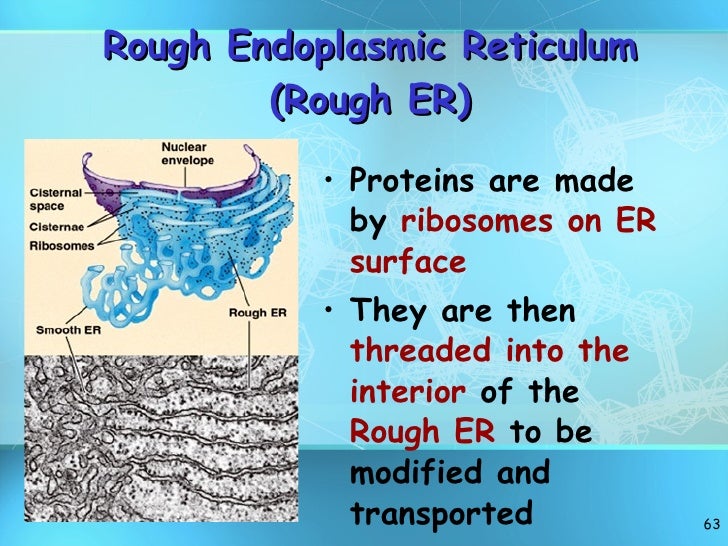
- Endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes on the outer surface of the endoplasmic reticulum play an important role in protein synthesis within cells.
- Golgi apparatus. Golgi apparatus.
- Chloroplasts.
- Mitochondria.
What are facts about ribosomes?
What are 3 facts about ribosomes?
- The “rib” in ribosome comes from ribonucleic acid (RNA) which provides the instructions on making proteins.
- They are made inside the nucleolus of the nucleus.
- Ribosomes are different from most organelles in that they are not surrounded by a protective membrane.
How do ribosomes work with other organelles?
Ribosomes work along with most of the organelles because they make the proteins that they need to perform. Ribosomes form proteins which act like the bricks to build a house. They take orders from the RNA and Nucleus just as workers have to pay attention to the building plans and instructions from a forman.

What determines what kind of proteins are created?
The location of the ribosomes determines what kind of proteins are created. If the ribosomes are free-floating in the cytoplasm, then they make proteins that are used solely within the cell. If the ribosomes are a part the ER, then they make proteins that are used in or out of the cell.
Where are ribosomes located?
Ribosomes are small organelles that can be found attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) or free-floating in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes help to transcribe DNA in order to make proteins.
What is a certified educator?
Our certified Educators are real professors, teachers, and scholars who use their academic expertise to tackle your toughest questions. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team.